Grade 10 Nutrition Worksheet: Food Guide & Eat Tracker
advertisement

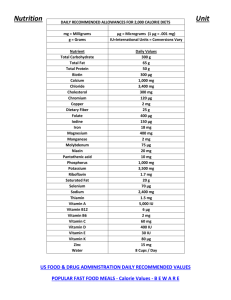
GRADE 10 HEALTH 1 - NUTRITION Instructions: Read over the set of notes below, highlight key points, complete the activities and/or write down any questions you may have about the material covered so that you can ask your teacher to explain the material in more detail as needed. You must also complete the “EAT TRACKER” assignment outlined at end of this note and submit it for evaluation. When you are ready, you can ask to write the test for this unit. Seven Benefits Of Nutrition 1. An improved quality of life Higher energy & self esteem 2. Slow Down the Aging Process Add life to your years & add years to your life! 3. Improved Psychological Health Lower levels of depression, less anxious 4. Consistent Weight Control Muscle growth and reduction of fat Stable blood sugar levels 5. Improved Cardiovascular Health Lower cholesterol and blood pressure = Healthier heart 6. Increased Strength and Muscle Mass Muscle is more metabolically active than fat, therefore it burns more calories than fat (24 hours/day, 7 days/week) 7. Improved Body Chemistry. Cleaner arteries = Reduced risk of atherosclerosis Less insulin - prevents adult onset diabetes Canada Food Guide Activity Download a copy of the Canada Food Guide from Classnet and answer the following questions in order to become more familiar with the guides design and contents. Questions: What are the recommended number of servings for you? How do the number of servings change from person to person? Why? What food group do peanuts fall under? Why? What food group do potatoes fall under? Why? What food group do beans & lentils fall under? Why? What food group would a V8 fall under? Why? What food group does mustard fall under? What food group does a can of pop fall under? Do you know what “Kefir” is? Use the internet to figure it out if you don’t. What are the recommendations for oils and fats? Identify one key recommendation for each food group. Looking at the back of the guide, write down three key recommendations that you could include in your daily nutrition rituals. Nutrition Terms What is Nutrition: The process by which our body takes in and uses food. Proper nutrient intake is important because: It provides the energy for vital functions (e.g. breathing) It helps us feel and look our best. It promotes proper growth and development. It helps prevent chronic diseases e.g. heart disease, certain cancers, diabetes, and stroke What is a Nutrient? Nutrients are chemical substances obtained from food that your body needs to grow, repair itself, and supply you with energy. What are Essential Nutrients? Essential Nutrients are substances our body cannot make itself or cannot make in sufficient amounts, thus it must be eaten in our diet. What is a Calorie? Calories are units that measure energy. Used to measure the energy in food and the energy your body burns. Usually expressed in kilojoules (kJ) or kilocalories (kcal). One pound of fat contains 3,500 calories. What is a Macronutrient? Macronutrients comprise the greatest portion of our dietary intake. There are three types of macronutrients: 1) Carbohydrates (4 calories per gram) Main energy source in our diet (most readily used by the body) Come from sugars, starches & fibres. 2) Proteins (4 calories per gram) Part of all body tissues (e.g., muscle, skin, hair) Needed for growth and repair of body tissues Component of hormones, enzymes, and the immune system 3) Fats (9 calories per gram) Fatty substances that do not dissolve in water Used for energy storage, insulation, protection, cell membrane, hormone production, etc. What are Micronutrients? Micronutrients are substances that we only need in small amounts (micro or milligrams). There are 2 types of micronutrients: 1) Vitamins (0 calories per gram) Help our body perform specific functions such as growth, reproduction and maintenance of health. Vitamin A = Vision Vitamin C = Cancer protection Vitamin D = Bone growth, and skin maintenance 2) Minerals (0 calories per gram) Help our body carry out vital functions such as muscle contraction and build strong bones. Calcium = Bone and teeth health Potassium = Fluid and electrolyte balance Sodium = Nerve conduction and muscle contraction What is a Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA)? The RDA defines the amounts of energy, nutrients and other dietary components that we require in our diet that promote our health. In Canada we use the RNI = Recommended Nutrient Intake We also see the term; DRI = Dietary Reference Intake Most essential nutrients have an RDA. For example a 15 year old person has the following requirements: o Calories: 2500 – 3000 o Vitamin A = 1000µg o Vitamin C = 60mg o Calcium = 1300mg Seven key healthy eating habits? Always eat breakfast, it kick starts your metabolism Eat a variety of foods each day Eat foods from all four food groups Eat according to your activity level Choose fruits and vegetables more often (dark colours) Choose low fat, salt & sugar options more often. Drink at least 2000ml (2 litres) of water every day and even more if you exercise. Weight Maintenance Energy In: All foods supply the body with energy. 1 carrot = 105 kj 1 apple = 420 kj 250ml of ice cream = 1260 kj 100g hamburger = 1890 kj Energy Out: The body expends energy in 3 ways: 1. Through basic metabolism (heart, lungs, digestion, thinking, etc.) 2. Through activities of daily living (making beds, laundry, mowing lawn, shoveling, etc.) 3. Through exercise Energy Stored The energy that the body consumes that doesn’t get used up in activity or in basic metabolism will be stored as fat. Energy Balance: 3 Scenarios if Energy out = Energy in ----- weight remains same if Energy out < Energy in ----- weight gained if Energy out > Energy in ----- weight lost Energy of Fitness Vigorous activity increases metabolic rate up to 8 hours after activity stops. Increased muscle mass means more calories burned every day (higher metabolism) EAT TRACKER ASSIGNMENT Instructions: Go to the website www.eatracker.ca EATracker lets you track your day's food and activity choices and compares them to the guidelines laid out by Health Canada. Click on Sign Up to create an account. You will need to register onto EATracker to be able to track your eating and activity level. You must accept the terms and conditions in order to use the site. Complete the registration process including your real date of birth, height & weight. Step 1: Once registered, you can begin to track the foods you have eaten that day. Search for each food item you ate yesterday by typing in a key word. Select the meal it was eaten, the number of servings then click “add to” and select the meal that you consumed that food. You will see the food item appear near the top of the screen under each meal. Continue to add to your menu until you have completed the day, don’t forget about drinks. You should see the menu building at the top of the screen. Print your menu (to hand in with this sheet). NOTE: Some food items might not appear in their database so you may have to search for a suitable alternative. Also be careful with things like “sandwich”, you will have to break it down into the ingredients. Once done entering all the food for the day click on the “Food Groups” link on the left side of the page and complete this chart. My Intake Recommended Amount Fruit and Vegetables Grain Products Milk and alternatives Step 2: Meat and alternatives Read the information on this page and identify how well your food choices meet up to Canada’s Food Guide? Explain your results. Did you meet or exceed any of the requirements? Is this a typical day? Explain how your diet changes from day-to-day? What you can do to improve? Step 3: Click on the “My Activities” tab near the top of the screen. Select the activities you did during the day & add each to your activity log. Be sure to add any walking, sports, even chores! You will see them appear near the top as you enter them. Click on “My Activity Feedback” on the left side of the screen (Read the information provided) How many minutes of moderate and high effort physical activity do you need for that day? ________________ Did you get enough activity for that day? ___________ Based on this assessment and information what are some things that you could do to improve your activity level (be specific)? Step 4: Click on the “My Food” tab at the top of the screen then click on “Calories” on the left hand side of the screen. Read the information on this page about My Eating Feedback. Find the section on Calorie Intake. Compare your energy intake to your estimated energy requirement (EER) which is based on your age, height, weight and activity level. My energy intake is _________ calories in comparison to my EER which is ____________ calories. Based upon this eating/activity pattern, what would happen to your weight over time? Is this a typical day? Explain how your diet and activity pattern changes from day-to-day. Scroll down further on this page and find the section on “Calories from protein, fat, carbohydrates and alcohol” and read the information. Complete the table below using your results. My Intake (grams) My Intake (Percent of energy/calories) Analysis W = Within; B = Below Recommended Range A = Above Protein Fat Carbohydrate Click on “Nutrients” on the left side of the screen and look at the “My Nutrient Feedback compared to Recommended Daily Intakes” table and graph which show you the amount of calories, fat, sodium, carbohydrates, fibre, sugar, protein, vitamins and minerals, etc. contained in the food you entered. It also lists the recommended daily amounts for your age and gender. Using the table/graph identify two nutrients that you exceed the recommended amount? What is the role of this Recommended Nutrient Name My Intake nutrient in the body? Intake (GOOGLE it!) What foods do you find this nutrient in? (GOOGLE it!) 1) 2) Using the table/graph identify two nutrients that you need to eat more of? What is the role of this Recommended Nutrient Name My Intake nutrient in the body? Intake (GOOGLE it!) 1) 2) What foods do you find this nutrient in? (GOOGLE it!)