Early Humans & Mesopotamia Vocabulary List
advertisement

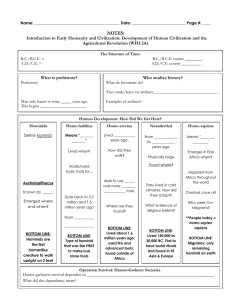
Name _____________________________________________________________________ Basic _____________ Unit 1 Vocabulary: EARLY HUMANS & MESOPOTAMIA 1) Ancient history: stories of the distant past, from the earliest humans to the first great civilizations 2) Social scientists: scholars who study human society; considered “history detectives”, such as archeologists, historians, anthropologists, and geographers 3) Archeologist: an expert who studies the past by examining objects that people have left behind 4) Historian: an expert who studies and records the past 5) Anthropologist: a scientist who studies human development and culture 6) Geographer: an expert who studies the Earth and creates maps of its natural and human-made features 7) Artifact: an object made or used by people in the past 8) Prehistoric: occurring before history was recorded or written down 9) Ritual: an action or tradition that takes place during a ceremony, such as during a religious ceremony 10) Hominid: a prehistoric human 11) Capabilities: skills, abilities, or talents 12) Remains: a dead body or the bones of a dead body 13) Biped: a two-footed animal 14) Migrate: to move from one geographic region to another 15) Land bridge: a piece of land connecting two continents 16) Australopithecus Afarensis: “Southern Ape”; “Lucy”; 3 feet tall biped which lived approximately 3-4 million years ago 17) Homo Habilis: “Handy Man”; could make tools and lived in groups about 1.5-2 million years ago 18) Homo Erectus: “Upright Man”; used fire and more complex tools; lived 1.8 million – 200,000 BCE; longest living group 19) Homo Sapiens Neanderthalensis: “Wise Man”; large brains and extremely strong, made better tools and lived/traveled in groups; lived 230,000 – 30, 000 BCE 20) Homo Sapiens Sapiens: “Doubly Wise Man”; created better tools, built shelters, and made clothing; first artists; lived 35,000 – 12, 000 BCE 21) Paleolithic Age: the first period of the Stone Age from about 2 million years ago to around 8000 BCE (also known as the Old Stone Age) 22) Neolithic Age: the later part of the Stone Age from 8000-3000 BCE (also known as the New Stone Age) 23) Domesticate: to train wild animals to be useful to humans 24) Agriculture: the business of farming 25) Trade: the business of buying and selling or exchanging items 26) Ore: a mineral mined for its valuable uses 27) Mesopotamia: “land between two rivers”; located in the present-day Middle East 28) Sumer: an area in the southern part of Mesopotamia where cities first appeared 29) Sumerians: ancient people who lived in the geographic region of Sumer 30) City-state: an early city that was like a small independent country with its own laws and government 31) Irrigation system: a means of supplying land with water 32) Levee: a wall of earth built to prevent a river from flooding its banks 33) Culture: a characteristic of civilization that includes the beliefs and behaviors of a society or group of people 34) Civilization: a culture marked by developments in the arts, sciences, government, and social structure 35) Social structure: the way a civilization is organized 36) Technology: the use of tools and other inventions for practical purposes 37) Status: importance 38) Chariot: a two-wheeled vehicle pulled by a horse 39) Scribe: a person who writes 40) Ziggurat: an ancient Mesopotamian temple tower 41) Lyre: a small harp made of a wooden sound box and strings 42) Arch: an upside down U or V-shaped structure that supports weight above it, as in a doorway 43) Cuneiform: writing that uses wedge-shaped characters 44) Pictograph: a symbol that stands for an object 45) Empire: a large territory in which several groups of people are ruled by a single leader or government 46) Capital: a city that is the center of government 47) Tribute: wealth sent from one country or ruler to another as a sign that the receiver is superior 48) Stele: carved stones containing three-dimensional sculptures 49) Siege: a military blockade and attack on a city to force it to surrender 50) Aqueduct: a pipe or channel that brings water from distant places 51) Bas-relief: a sculpture in which the image projects out from a flat surface 52) Astronomy: the study of stars and planets 53) 4 Empires which ruled Mesopotamia: AKKADIAN, BABYLONIAN, ASSYRIAN, NEOBABYLONIAN