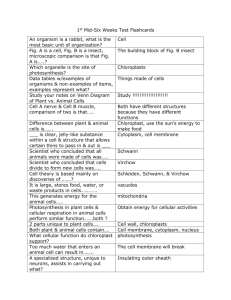
Cell Review
advertisement
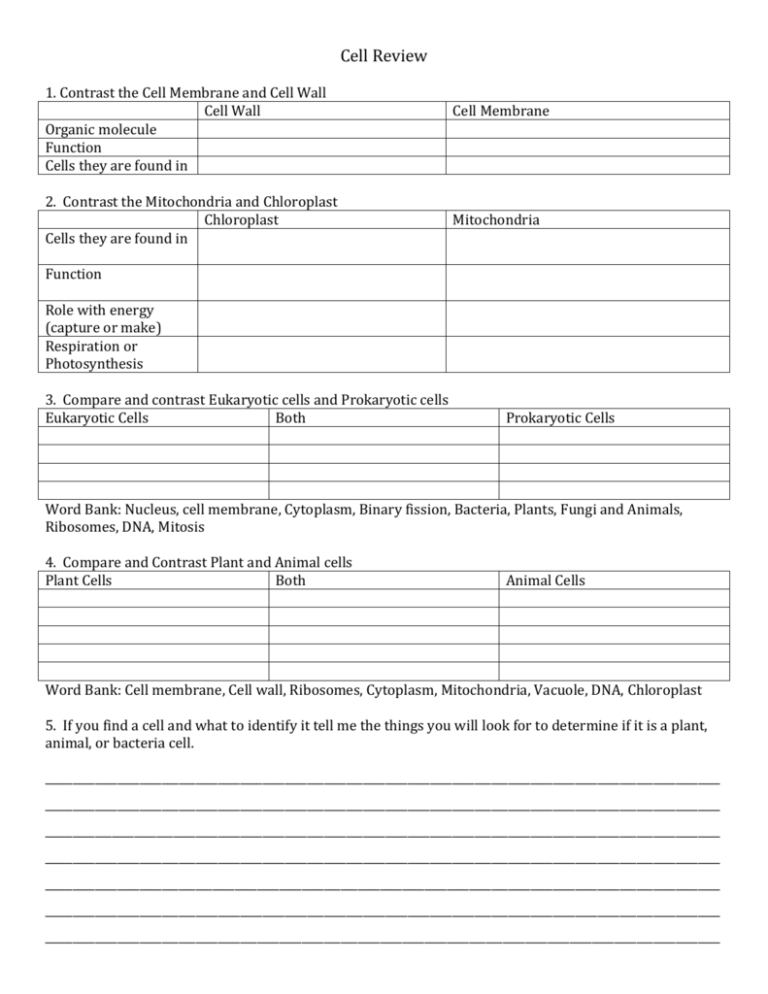
Cell Review 1. Contrast the Cell Membrane and Cell Wall Cell Wall Organic molecule Function Cells they are found in 2. Contrast the Mitochondria and Chloroplast Chloroplast Cells they are found in Cell Membrane Mitochondria Function Role with energy (capture or make) Respiration or Photosynthesis 3. Compare and contrast Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic Cells Both Prokaryotic Cells Word Bank: Nucleus, cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Binary fission, Bacteria, Plants, Fungi and Animals, Ribosomes, DNA, Mitosis 4. Compare and Contrast Plant and Animal cells Plant Cells Both Animal Cells Word Bank: Cell membrane, Cell wall, Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Vacuole, DNA, Chloroplast 5. If you find a cell and what to identify it tell me the things you will look for to determine if it is a plant, animal, or bacteria cell. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Matching: ________ 6. Cell membrane A. Organic molecule making up the cell wall of plants ________ 7. Nucleus B. Controls what passes into and out of a cell ________ 8. Cell Wall C. Molecules that are affected by temperature and pH ________ 9. Cytoplasm D. Contains the genetic information for the cell and controls cell ________ 10. Cellulose E. Rigid covering that gives plants support ________ 11. DNA F. Organic molecule that makes up the cell membrane ________ 12. Lipids G. Inorganic compound that cannot pass easily through membranes ________ 13. Salt H. Nucleic Acid that contains information for heredity ________ 14. Water I. Fluid area of the cell that mainly contains enzymes ________ 15. Enzymes J. Polar, inorganic molecule that can pass through the cell membrane _______ 16. Osmosis A. Hairs used for movement _______ 17. Diffusion B. Uses sunlight to make food, Photosythesis _______ 18. Mitochondria C. Movement of substances from high to low concentrations _______ 19. Chloroplast D. Projections of a cell used for movement _______ 20. Ribosomes E. Cell division by bacteria _______ 21. Flagella F. Movement of water from high to low concentrations of water _______ 22. Psuedopodia G. Organelle that puts amino acids together _______ 23. Cilia I. Tail used for movement _______ 24. Mitosis J. Uses carbohydrates to make ATP _______ 25. Binary Fission K. Cell division used to repair body cells 26. Drawings of the structures used for movement in cells Cilia Flagella Psuedopodia 27. Cell City: Compare each part of the cell to a part in a city Cell Part Mitochondria City Comparison Nucleus DNA Chloroplast Cell membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Ribosomes 28. Mitosis Give the three main purposes of Mitosis 1. ______________________________________ 2. ______________________________________ 3. ______________________________________ What does the cell do in mitosis? ______________________________ How many cells does mitosis make? ______________________________ How do the cells compare to the original cell? ________________________ How do the cells compare to each other? _______________________________ 29. Draw a cell going through mitosis if it starts with 2 pairs of chromosomes: 30. How is Binary Fission different Mitosis? ______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 31. Draw a small section of the cell membrane below: Label the polar and non-polar parts. Put a bracket around one phospholipid. 32. For each of the following draw arrows to show the direction of osmosis and write how the cell changes. Salt Concentration = 50% Salt Concentration = 20% Salt Concentration = 25% Salt Concentration = 20% Salt Concentration = 10% Salt Concentration = 20% 33. Which of these is the process by which water moves across a selectively permeable membrane? A. Osmosis B. Transpiration C. Capillary action D. Adhesion 37. Streptococcus is a type of bacteria that causes strep throat in humans. Which of these is the type of reproduction used by Streptococcus? A. Binary fission B. Meiosis C. Crossing-over D. Budding 34. Which of these substances moves across cell membranes easily? A. Salt B. Water C. Sugar D. Protein 38. In the eukaryote, which of these organelles are used to make sugars? A. Flagella B. Ribosomes C. Mitochondria D. Chloroplast 35. Freshwater fish have cells that are adapted to freshwater. What will happen the fish cells if you put the fish in salt water? A. Water leaves the cell, cell expands B. Water leaves the cell, cell shrinks C. Water enters the cell, cell expands D. Water enters the cell, cell shrinks 39. A protein called p53 can keep cells from dividing. To prevent cell division this protein most likely prevents: A. Osmosis B. Mitosis C. Respiration D. Mutation 36. Cyanide is a poison the prevents mitochondria from using oxygen. As a result the cell will not have A. lipids B. sugar C. minerals D. energy 40. Which cell structure contains molecules that direct cell activities? A. Nucleus B. Ribosome C. Mitochondria D. Chloroplast