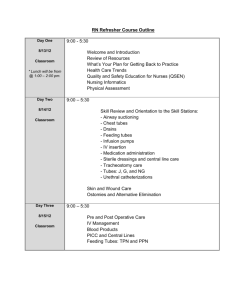
Blood Preparation at Necropsy

SOP Number: CP001.00
Title: Processing Whole Blood
Revision No:
00
Replaces:
N/A
Date in effect:
7/8/2010
Page:
Page 1 of 6
I
Author: Dylan Lennon, Kristin
Smith
MAL Director: Dr. Peggy Borum FSHN Chair: Dr. Neil Shay
PURPOSE
The purpose of processing whole blood is to separate the blood that is collected into plasma and washed red blood cells. Once separated further analysis can be performed.
II SCOPE
Blood collected from the piglet can be processed for use in three separate assays and hematocrit measurements. Figure 1 illustrates an area that has been prepared for such processing.
III RESPONSIBILITIES
It is the responsibility of Metabolic Assessment Laboratory personnel to follow this procedure. It is the responsibility of supervisory personnel to ensure compliance with this procedure and to train employees and students responsible for performing this procedure. Students will report accidents to the principal investigators immediately.
IV REFERENCES
N/A
V REAGENTS AND MATERIALS
V.A.
Large Vacutainer tubes containing EDTA.
V.B.
Plastic 17 x 100 tubes.
V.C.
Deionized water.
V.D.
Parafilm.
V.E.
Saline.
V.F.
Capillary tubes.
V.G.
Critoseal.
V.H.
Plastic transfer pipettes.
V.I.
Kimwipes.
V.J.
1000 and 100 microliter pipets.
V.K.
Microfuge.
V.L.
Test tube centrifuge baskets.
V.M.
Solid waste beaker.
V.N.
Liquid waste beaker.
V.O.
Biohazard sharps box.
V.P.
Vacuum bulbs.
V.Q.
4000mL beaker.
Uncontrolled Copy
Документ1
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT-DO NOT DUPLICATE Controlled Copy No._______
SOP Number: CP001.00
Title: Processing Whole Blood
Revision No:
00
Replaces:
N/A
Ice
Bin
Extra transfer pipettes
Date in effect:
7/8/2010
Biohazard
Box Vortex
Beam balance
Page:
Page 2 of 6
Test tube rack Saline on ice
Ice
Bin
Solid waste
Test Tube Holder
Specimen mixer
Parafilm
Liquid waste
Microfuge Lab Counter
Hematocrit
Reader
Pipette, tips, transfer pipettes, capillary tubes,
Kimwipes
Microfuge
Med Record 1 Med Record 2
Lab Counter
Figure 1.
VI EQUIPMENT
V.A.
Hematocrit reader.
V.B.
Specimen rocker.
V.C. Centrifuge.
V.D. Balance.
VII SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
VII.A. Members of the MAL have been trained extensively in the procedures described in this SOP.
VII.B. Members of the MAL have been approved to work with human blood and piglet blood, tissues, and urine.
VIII DEFINITIONS
VIII.A. Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) – Standard Operating Procedure is a document that provides instructions for completing a specific task in the lab.
VIII.B. Metabolic Assessment Laboratory (MAL) – The Metabolic Assessment Laboratory is the laboratory that will use this SOP.
IX PROCEDURE
IX.A. Preparation
Uncontrolled Copy
Документ1
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT-DO NOT DUPLICATE Controlled Copy No._______
SOP Number: CP001.00
Title: Processing Whole Blood
Revision No:
00
Replaces:
N/A
Date in effect:
7/8/2010
Page:
Page 3 of 6
IX.A.1. Set up lab counter according to Figure 1.
IX.A.2. Refer to SOP# CP034.00 for procedures on how to label blood tubes.
IX.B. Blood analysis
IX.B.1. Determining hematocrit
IX.B.1.a. Prepare a capillary tube with whole blood sample.
IX.B.1.b. Fill capillary tube to about 90% capacity with central blood, tilting the tube towards the horizontal if necessary. Blood is drawn by suction, so do not cover the end of the capillary tube sticking out at you.
IX.B.1.c. Seal the end of the capillary tube inserted into the blood with Critoseal (see
Figure 2). Do not press hard on the Critoseal as this will break the tube.
IX.B.1.c.(1). Create three capillary tubes per sample.
IX.B.1.c.(2). Place these tubes into the Microfuge with the end with the CritoSeal plug facing outward.
Also ensure that the ends of the capillary tubes are touching the edge of the centrifuge.
IX.B.1.c.(3). Balance the three tubes.
IX.B.1.c.(4). Screw lid on rotor and close Microfuge.
IX.B.1.c.(5). Set to High for 5 minutes.
Figure 2.
Ix.B.1.c.(6). Determine the hematocrit (Hct) by using instructions on the hematocrit reader.
IX.C. Blood for hemoglobin assay
IX.C.1. Using P1000 pipette, aliquot 450μL distilled water into the plastic tubes designated for hemoglobin.
IX.C.2. Using P200 pipette, add 50μL of blood from the sample to the hemoglobin tube. This will create a 1:10 ratio of blood to water solution.
IX.C.3. Vortex for 10 seconds (See Figure 3).
IX.C.4. Place into freezer.
IX.D. Separating plasma from whole blood
IX.D.1. Centrifuging Whole Blood Samples
Uncontrolled Copy
Документ1
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT-DO NOT DUPLICATE Controlled Copy No._______
SOP Number: CP001.00
Title: Processing Whole Blood
Revision No:
00
Replaces:
N/A
Date in effect:
7/8/2010
Page:
Page 4 of 6
IX.D.1.a. Fill 2 black buckets with ice. In one bucket, prepunch diagonal holes (45 degrees) using an empty vacutainer tube. In the other bucket, prepunch the ice with vertical holes. The bucket with vertical holes will be used to transport the blood once collected. The bucket with diagonal holes will be used to transport blood during separation.
IX.D.1.b. Balance sample tubes, ensuring that blood from the same origin (i.e. central or portal) is transferred to a tube of the same origin from the same piglet.
IX.D.1.c. Centrifuge for 15 minutes at 2,000-3,000 rpm (4-6 o
C) using the centrifuge located in the cold room.
IX.D.1.d. Transfer supernatant into clean test tubes pre-labeled “Plasma,” using a plastic transfer pipet. Avoid the buffy coat and red blood cells in this step.
If possible, combine plasma from multiple tubes (of the same origin), but be sure not to fill the tubes over two-thirds full (as they will expand upon freezing).
IX.D.1.e. Store in freezer.
IX.E. Preparing washed red blood cells (RBCs)
IX.E.1. Isolating RBCs
IX.E.1.a. Discard the buffy coat into liquid waste container (a large beaker designated for liquid waste).
IX.E.2. Rinsing the RBCs
IX.E.2.a. Add ice-cold saline to the test tubes containing the RBCs. Use a volume of saline approximately equal to the volume of the RBCs.
IX.E.2.b. Covering the Vacutainer tube with parafilm, mix the cells by gentle inversion.
IX.E.2.c. If any of the packed cells remain on the parafilm, gently slide the surface of the parafilm containing the sample across the mouth of the test tube to minimize sample loss.
IX.E.3. Centrifuge again for 15 minutes at 2,000-3,000 rpm (4-6ºC).
IX.E.4. Dispose of the supernatant and buffy coat in liquid waste.
IX.E.5. Add slightly more saline than the volume of RBCs to the Vacutainer tube.
IX.E.6. Mix the cells by inversion as before.
IX.E.7. Transfer the suspension to a new plastic test tube, pre-labeled “Washed RBC.”
IX.E.8. Centrifuge a third time for 15 minutes at 2,000-3,000 rpm (4-6oC).
IX.E.9. Dispose of the supernatant and buffy coat in liquid waste.
IX.E.10. Cap the test tubes containing the washed RBC’s and place in freezer.
Uncontrolled Copy
Документ1
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT-DO NOT DUPLICATE Controlled Copy No._______
SOP Number: CP001.00
Title: Processing Whole Blood
Revision No:
00
Replaces:
N/A
Figure 3.
Date in effect:
7/8/2010
Page:
Page 5 of 6
Uncontrolled Copy
Документ1
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT-DO NOT DUPLICATE Controlled Copy No._______
SOP Number: CP001.00
Title: Processing Whole Blood
Revision No:
00
X
Replaces:
N/A
ATTACHMENTS
Date in effect:
7/8/2010
Page:
Page 6 of 6
X.A. For a list of materials and their locations, refer to SOP# CG098.00.
Uncontrolled Copy
Документ1
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT-DO NOT DUPLICATE Controlled Copy No._______