Document
advertisement

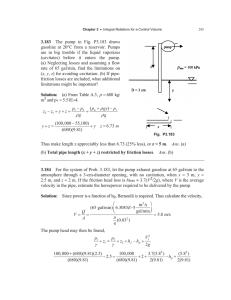
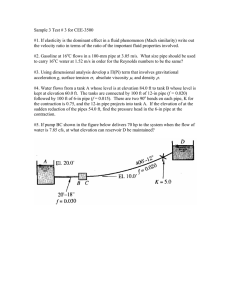
Fluid Mechanics 07 Hydraulic and Energy Grade Lines EGL:- Energy Grade line indicate the total head at any point in the system. 𝐸𝐺𝐿 = 𝑉𝑒𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 + 𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒 ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 + 𝐸𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝐻𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑣2 𝑝 𝐸𝐺𝐿 = + +𝑍 2∗𝑔 ɣ HGL:- Hydraulic Grade Line indicate the piezometric head at any point in the system 𝐻𝐺𝐿 = 𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒 ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 + 𝐸𝑙𝑒𝑣𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑 𝑝 𝐻𝐺𝐿 = + 𝑧 Hydraulic and Energy Grade Lines Pump Add head to the System Turbine Nozzle Nozzle increase the velocity and if discharge to atmospheric the term of pressure head will be zero Change in pipe diameter Negative Pressure Example A pump draws water (50°F) from a reservoir, where the water-surface elevation is 520 ft, and forces the water through a pipe 5000 ft long and 1 ft in diameter. This pipe then discharges the water into a reservoir with water-surface elevation of 620 ft. The flow rate is 7.85 cfs, and the head loss in the pipe is given by Determine the head supplied by the pump, hp, and the power supplied to the flow, and draw the HGL and EGL for the system. Assume that the pipe is horizontal and is 510 ft in elevation. Solution 𝑝1 ɣ + 𝑧1 𝑣12 + 2∗𝑔 + ℎ𝑝 = 𝑝2 + ɣ 𝑧2 𝑣22 + 2∗𝑔 + ℎ𝑡 + ℎ𝐿 Where P1=P2=Patm=zero V1=v2=zero Ht=zero, z1=520 ft, z2=620 ft 𝑄 7.85 𝑣= = = 10𝑓𝑡/𝑠 2 𝐴 (Π/4) ∗ (1 ) hL= 0.01 ∗ =77.6 ft 𝐿 𝐷 ∗ 𝑣2 ( )=0.01 2∗𝑔 ∗ 5000 1 ∗ 102 ( ) 2∗32.2 ℎ𝑝 = 𝑧2 − 𝑧1 + ℎ𝐿 = 620 − 510 + 77.6 =178 ft 𝑃𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 = ɣ ∗ 𝑄 ∗ ℎ𝑝 = 62.4 ∗ 7.85 ∗ 178 = 159ℎ𝑝