PROCEDURE - Confined Spaces - Entry
advertisement

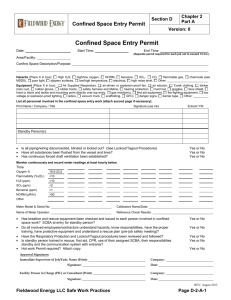
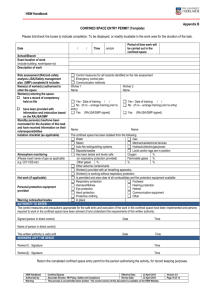
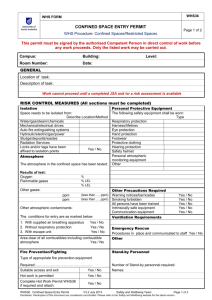
PROCEDURE: CONFINED SPACES – ENTER RISK RANKING: HIGH HAZARD ASSESSMENT: HAZARD 1. O2 Deficiency. 2. Toxic or Irritating atmosphere. 3. Mechanical equipment. POTENTIAL EFFECTS 1. Worker could stop breathing. 2. Worker could be exposed to airborne contaminants above the occupational exposure level. 3. Agitators may be in the space that could potentially harm workers. 4. Fluids. 4. Fluids present slip and trip hazard. 5. Engulfment. 5. Material within the space could fall on top of worker causing the worker to be buried. 6. N.O.R.M. 6. Overexposure to radiation present in vessel. 7. Flammable vapors / LEL. 7. Possibility of worker injury or equipment damage if explosion occurs with the presence of an ignition source. 8. Lack of visibility could result in worker injury and disorientation. 8. Illumination. Procedure: CONFINED SPACE – ENTER Date of Preparation: July 29, 2004 CONTROL 1. Perform atmospheric test and ensure O2 content is between 19.5% and 23.5%. 2. Perform atmospheric test (under SCBA or SABA) to determine if breathing apparatus are to be worn. 3. Lockout all potential energy sources prior to allowing worker to enter confined space. 4. Workers to wear appropriate footwear to enter the confined space. 5. Workers entering confined space are to don full body harness with a lifeline attached which is monitored by safety standby person (if applicable). 6. Perform N.O.R.M. survey prior entry. Don appropriate PPE before entering space. 7. Perform atmospheric test to ensure no LEL is present. Use only intrinsically safe equipment in the confined space. 8. Ensure intrinsically safe lighting is present. Page 1 Date of Revision: July 29, 2004 PROCEDURE: CONFINED SPACES – ENTER RISK RANKING: HIGH SAFETY EQUIPMENT: Safety Glasses with side shields, hard hat, steel toe boots, fire retardant clothing, gloves, life line and harness (if applicable), Air movers (explosion proof if applicable), portable lighting (explosion proof if applicable), MSDS, Lockout equipment, Personal Gas Monitor, communication means if applicable (intrinsically safe), fire extinguisher, warning signs (if applicable), SCBA/SABA, Formal training in confined space entry. H2S Alive or H2S Rescue are mandatory for any person expecting to utilize respiratory equipment. This training should be reinforced with safety exercises at safety meetings. PROCEDURES: 1 . Use the Buddy System — one trained person, equipped with the same respiratory protection as the workers in the confined space, is always stationed at the entrance ready to rescue the other in an emergency. The standby person remains in constant communication with those inside and is prepared to pull them out by their lifelines if anyone is having trouble. Note: the standby person never leaves their post to enter unless relieved by another person. The function is to perform all necessary rescues from outside the confined space and summon help in case of trouble. 2. Positive pressure SCBA or SABA must be used upon initial entry of a vessel for testing as the oxygen content and extent of other harmful substances is not known. Put on your breathing apparatus correctly, and attach your lifel me. 3. The following preparations must be made prior to entry: • Depressurize the workspace and pump any fluids as low as possible. • Isolate the workspace by using appropriate blanks and blinds on all inlets and outlets. • Lockout and tag all energy sources to the workspace. • Purge the workspace as necessary (if possible). • Ventilate the workspace using a positive method of mechanical ventilation if possible. Caution must be exercised with any exhaust vapors. • Test the atmosphere with a combustible gas detector, if the combustible gas level is below the acceptable LEL, as noted below, enter the confined space. If the combustible gas level is above the acceptable LEL level, re-ventilate the area; take any necessary measures to ensure the combustible gas level if any is safe to work in. • Ventilation should continue throughout the project. • If ventilation requires opening manways or clean-out doors, a catch-pan or vacuum truck should be made available to address liquids or sludge coming out of the space. Any wastes should be disposed of in accordance with established company policy. 4. Monitor the work area regularly with combustible gas detector to ensure the area remains safe. • Breathing apparatus must be worn at all times unless it is proven that no harmful gases or vapors above the occupational exposure levels, (e.g. 10 ppm H2S) and that oxygen content is no less than 19.5% by volume. Procedure: CONFINED SPACE – ENTER Date of Preparation: July 29, 2004 Page 2 Date of Revision: July 29, 2004 PROCEDURE: CONFINED SPACES – ENTER RISK RANKING: HIGH 5. Once inside, monitor constantly for any change in conditions and communicate them immediately to standby person. 6. Correct problems if possible or leave the confined space area and report conditions to supervisor. 7. If any ignition is to take place within the workspace, the atmosphere must be tested to confirm a 0% LEL. Issue a Hot Work permit. Procedure: CONFINED SPACE – ENTER Date of Preparation: July 29, 2004 Page 3 Date of Revision: July 29, 2004