AVMA core competence 1: Comprehensive patient diagnosis
advertisement

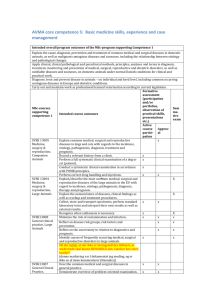
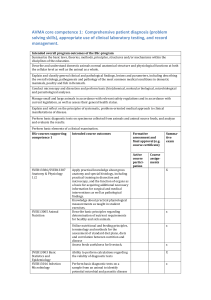
AVMA core competence 1: Comprehensive patient diagnosis (problem solving skills), appropriate use of clinical laboratory testing, and record management. Intended overall MSc-program outcomes supporting Competence 1 Explain the cause, diagnosis, prevention of and treatment of common medical and surgical diseases in domestic animals, as well as malignant contagious diseases and zoonoses, including the relationship between etiology and pathological changes. Account for practice appropriate clinical pathological analyses and their application in clinical work. Perform clinical examination and pregnancy diagnostics on common domestic mammals, including necropsies and assessment of overall necropsy findings. Diagnose, treat and prevent disease in animals – at individual and herd level, including common infectious diseases in Europe and obstetric conditions. Apply clinical, clinical pathological and paraclinical methods, principles, analyses and terms in diagnosis, treatment, monitoring and prevention of medical, surgical, reproductive and obstetric disorders, as well as notifiable diseases and zoonoses, on domestic animals under normal Danish conditions for clinical and practical work. Formative assessment (participation MSc core and/or portfolios, courses Sum observation of supporting mapractical skills, Intended course outcomes competence tive presentations etc.) 1 exam Active Approva course l participation SVEK 13005 Explain common medical, surgical and reproductive diseases X Medicine, in dogs and cats with regards to the incidence, etiology, surgery & pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. reproduction Explain the optimal work up and treatment plans for selected X , Companion clinical presentations. Animals Explain the nomenclature of diseases, clinical findings and X work up and treatment procedures. Explain the basic elements concerning workup of selected x medical, surgical and reproductive diseases in dogs and cats. Write a POMR (problem-oriented medical record) based on a x x x history and the clinical examination. Design a meaningful diagnostic and treatment plan for a x patient with a medical, surgical and or reproductive problem. SVEK 13004 Explain/describe the most common medical, surgical and x Medicine, reproductive diseases of the large animals in the EU with surgery & regard to incidence, etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, reproduction therapy and prognosis. , Large Explain the optimal workup and treatment plans for selected x Animals diseases. Record an accurate and relevant medical history of the individual animal or herd and its surroundings, and prepare clinical records in a form that is comprehensible to colleagues and laymen. Explain the nomenclature of diseases, clinical findings as well as workup and treatment procedures. Explain the nomenclature of diseases, clinical findings as well as workup and treatment procedures. (Samme læringsmål gentages x2) Explain the basic elements concerning workup of selected medical, surgical and reproductive diseases of the large animals, x x x x x x x x SVEK13008 General clinical practice, Large Animals SVEK13007 General Clinical Practice, Companion Animals SVEK13003 Veterinary Imaging SVEK13001 Veterinary Paraclinics Handling and restraint of an animal in a secure and humane manner, as well as instructing others in exercising these techniques. Perform a clinical examination on a patient. x x x x Collect, store and transport specimens, perform standard laboratory tests and interpret their own results as well as external results. Produce accurate records and maintain regular records in a satisfactory manner comprehensible to colleagues and the public. Ability to record a relevant history for a single animal or a herd. Collect, store and handle specimens, perform standard laboratory tests and interpret the results of the various laboratory tests. Identify causes of frequently occurring medical, surgical and reproductive disorders in large animals. Knowledge of the criteria for diagnosis of pregnancy and the course of the estrus cycle, and knowledge of the basic techniques for insemination of cattle and horses. Describe common medical and surgical diseases in general practice. Demonstrate overview of problem-oriented examination, interpretation and localization of clinical symptoms, workup, diagnosis, treatment, monitoring and referral of medical and surgical patients in general family animal practice. Select and justify the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis for a specific patient Select, justify and interpret relevant paraclinical and clinical examinations. Identify, evaluate and interpret issues related to the recording of history and clinical- and paraclinical examination of the patient, as well as formulating and implementing a diagnostic and therapeutic plan. Collect and analyze diagnostic specimens. x x Be able to produce a selection of common radiographic projections in a safe manner from canine, feline and equine patients. List the radiographic changes that are commonly encountered in common diseases in dogs, cats and horses Identify normal and abnormal radiographic findings on radiographic images in selected cases commonly encountered in veterinary practice Recognize and find normal abdominal and thoracic structures commonly encountered in ultrasound examinations Perform a standard radiological examination. Demonstrate a methodical approach to image evaluation of radiographs, and ultrasound. Choose the appropriate imaging modality for common clinical presentations Speculate on and discuss the changes one might expect to encounter given various disease scenarios Behave in accordance with the legislation (Bekendtgørelse om røntgendiagnostik anlæg til veterinært brug. Nr. 494 af 12. september 1977 & Bekendtgørelse om ændringer af bekendtgørelse om røntgendisgnostik anlæg til veterinært brug. Nr. 1089 af september 2007). Explain how to address and/or counteract common causes for variation in the results of diagnostic tests. Explain functions and main disorders of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets; and the appropriate procedures to evaluate these cells in a blood smear. Interpret common clinical pathological and microbiological x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x X x x X x x X x x X X X X x x x X x x X X x x x X x test results. SVEK13002 Emergency, obstetrics, critical care, clinical anesthesiolo gy SVEK13006 Practical herd health consultancy & meat inspection SVEK19009 Veterinary jurisprudenc e and animal welfare assessment MScelective courses supporting competence 1 SVEK13013 Advanced companion animals Explain the principles of routine diagnostic methods. Explain the principles of use of serological tests in surveillance of disease. X x X x Prepare a blood smear. Identify healthy and abnormal erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. X x X x Perform a leukocyte differential count. X x Perform urinalysis (sticks, refractometry, sediment analysis). X x Assess quality of cytological specimens. Identify and classify inflammatory reactions in cytological specimens. Identify and classify neoplastic tissue types and criteria of malignancy in cytological specimens Identify and characterize bacteria by phenotypic and genotypic methods. X x X x X x X x Perform and interpret antimicrobial susceptibility tests. X x Detect multidrug-resistant bacteria of clinical interest X x Perform clear case reports Choose appropriate samples and methods for laboratory analysis Identify optimal diagnostic workup plans as well as treatment plans for selected diseases in emergency medicine and obstetrics. Record patient history and perform clinical examination on an acute/critically ill patient. Write a problem-oriented medical record (POMR) based on history and clinical examination. Independently obtain and implement relevant literature in a field and convert it to diagnostic workup plans and treatment plans for patients with critical or acute illness Perform clinical assessments of all groups of animals in cattle and pig herds. Assess deficiencies in feeding, climate, stables and management. Assess key indicators of health, production, reproduction and welfare. X x x X Perform post-mortem examinations on fish. Management of veterinary legislation, the veterinary law, disease control, protection and welfare of animals. To understand the difference between animal, management and resource-based indicators of welfare and their advantages and disadvantages. To understand the difference between physiological and behavioral requirements. Furthermore, the ability to identify if the behavioral and physiological requirements are met. x Explain physical examination, problem oriented approach to diagnostic work up and initial problem list formulation for patients. Explain the systematic four step (confirm, localize, disease process, diagnosis) basis for formulation of diagnostic, therapeutic and client information plans. To explain the indications and use of relevant clinical pathological, diagnostic imaging and other paraclinical diagnostic methods including their evaluation and x x x x X X X X X x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x X interpretation as well as any possible risks of adverse effects. SVEK13020 Equine Clinic SVEK13020 Herd Health SVEK13112 One Health SVEK13010 Biomedicine To explain clinical decision-making, pathophysiological mechanisms, treatment, management and follow up for diseases relevant in a specialized companion animal practice setting. To perform independent history taking, physical examination, problem identification, problem oriented diagnostic work up including plan formulation (diagnostic, therapeutic, client informational) as well as evaluate and interpret results of diagnostic tests and modalities. To perform client communication, and POMR based clinical decision making. To describe pathophysiological mechanisms. During hospital and field practice the students are trained in obtaining patient diagnosis supported by clinical laboratory testing. Record management is performed in the electronic patient record system. Being able to organize (study design) and implement the collection of data (incl. disease diagnostics in herd context and at the individual level), as well as manage and analyze data on health, welfare and fertility and the relation to production and production economy (quantitative and qualitative methods see the list of skills topics above). Knowledge about methods to analyze the impact on human and animal health issues related to microbial and parasitic contamination of food and the environment Understand the principles for prioritizing and selecting between intervention strategies for different health issues Utilize acquired knowledge to assess novel problems or problem areas and confidently apply knowledge-based suggestions for solutions. Ability to work independently with basic genetic laboratory procedures. Work independently with problem solving, diagnosing and presenting relevant findings in clinical microbiology, clinical pathology and In vivo pharmacology. Analyze, evaluate and present results from simple diagnostic tests in mammals. x x x x x x x x x x x x Describe and perform main molecular biological methods. Evaluate histological lesions and reactions in laboratory animals. Explain how to address and/or counteract common causes of misclassification in clinical microbiological, parasitological and pathological tests. x x x x X X x x x x x x