Ch. 6 Concept Checks
advertisement

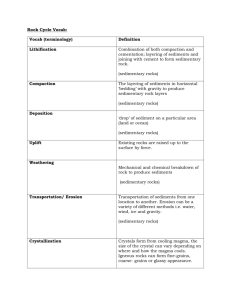
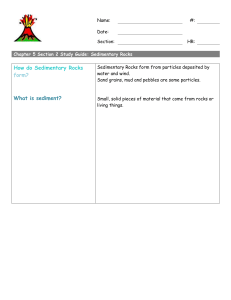
CH. 6 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS 6.1 1. How does the volume of sedimentary rocks in Earth’s crust compare to igneous and metamorphic rocks? 2. Why are sedimentary rocks important? 6.2 1. Outline the steps that would transform an exposure of granite in the mountains into various sedimentary rocks. 2. List and briefly distinguish among the three basic sedimentary rock categories. 6.3 1. What minerals are most abundant in detrital sedimentary rocks? In which rocks do these sediments predominate? 2. What is the primary basis for distinguishing among detrital rocks? 3. Describe how sediments become sorted. 4. Distinguish between conglomerate and breccia. 6.4 1. What are the two categories of chemical sedimentary rock? Give an example of a rock that belongs to each category. 2. Distinguish among limestone, dolostone, and chert. 3. How do evaporites form? Give an example. 6.5 1. Outline the successive stages in the formation of coal. 6.6 1. What is diagenesis? 2. List three common cements. How might each be identified? 6.7 1. What is the primary basis for distinguishing (naming) different chemical sedimentary rocks? 2. Distinguish between clastic and nonclastic. Which texture is associated with all detrital rocks? 6.8 1. What are the three categories of sedimentary environments? 6.9 1. What is the single most characteristic feature of sedimentary rocks? 2. What is the difference between cross-bedding and graded bedding? 3. How might mud cracks and ripple marks be useful clues about the geologic past? 6.10 1. List the two groups of nonmetallic resources and some examples of each. 6.11 1. Coal has the advantage of being plentiful. What are some of coal’s disadvantages? 2. What is an oil trap? List two conditions common to all traps. 6.12 1. Describe how chemical weathering and the formation of biochemical sediment removes carbon from the atmosphere and stores it in the geosphere.