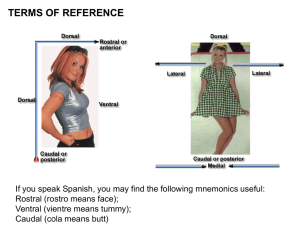
Supplementary Information (docx 1105K)
advertisement

Supplementary Information Overlapping expression of serotonin transporters and neurokinin-1 receptors in posttraumatic stress disorder: a multi-tracer PET study Andreas Frick, Fredrik Åhs, Åsa Michelgård Palmquist, Anna Pissiota, Ulrika Wallenquist, Manuel Fernandez, My Jonasson, Lieuwe Appel, Örjan Frans, Mark Lubberink, Tomas Furmark, Lars von Knorring, Mats Fredrikson Additional analyses Correlation analyses When substituting the original Pearson’s correlations with Spearman’s rank-order correlations, the difference in correlations between patients and controls remained (Supplementary Table 2). Regression analyses In addition to the ordinary least squares regressions used in our original analyses, we conducted both robust and rank-based multiple regressions for the amygdala, safeguarding against the effects of potential outliers and/or extreme values as well as non-normally distributed data using two different techniques. These analyses yielded results almost identical to those obtained originally because all p-values remained significant (Supplementary Table 3), including a significant interaction term. Supplementary Table 1. Participant demographic and clinical characteristics. PTSD patients Control group Statistic P Age mean (SD) 38.7 (13.0) 34.0 (9.7) t=1.156 .257 Sex, men, women 8M, 8W 8M, 8W χ2=0 1 2 Handedness 16 right, 0 left 16 right, 0 left χ =0 1 Symptom duration years mean (SD) 11.5 (8.8) Trauma type Combat 8 Traffic accident 3 Witness suicide 2 Sexual assault 2 Domestic violence 1 CAPS Total score 68.3 (16.7) Arousal 19.9 (5.9) Avoidance 26.5 (5.4) Intrusion 22.0 (8.0) MADRS Total score 20.9 (7.1) Comorbidity Depression 12 GAD 3 OCD 3 PD 4 CAPS: Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale, GAD: General Anxiety Disorder, MADRS: Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, OCD: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, PD: Panic Disorder, PTSD: Posttraumatic stress disorder Supplementary Table 2. Overlapping expression of serotonin transporters (SERT; [11C]DASB binding potential, BPND) and neurokinin-1 receptors (NK1R; [11C]GR205171 influx rate, Ki) in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as compared to healthy controls (HC) using Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlations. Pearson’s Spearman’s MNI x, y, z p p diff ra diff rb HC>PTSD Putamen 26 8 -10 1.25 <.001 1.12 .002 Thalamus -14 -20 6 1.16 .001 1.12 .003 Insula -38 -20 -2 1.09 .004 0.94 .016 Orbitofrontal gyrus 34 56 -2 0.99 .005 0.95 .011 Insula -26 16c -14 0.83 .020 0.67 .041 PTSD>HC Inferior temporal gyrus 46 -52 -22 -1.28 <.001 -1.04 .007 Cuneus -6 -84 30 -1.28 <.001 -1.20 <.001 Middle cingulate cortex 10 8 34 -1.11 <.001 -1.07 .002 Orbitofrontal gyrus 6 56 -10 -1.04 .001 -.072 .026 MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute a Differences in Pearson’s r correlation coefficient between groups: rHC - rPTSD, as an index of difference in overlapping expression. b Differences in Spearman’s r correlation coefficient between groups: rHC - rPTSD, as an index of difference in overlapping expression. c The coordinate for the Spearman correlations was in -26, 16, -14. Supplementary Table 3. Multiple ordinary least square regressions, robust regressions, and rank-based regressions regressing CAPS total score on amygdala neurochemical parameters, including age and sex as covariates. SERT NK1R SERT×NK1R β p β p β p -0.31 .195 -0.08 .656 Ordinary least square regression -0.49 .013 -0.32 .227 -0.08 .671 Robust regression -0.48 .020 -0.36 .211 -0.10 .643 Rank-based regression -0.45 .037 SERT: Serotonin transporter, NK1R: Neurokinin-1 receptor Supplementary Table 4. Relationship between arousal symptom severity (Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale; CAPS Arousal score) and the overlapping expression between neurotransmitter systems, serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ( [11C]DASB binding potential, BPND) and neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) availability ( [11C]GR205171 influx rate, Ki), in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). BA Hemisphere MNI x, y, z βa Negative relationship with CAPS Arousal score Insula 47 Left -26 16 -10 1.689 PAG Left -6 -32 -2 1.212 Parahippocampal gyrus 28 Right 18 -8 -26 1.167 Precuneus 31 Right 6 -52 22 1.016 Calcarine 17 Left -2 -84 6 0.969 Cuneus 7 Left -14 -80 34 0.962 Superior frontal gyrus 10 Right 26 48 22 0.955 Precuneus 31 Right 18 -64 22 0.947 Supramarginal gyrus 40 Right 62 -40 34 0.935 Inferior temporal gyrus 37 Right 50 -64 -6 0.890 Middle temporal gyrus 21 Right 54 -4 -22 0.836 Cuneus 31 Left -10 -64 22 0.816 Ventromedial prefrontal cortex 25 Left -2 20 -10 0.806 Superior frontal gyrus 10 Left -14 60 10 0.781 Fusiform gyrus 19 Left -26 -52 -14 0.767 BA: Brodmann area, CAPS: Clinician-administered PTSD scale, MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute a Regression coefficient; b Cluster volume in mm3 p-value Cluster volumeb .001 <.001 .006 <.001 .003 .003 .016 .004 .001 <.001 .047 .001 .002 .006 .029 9216 2304 12544 4800 1728 832 768 1216 3968 1024 960 960 768 896 640 Supplementary Table 5. Relationship between avoidance symptom severity (Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale; CAPS Avoidance score) and the overlapping expression between neurotransmitter systems, serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ( [11C]DASB binding potential, BPND) and neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) availability ( [11C]GR205171 influx rate, Ki), in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). BA Hemisphere MNI x, y, z βa Negative relationship with CAPS Avoidance score Inferior temporal gyrus 21 Left -38 4 -38 1.540 Inferior temporal gyrus 20 Right 42 -8 -34 1.429 Lingual gyrus 30 Right 14 -56 6 1.347 Inferior frontal gyrus 45 Right 50 20 18 1.245 Precentral gyrus 6 Right 38 -8 54 1.191 Middle frontal gyrus 8 Left -26 24 42 1.157 Parahippocampal gyrus 35 Right 22 -12 -30 1.096 Anterior cingulate cortex 10 Right 10 48 10 1.087 Caudate Right 14 24 -2 1.085 Middle frontal gyrus 9 Right 42 20 34 1.055 Inferior occipital gyrus 37 Left -50 -64 -18 1.013 Middle temporal gyrus 22 Right 62 -36 6 0.973 Brainstem Right 2 -28 -50 0.900 Middle temporal gyrus 21 Left -62 -44 -14 0.883 Superior frontal gyrus 10 Right 18 60 -2 0.843 Hippocampus Left -18 -32 -2 0.832 Posterior cingulate cortex 31 Right 6 -44 30 0.824 Supramarginal gyrus 40 Left -54 -28 22 0.793 Inferior frontal gyrus 11 Left -38 36 -10 0.788 Calcarine gyrus 30 Left -14 -56 6 0.751 BA: Brodmann area, CAPS: Clinician-administered PTSD scale, MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute a Regression coefficient; b Cluster volume in mm3 p-value Cluster volumeb .009 .001 <.001 .023 .008 .011 .005 .004 .001 .019 .030 <.001 .008 <.001 .038 .025 .003 .025 .002 .010 2752 2176 1216 1280 1600 768 1344 4416 896 704 832 1600 640 1024 768 960 1728 704 704 896 Supplementary Table 6. Relationship between intrusion symptom severity (Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale; CAPS Intrusion score) and the overlapping expression between neurotransmitter systems, serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ( [11C]DASB binding potential, BPND) and neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) availability ( [11C]GR205171 influx rate, Ki), in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Negative relationship with CAPS Intrusion score Inferior temporal gyrus Inferior frontal gyrus Anterior cingulate cortex Hippocampus Lingual gyrus Inferior occipital cortex Precentral gyrus Middle frontal gyrus Supramarginal gyrus Fusiform gyrus Orbitofrontal gyrus Precuneus Rolandic operculum Anterior cingulate cortex Supramarginal gyrus Inferior frontal gyrus BA Hemisphere 20 46 32 19 37 6 9 40 38 47 31 13 32 40 47 Right Right Left Left Right Left Right Right Right Right Right Right Right Right Left Right MNI x, y, z 46 46 -6 -26 22 -50 38 34 62 30 26 2 42 10 -54 46 0 24 40 -12 -56 -64 -8 40 -36 4 8 -64 -4 44 -28 40 -38 22 22 -18 -6 -18 54 30 34 -42 -18 30 10 6 22 -6 βa p-value Cluster volumeb 0.727 0.701 0.697 0.693 0.676 0.669 0.647 0.605 0.573 0.548 0.546 0.520 0.507 0.481 0.455 0.454 .009 .042 .018 <.001 .005 .004 .008 .037 .043 <.001 .012 .041 <.001 .005 .030 .009 1984 896 704 3904 1408 3072 704 704 1536 1024 2816 1728 640 640 1024 1024 .003 .015 .018 .042 .001 .013 .011 640 832 640 960 1600 1408 704 Positive relationship with CAPS Intrusion score Fusiform gyrus 35 Left -30 -28 -22 0.648 Midbrain Right 18 -16 -10 0.613 Middle temporal gyrus 22 Left -54 -52 14 0.607 Fusiform gyrus 37 Right 30 -36 -14 0.579 Raphe region Right 6 -40 -26 0.570 Insula 13 Left -30 16 -6 0.501 Lingual gyrus 18 Right 14 -84 -10 0.401 BA: Brodmann area, CAPS: Clinician-administered PTSD scale, MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute a Regression coefficient; b Cluster volume in mm3 Supplementary Figure 1. Box-and-whisker plot of [11C]DASB binding potential (BPND), an index of serotonin transporter availability, in the amygdala in healthy controls (red) and patients with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD; blue). No statistical difference in [11C]DASB BPND was detected between the groups (t(29)=0.825, p=.416). 11 [ C]DASB Binding potential 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 Controls PTSD Supplementary Figure 2. Altered correlation between serotonin transporter ([11C]DASB Binding potential) and NK1 receptor ([11C]GR205171 Ki) availability in the (A) putamen and (B) inferior temporal gyrus (ITG) of patients with PTSD relative to healthy controls. Supplementary Figure 3. Scatterplot and linear regression line depicting the simple relationship between serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ([11C]DASB binding potential) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptom severity, indexed by the ClinicianAdministered PTSD Scale (CAPS). 90 80 CAPS 70 60 50 40 30 -0.1 0.0 11 0.1 Amygdala [ C]DASB Binding potential 0.2 Supplementary Figure 4. Scatterplot and linear regression line depicting the simple relationship between neurokinin-1 receptor availability ([11C]GR205171 Ki) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptom severity, indexed by the ClinicianAdministered PTSD Scale (CAPS). 90 80 CAPS 70 60 50 40 30 -0.002 -0.001 0.000 11 0.001 Amygdala [ C]GR205171 Ki 0.002 Supplementary Figure 5. Neurotransmitter system associations and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) arousal symptom severity, indexed by the Clinician-administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) Arousal Subscale. Top panel shows beta weights for relationship between arousal CAPS score for separate simple regression models including (A) serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ([11C]DASB BPND) and (B) neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) availability ([11C]GR205171 Ki) respectively, and (C) for the interaction between SERT and NK1R availability in a multiple regression model including both SERT and NK1R availability and the interaction. Beta coefficient images overlaid on a standard MRI image. All rows depict slices at MNI coordinate (5, 3, -8). The colorbar indicates regression coefficients (β). Supplementary Figure 6. Neurotransmitter system associations and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) avoidance symptom severity, indexed by the Clinician-administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) Avoidance Subscale. Top panel shows beta weights for relationship between arousal CAPS score for separate simple regression models including (A) serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ([11C]DASB BPND) and (B) neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) availability ([11C]GR205171 Ki) respectively, and (C) for the interaction between SERT and NK1R availability in a multiple regression model including both SERT and NK1R availability and the interaction. Beta coefficient images overlaid on a standard MRI image. All rows depict slices at MNI coordinate (5, 3, -8). The colorbar indicates regression coefficients (β). Supplementary Figure 7. Neurotransmitter system associations and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) intrusion symptom severity, indexed by the Clinician-administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) Intrusion Subscale. Top panel shows beta weights for relationship between arousal CAPS score for separate simple regression models including (A) serotonin transporter (SERT) availability ([11C]DASB BPND) and (B) neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) availability ([11C]GR205171 Ki) respectively, and (C) for the interaction between SERT and NK1R availability in a multiple regression model including both SERT and NK1R availability and the interaction. Beta coefficient images overlaid on a standard MRI image. All rows depict slices at MNI coordinate (5, 3, -8). The colorbar indicates regression coefficients (β).