display
advertisement

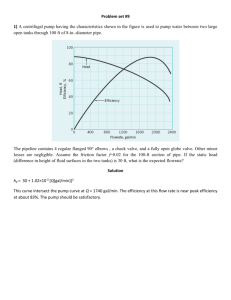
Pump Testing Procedure This procedure will also cover testing that determines if the system is safe to operate. It ensures there is no damage to the pump system or lung model and no injury to the operators. The following parameters will be tested to guarantee the safety of equipment and researchers: 1) Pressure does not exceed the rated pressure of the system components 2) Pressure supplied by the pump does not exceed critical value at pressure sensor This procedure will ensure the following specifications are met: 3) Experimental flow rate is determined within 10% of expected flow rate 4) There is no leakage from the system 5) Flow direction is able to be reversed This procedure will also be used to verify the correctness of an assumption. 6) Temperature change of the fluid is negligible Part 1: Flow Rate Measurement This test will determine the experimental flow rate from its minimum value to its maximum value. It will then be compared to its expected value using the Viking Online Pipe Curve. The RPM’s will also be recorded in order to determine a relationship between RPM and flow rate. This test is listed first since it does not require the entire pump system. Time/Place: 6 hours/Can be done outside laser lab Caution: Watch fluid level in reservoir tank to ensure the pump does not run dry. Parts Needed: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) _____ Viking Gear Pump and Motor _____ Variable Frequency Drive (installed) _____ Reservoir Tank (with installed bulkheads and tube adapters) _____ 1 ½ ’’ ID Tubing (as needed) _____ 1 ½ NPT Pipe (with coupling and 1 ½’’ tube adapter) (as needed) _____ Graduated Container _____ Stopwatch Procedure: 1) Install piping so that the suction side of pump is connected to the reservoir tank and the pump outlet leads to the graduated container. The tube should discharge into the container. 2) Using the Viking Online Calculator, determine the RPM associated with each flow rate to be tested. Record the values in the chart below. At a minimum, flow rates of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 32 gpm must be tested. Reading RPM Flow Rate from Viking (gpm) Measured Flow Rate (gpm) Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Average Percent Difference 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3) Turn on pump and increase RPM’s to match the flow rate being tested. 4) Have pump outlet discharge into the graduated cylinder. Use stopwatch to measure the time it takes to fill up a known volume. Turn off pump when finished. 5) Divide volume by time to calculate the measured flow rate and place it in the table above. 6) Empty graduated container into the reservoir tank 7) Repeat steps 3-6 with next flow rate. 8) Complete a 2nd and 3rd trial in order to get more accurate results. 9) Calculate the average percent difference for each flow rate. If a value is greater than 10%, a correction factor needs to be determined in order to calculate the measured flow rate from the RPM’s. Pass/Fail Criteria: A pass is given if all percent difference values are less than 10% Action if fail: Using given data, compute a correction factor to relate RPM to actual flow rate. End of Flow Rate Measurement Part 2: Pressure Measurement – Pump Outlet The following test requires that the system is assembled similar to the final design. The pressure sensors should not be installed, in order to avoid damage. A pressure sensor should be installed near the pump outlet. It should be able to handle pressures as high as 100 psi. This will not be included in the final design. If there are limitations on the system (flow rate, pressure), be aware of them and do not exceed them. Time/Place: 2 hr/Laser Lab Use of Laser Lab will require permission from Dr. Day or Dr. Robinson. Parts Needed: 1) ____ Pressure Measurement device (Max Pressure – 100 psi) Caution: Decrease flow rate if pressure is above 75 psi. 1) Verify system is correctly assembled according to the inhalation pipe schematic and assembly documents. 2) Turn on motor and increase the RPM to the first RPM value. Intervals can be user defined but at a minimum must include flow rates of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 32 gpm. 3) At specified intervals, record the pressure values below. Abort test if pressure at the pump outlet reaches a pressure greater than 75 psi. Reading (#) RPM Pressure (psi) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Pass/Fail Criteria: A pass is given if pressure at pump outlet is under 75 psi for all flow rates. Action if fail: The system needs to be redesigned in order to decrease the pressure loss in the system. Use the excel spreadsheet attached for assistance. End of Pressure Measurement – Pump Outlet Part 3 Pressure Measurement – Pressure Sensor This test will determine the pressures where the pressure sensors are located. The flow will be varied from the minimum value to the maximum value. The entire, final design will need to be assembled in order to complete this test. Time/Place: 3 hrs/Laser Lab Use of Laser Lab will require permission from Dr. Day or Dr. Robinson. Caution: Decrease flow rate if pressure is above 45 psi for any pressure sensor. (Sensors are rated for 50 psi) 1) Verify system is correctly assembled according to the inhalation pipe schematic and assembly documents. 2) Turn on the motor and increase the RPM to the first RPM value. Intervals can be user defined but at a minimum must include flow rates of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 32 gpm. 3) Record the maximum pressure value for each generation and the current RPM in the table below. Reading (#) RPM Generation Pressure (psi) 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Pass/Fail Criteria: A pass is given if pressure at the pressure sensor under 45 psi for all flow rates and all sensors. Action if fail: The system needs to be redesigned after the pressure sensor in order to decrease the pressure loss in the system. Use the excel spreadsheet attached for assistance. End of Pressure Measurement – Pressure Sensor Part 4: Total Leakage Observation This test is used to determine if there are leaks in the system. The complete system will need to be assembled and all above testing completed. Time/Place: 2 hr/Laser Lab Use of Laser Lab will require permission from Dr. Day or Dr. Robinson. Caution: If non-PIV lung model is used, be aware that it is not designed for high flow rates. Abort test immediately if any damage is found on the lung model. 1) Verify system is correctly assembled according to the inhalation pipe schematic and assembly documents. 2) Turn on motor and increase flow rate to 30 GPM. 3) Hold flow rate constant for 60 minutes and observe system for leakage. 4) Record observations below. At minimum, include system observation every 15 minutes. Time Elapsed Comments Pass/Fail Criteria: A pass is given no leakage is observed. Action if fail: All leaks are repaired. Test is rerun until pass. End of Total Leakage Observation Part 5: Flow Direction Reversal This test is used to ensure the system can be used to mimic exhalation, in addition to the inhalation setup that was previously tested. The system needs to be disconnected and then reassembled as shown in the exhalation pipe schematic diagram. Time/Place: 14 hr/Laser Lab Use of Laser Lab will require permission from Dr. Day or Dr. Robinson. Caution: If non-PIV lung model is used, be aware that it is not designed for high flow rates. Abort test immediately if any damage is found on the lung model. 1) Verify system is correctly assembled according to the exhalation pipe schematic and assembly documents. 2) Run Parts 2,3, and 4 of this testing plan. Ensure that data meets the pass criteria. Pass/Fail Criteria: A pass is given if no criteria are violated. Action if fail: The test receiving the ‘fail’ is repeated until it receives a ‘pass’. Follow violated procedure for proposed solutions. Part 6: Temperature Measurements This test is run to verify the assumption that temperature is constant. It does not change in space or time. The full, completed pump system is needed for this test. Time/Place: 5 hr/Laser Lab Use of Laser Lab will require permission from Dr. Day or Dr. Robinson. Parts Needed: 1) _____Thermocouple and thermocouple reader Caution: If non-PIV lung model is used, be aware that it is not designed for high flow rates. Abort test immediately if any damage is found on the lung model. 1) Verify system is correctly assembled according to the inhalation pipe schematic and assembly documents. 2) Turn on motor and run pump at 30 GPM for 4 hours. 3) Record temperatures below every 15 minutes Time (minute) Temperature (degC) 4) Using equation below, calculate the change in temperature per time. ∆𝑇 𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇𝑖 = ∆𝑡 𝑡𝑓 − 𝑡𝑖 Pass/Fail Criteria: A pass is given if change of temperature per change in time is less than 2 degC/hr Action if fail: Operation guidelines will have to be re-written to limit the amount of continuous use that the test rig can handle. Per user discretion, fluid can be retested for viscosity at a higher temperature.