1.2 vocab and grammar packet
advertisement

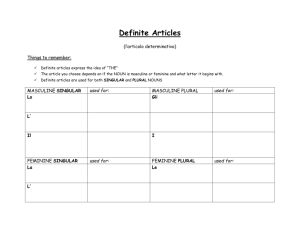
Nombre ____________________________________ In this lesson you will be able to: *Describe yourself and others *Identify people and things Español 1: El paquete de 1.2 Using: *Ser to describe what someone is like *Definite and indefinite articles *Noun-adjective agreement Describe Yourself and Others ¿Cómo eres? pelirrojo(a) artístico(a) pequeño(a) atlético(a) viejo(a) bueno(a) Tengo... cómico(a) Tiene... desorganizado(a) pelo rubio estudioso(a) pelo castaño inteligente People malo(a) el (la) amigo(a) organizado(a) la chica perezoso(a) el chico serio(a) el (la) estudiante simpático(a) el hombre trabajador(a) la mujer alto(a) la persona bajo(a) Other Words and Phrases bonito(a) muy grande un poco guapo(a) porque joven (pl. jóvenes) todos(as) 1 Nota Gramatical: You already know that ser means __________________. people are from. You have used ser to say where You can also use ser to _____________________________________________________. Ejemplos: La mujer es alta. The woman is tall. Los chicos son organizados. The boys are organized. Definite Articles Definite articles are used with nouns to indicate _______________ persons places or things. In English, ______________ is a definite article. In Spanish, there are four ways to say the word __________. The definite articles match the nouns in __________________ (masculine/feminine) and _____________________ (singular/plural). Unlike English, all Spanish nouns, even if they refer to objects, are either masculine or feminine. You can tell if most nouns are masculine or feminine by the ending of the word. *Nouns ending in _____________ are usually masculine. *Nouns ending in _____________ are usually feminine. Some nouns do not follow this pattern and will have to be memorized (el agua-water). Others will end in a consonant and the gender will have to be memorized (el reloj-clock). You can tell if nouns are plural in Spanish because they end in _______________. Here are the four ways of saying “the” in Spanish: masculine singular feminine singular masculine plural Ejemplos: Práctica: feminine plural el chico-the boy la chica-the girl los chicos-the boys las chicas-the girls Fill in the appropriate definite article for each noun. 1. _______ amigo 4. _______ personas 7. _______ escuelas 2. _______ comida 5. _______ amigos 8. _______ guitarra 3. _______ refrescos 6. _______ helado 9. _______ papas fritas 2 Indefinite Articles You have already learned that definite articles are used to indicate specific personas, places or things. Indefinite articles are used with nouns to indicate _________________ persons, places or things. In English, ______________ are definite articles. Ejemplo: I want the pencil. vs. I want a pencil. There are two ways to say the word _____ or _____ in Spanish. Like definite articles, indefinite articles match the nouns in __________________ (masculine/feminine) and _____________________ (singular/plural). Here are the two ways of saying “a/an” in Spanish: masculine singular feminine singular If you make an indefinite article plural (________________ or _______________), it translates as __________________. Here are the four indefinite articles: masculine singular feminine singular (a/an) (a/an) masculine plural (some) feminine plural (some) Ejemplos: Tengo un libro. I have a book. Tengo unos libros. I have some books. Práctica: Fill in the appropriate indefinite article for each noun. 1. _______ amigo 4. _______ personas 7. _______ escuelas 2. _______ comida 5. _______ amigos 8. _______ guitarra 3. _______ refrescos 6. _______ helado 9. _______ papas fritas Making Nouns Plural You have already seen that to make most Spanish nouns plural, you add the letter ______. However, if the word ends in a consonant, you must add ______ to the end of the word to make it plural. Ejemplos: Práctica: 1. estudiante-estudiantes (this word ends in a vowel so an –s is added) mujer-mujeres (this word ends in a consonant so –es is added) Make each noun plural. hombre-_________________ 2. español-__________________ 3. chico-_________________ 3 Noun-Adjective Agreement In Spanish, adjectives match the ____________________ (masculine/feminine) and the ____________________ (singular/plural) of the nouns they describe (just like definite/indefinite articles). So, every adjective has four forms (singular/masculine, singular/feminine/plural masculine/plural feminine). Most Spanish adjectives end in _____. To make them feminine, change the _____ to an _____. To make them plural, add _____. masculine singular feminine singular masculine plural feminine plural bueno perezosa simpáticos organizadas Some adjectives end in _____ and match both genders (you don’t change it for masc/fem). To make them plural, add _____. masculine singular feminine singular masculine plural feminine plural inteligente inteligente inteligentes inteligentes Some adjectives end in a ___________________ and match both genders. To make them plural you add _____. masculine singular feminine singular masculine plural feminine plural joven joven jóvenes jóvenes Some adjectives end in a ___________________ and can be made feminine by adding the letter _______ to the end. masculine singular feminine singular masculine plural feminine plural Trabajador Práctica: Trabajadora Trabajadores Trabajadoras Translate the following expressions into Spanish: 1. The good-looking girl=____________________________________________________________ 2. The serious students=_____________________________________________________________ 3. The big schools=__________________________________________________________________ 4. The hard-working man=_____________________________________________________________ 5. The young woman=__________________________________________________________________ 4