NS and Maths @ TKP - LearningTogether-TKP
advertisement

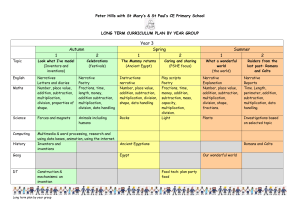
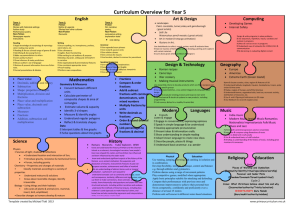
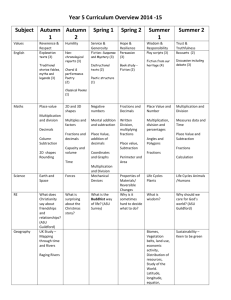
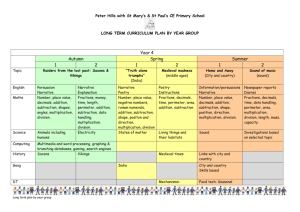
National Standards and Maths @ TKP Reference / Resource National Standard TKP2012 After 1 year at school (A1) After one year at school, students will be achieving at early level 1 in the mathematics and statistics learning area of the NZC In contexts that require them to solve problems or model situations, students will be able to: Apply counting-all strategies Continue sequential patterns and number patterns based on ones. After 2 years at school (A2) After two years at school, students will be achieving at level 1 in the mathematics and statistics learning area of the NZC In contexts that require them to solve problems or model situations, students will be able to: Number and Algebra Geometry and Measurement compare the lengths, areas and volumes or capacities, and weights of objects directly sort objects and shapes by a single features and describe the feature, using everyday language represent reflections and translations by creating patterns describe personal locations and give directions, using everyday language apply counting-on, countingback, skip-counting, and simple grouping strategies to combine or partition whole numbers use equal sharing and symmetry to find fractions of sets, shapes, and quantities create and continue sequential patterns by identifying the unit of repeat continue number patterns based on ones, twos, fives, and tens. compare the lengths, areas, volumes or capacities, and weights of objects and the durations of events, using selfchosen units of measurement sort objects and shapes by different features and describe the features, using mathematical language represent reflections and translations by creating and describing patterns describe personal locations and give directions, using steps and half- or quarter-turns. After 3 years at school (A3) By the end of year 4 (Y4) By the end of year 5 (Y5) By the end of year 6 (Y6) After three years at school, students will be achieving at early level 2 in the mathematics and statistics learning area of the NZC In contexts that require them to solve problems or model situations, students will be able to By the end of year 4, students will be achieving at level 2 in the mathematics and statistics learning area of the NZC In contexts that require them to solve problems or model situations, students will be able to: By the end of year 5, students will be achieving at early level 3 in the mathematics and statistics learning area of the NZC In contexts that require them to solve problems or model situations, students will be able to: By the end of year 6, students will be achieving at level 3 in the mathematics and statistics learning area of the NZC In contexts that require them to solve problems or model situations, students will be able to: apply basic addition facts and knowledge of place value and symmetry to: - combine or partition whole numbers - find fractions of sets, shapes, and quantities create and continue sequential patterns with one or two variables by identifying the unit of repeat continue spatial patterns and number patterns based on simple addition or subtraction. apply basic addition and subtraction facts, simple multiplication facts, and knowledge of place value and symmetry to: - combine or partition whole numbers - find fractions of sets, shapes, and quantities create, continue, and give the rule for sequential patterns with two variables create and continue spatial patterns and number patterns based on repeated addition or subtraction. apply additive and simple multiplicative strategies and knowledge of symmetry to: - combine or partition whole numbers - find fractions of sets, shapes, and quantities create, continue, and predict further members of sequential patterns with two variables describe spatial and number patterns, using rules that involve spatial features, repeated addition or subtraction, and simple multiplication measure the lengths, areas, volumes or capacities, and weights of objects and the duration of events, using linear whole-number scales and applying basic addition facts to standard units sort objects and two- and threedimensional shapes by their features, identifying categories within categories represent reflections, translations, and rotations by creating and describing patterns describe personal locations and give directions, using wholenumber measures and half- or quarter-turns. measure the lengths, areas, volumes or capacities, weights, and temperatures of objects and the duration of events, reading scales to the nearest whole number and applying addition, subtraction, and simple multiplication to standard units sort objects and two- and threedimensional shapes by two features simultaneously represent and describe the symmetries of a shape create nets for cubes describe personal locations and give directions, using simple maps. measure time and the attributes of objects, choosing appropriate standard units and working with them to the nearest tenth sort two- and three-dimensional shapes, considering the presence and/or absence of features simultaneously and justifying the decisions made represent and describe the results of reflection, rotation, and translation on shapes create nets for rectangular prisms draw plan, front, and side views of objects describe locations and give directions, using grid references and points of the compass. investigate summary and comparison questions by using the statistical enquiry cycle: - gather, display, and identify patterns in category and wholenumber data - interpret results in context order the likelihoods of outcomes for simple situations investigate questions by using the statistical enquiry cycle (with support), gathering, displaying, and/or counting category data Statistics investigate questions by using the statistical enquiry cycle (with support), gathering, displaying, and/or identifying similarities and differences in category data describe the likelihoods of outcomes for a simple situation involving chance, using investigate questions by using the statistical enquiry cycle (with support): - gather and display category and simple whole-number data - interpret displays in context compare and explain the likelihoods of outcomes for investigate questions by using the statistical enquiry cycle independently: - gather and display category and simple whole-number data - interpret displays in context compare and explain the likelihoods of outcomes for a simple situation involving apply additive and simple multiplicative strategies flexibly to: - combine or partition whole numbers, including performing mixed operations and using addition and subtraction as inverse operations - find fractions of sets, shapes, and quantities determine members of sequential patterns, given their ordinal positions describe spatial and number patterns, using: - tables and graphs - rules that involve spatial features, repeated addition or subtraction, and simple multiplication. measure time and the attributes of objects, choosing appropriate standard units use arrays to find the areas of rectangles and the volumes of cuboids, given whole-number dimensions sort two- and three-dimensional shapes (including prisms), considering given properties simultaneously and justifying the decisions made represent and describe the results of reflection, rotation, and translation on shapes or patterns identify nets for rectangular prisms draw or make objects, given their plan, front, and side views describe locations and give directions, using grid references, turns, and points of the compass. investigate summary and comparison questions by using the statistical enquiry cycle: - gather or access multivariate category and whole-number data - sort data into categories or intervals, display it in different ways, and identify patterns everyday language. a simple situation involving chance. chance, acknowledging uncertainty. JAM (Junior Assessment in Maths) Additive Strategies Forwards and backwards sequences knowledge Multiplicative and Fraction Strategies Stages 2 and 3 Applying ‘Counting all’ strategies Stages 2 and 3 Says forward and backward sequences and the number before or after in range 0-20 Stages 2 and 3 Applying ‘Counting all’ strategies Fraction Knowledge Grouping and Place Value Stages 2 and 3 Knows grouping within 5, with 5, and within 10 Recognises patterns and doubles to 10 Basic Facts Stages 2 and 3 Recalls facts to 5, doubles to 10, and groupings within 10 Early Stage 5 Apply basic addition facts and knowledge of place value and symmetry to combine or partition whole numbers Early Stage 5 Says forward and backward sequences and the number before or after in the range 0-1000 Stage 4 Advanced counting Applying counting on, counting back, skip-counting, and simple grouping strategies, and, Use equal sharing to find fractions of sets Identifies symbols for halves, quarters, thirds and fifths Early Stage 5 Apply basic addition facts and knowledge of place value and symmetry to combine or partition whole numbers, and find fractions of sets, and quantities Algebra (patterns) Continue sequential patterns Geometry (shapes) Sort objects and shapes by a single feature and describe the feature, using everyday language Sort objects and shapes by different features and describe the features, using mathematical language Measurement (length) Compare the lengths of objects directly Compare the lengths of objects using self-chosen units of measurement Can sort objects (eg. animals) into categories, using a set grouping or pictograph Can answer simple questions about results Can make comparisons between groups of objects Can identify two possible outcomes (probability) Statistics - interpret results in context, accepting that samples vary order the likelihoods of outcomes for situations involving chance, considering experimental results and models of all possible outcomes. GLoSS Stage 4 Advanced counting Applying counting on, counting back, skip-counting, and simple grouping strategies Stage 4 Says forward and backward sequences and the number before or after in range 0-100 Stage 4 Knows groupings with 10 and the pattern of –teens Knows groupings within 20 Knows the number of tens in decades Stage 4 Recall facts to 10, doubles to 20, and corresponding halves and – teen facts Create and continue sequential patterns by identifying unit of repeat involving chance, experimenting or listing all possible outcomes. Early Stage 5 Identifies the symbols for the most common fractions, including halves, quarters, thirds, fifths and tenths Early Stage 5 Knows groupings within 100 and multiples of 5 Knows groupings of 10 in a 3-digit number Early Stage 5 Recall addition facts to 20 and subtraction facts to 10 Create and continue sequential patterns with one or two variables by identifying the unit of repeat Sort objects and two and threedimensional shapes by their features, identifying categories within categories Measure the lengths of objects, using linear, whole-number scales and applying basic addition facts to standard units Sort whole-number data into groups Display data in enclosed groupings or organised displays eg. bar graph Make comparison statements about data displayed Can classify probability eg. use likely and least likely; use fractions to describe likelihood Stage 5:Early Additive / Part whole (End of year 4 – achieving Stage 5) Stage 6: Advanced Additive / Early Multiplicative (End of year 5 – working within Stage 6: End of year 6 – achieving Stage 6) Addition and Subtraction Solve subtraction problems (separating, change/start unknown, or comparing) by going back through tens. Solve addition problems by forming tens from ones and forming hundreds from tens. Solve subtraction problems by operating on place values while “parking” ones, tens (hundreds). Solve subtraction problems using standard place value partitioning, e.g. 73 – 46 =␣as73–40 =33, 33– 6 =␣. Solve addition and subtraction problems by working from doubles. Solve addition and subtraction problems by using groupings with five. Solve addition problems by looking for compatible numbers that add to ten, other decades or one hundred. Solve addition problems by going up through tens. Solve addition and subtraction problems by combining and separating tens and ones. Solve addition problems by compensating with tidy numbers. Solve addition problems by looking for compatible numbers. Solve addition and subtraction problems by compensating with tidy numbers (including equal additions). Solve comparison and difference problems by reversing (adding instead of subtracting), e.g. 72 – 45 =␣as 45 +␣= 72. Solve addition and subtraction problems by exchanging ones for tens, and tens for hundreds (decomposition), leading to a written algorithm. Choose critically from a range of mental strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems. Multiplication and Division Solve multiplication problems using repeated addition Solve five times tables by doubling and halving (and learn them) Use the commutative property, e.g. 4 × 6 = 6 × 4 Dividing by sharing using addition to predict Dividing by making equal sets Proportions and Ratios Find a unit fraction of a set using addition facts, particularly doubles, e.g. 1 of16is4using 1 of 42 16 is 8. Find unit fractions of a continuous region, like a length or area, using halving. Order unit fractions and fractions with the same denominator and explain why they are larger or smaller Order fractions visually using materials, including improper fractions like 5/3 and 7/4 and explain what the numerator and denominator mean Use times five facts to work out times six, seven, and four facts (using the distributive property) Use times ten facts to work out times nine facts (using the distributive property) Change the order of the factors to make a multiplication problem easier, e.g. 26 x 3 = 3 x 26 Find out how many ones, tens, hundreds and thousands are in all of a whole number, Use two times facts to work out three, four, six, and eight times facts (using doubling and the distributive property) Multiply by tens, hundreds, thousands, and other multiples of ten Solve sharing problems by reversing multiplication facts Solve “How many equal sets of ?” problems by reversing multiplication facts Solve problems using a combination of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division mental strategies Find fractions of a set using multiplication and division Use symmetry to find fractions of continuous shapes like lengths, circles, and rectangles. Solve division problems that have fraction answers using halving. Create equivalent ratios by repeated copying. Measure how many times a unit fraction goes into a whole number, e.g. How many quarters are in five? Rename improper fractions as mixed numbers using materials with multiplication, and position improper fractions on a number-line Stage 5:Early Additive / Part whole (End of year 4 – achieving Stage 5) Addition and Subtraction IKAN Identify all of the numbers in the range 0-1000 Say the forwards and backwards number word sequences by ones, tens, and hundreds in the range 01000. Say the number 1, 10, or 100 more or less than a given number in the range 0-1000. Order numbers in the range 0-1000. Recalls groupings within 100, e.g. 49 and 51 (particularly multiples of 5 e.g. 25 & 75) Recall the number of groupings of tens that can be made from a three-digit number Recall addition and subtraction facts to 20 Recall the number of tens and hundreds in centuries and thousands. Round three-digit whole numbers to the nearest 10, or hundred Recall the multiples of 100 that add to 1000, e.g. 400 and 600. Record the results of addition calculations, using equations and diagrams. Multiplication and Division Say the forwards and backwards skip-counting sequences in the range 0- 100 for twos, threes, fives, and tens at least. Recall groupings of two in numbers to 20, groupings of five in numbers to 50, and groupings of 10 in numbers to 100. Automatically recall the multiplication and division facts for the multiples of 2, 5, and 10. Record the results of mental multiplication calculations using equations and diagrams Proportions and Ratios Identify the symbols for halves, quarters, thirds, fifths, and tenths including fractions greater than 1. Order fractions with like denominators, e.g. 1/4. and 2/4. PAT Maths Stage 6: Advanced Additive / Early Multiplicative (End of year 5 – working within Stage 6: End of year 6 – achieving Stage 6) Identify all of the numbers in the range 0 - 1 000 000. Say the forwards and backwards whole number word sequences by ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands in the range 0 – 1 000 000, including finding numbers that are 10, 100, and 1 000 more or less than a given number Order whole numbers in the range 0-1 000 000. Read decimals with tenths, count forwards and backwards in tenths, order decimals with tenths. Recall groupings within 1000, e.g., 240 + 760. Recall addition and subtraction facts to 20. Recall how many tens and hundreds there are in four- digit numbers. Record the results of mental calculation using addition and subtraction equations and diagrams Round whole numbers to the nearest ten, hundred, or thousand Carry out column addition and subtraction with whole numbers of up to four digits Recall groupings of twos, threes, fives, and tens that are in numbers to 100 and the resulting remainders Recall all the multiplication and division facts for 2, 3, 5, 10 x tables Recall groupings of 10 and 100 that can be made from a four-digit number Recall multiplication facts for squares to 100 Record the results of mental calculation using multiplication and division equations and diagrams Identify decimals to three places Identify symbols for any fraction, including tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and those greater than 1 Say the forwards and backwards word sequences for halves, quarters, thirds, fifths, and tenths Say the decimal number word sequences, forwards and backwards, in tenths and hundredths Order unit fractions for halves, quarters, thirds, fifths, and tenths Recall the number of tenths and hundredths in decimals to two places Round decimals with up to two places to the nearest whole number Students achieving at Stanine 5 or 6 are considered to be ‘meeting’ the standard References and Resources: NZC, JAM Assessment kit; Mathematics Standards, Numeracy Framework and texts. Teachers should refer to these for more detailed explanations and examples and also the National Standard Illustrations http://www.nzmaths.co.nz/national-standards-illustrations?parent_node=