File
advertisement

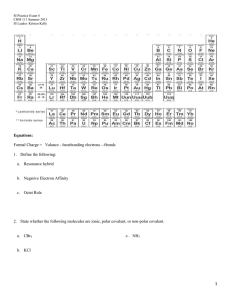
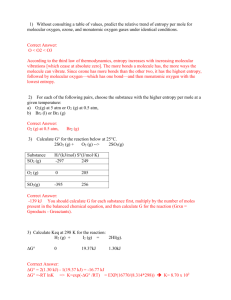
Chapter 8: Thermodynamics CHM 111 Summer 2013 SI Leader: Kristen Kelly 1. Define the following a. enthalpy b. +∆H c. -∆H d. entropy e. gibb's free energy f. spontaneous (exergonic) g. nonspontaneous (endergonic) 2. What is the enthalpy change ∆H for a reaction at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm if the internal energy change (∆E) is 44.0 kJ and the volume increase is 14.0 L? (1 atm= 101.325 J). 3. What is the specific heat of lead if it takes 97.2 J to raise the temperature of a 75.0 g block by 10.0 °C? 1 Chapter 8: Thermodynamics CHM 111 Summer 2013 SI Leader: Kristen Kelly 4. When 25.0 mL of 1.0 M H2SO4 is added to 50.0 mL of 1.0 M NaOH at 25 °C in a calorimeter, the temperature of the aqueous solution increases to 33.9 °C. Assuming the specific heat of the solution is 4.18 J/ g °C, and that the calorimeter itself absorbs a negligible amount of heat, calculate the ∆H in kJ for the reaction. H2SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH → 2H2O (l) + Na2SO4 (aq) 5. Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔHo, for the formation of 1 mol of strontium carbonate (the material that gives the red color in fireworks) from its elements. Sr (s) C(graphite ) 32 O2 (g) SrCO3 (s) The informatio n available is (1) Sr (s) 1 2 O2 (g) SrO (s) H - 592 kJ (2) SrO (s) CO2 (g) SrCO3 (s) H - 234 kJ (3) C(graphite ) O2 (g) CO2 (g) H - 394 kJ 2 Chapter 8: Thermodynamics CHM 111 Summer 2013 SI Leader: Kristen Kelly 6. Styrene (C8H8), the precursor for polystyrene polymers, has a standard heat of combustion of -4395 kJ/mol. Write a balanced equation for the combustion reaction and calculate ∆H°f for styrene in kJ/mol. ∆H°f (H2O) = -285.8 kJ/mol ∆H°f (CO2) = -393.5 kJ/mol 7. Tell whether the following entropy changes are likely to be positive or negative: a. Deposition (gas to a solid) b. N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) → 2 NH3 (g) c. The fizzing of a newly opened soda d. The growth of a plant from a seed 8. Use the bond dissociation energy Table 7.1 (pg 1) to combute the ∆H° in kJ for the reaction of ethylene with hydrogen to yield ethane. H2C=CH2 (g) + H2 (g) → CH3CH3 (g) 9. The boiling point of a substance is defined as the temperature at which liquid and vapor coexist in equilibrium. Use the heat of vaporization (∆H°vap= 30.91 kJ/mol) and the entropy of vaporization (∆S°vap=93.2 J/ K mol) to calculate the boiling point (°C) of liquid bromine. 3