C4 Vocabulary and Learning Targets packet
advertisement
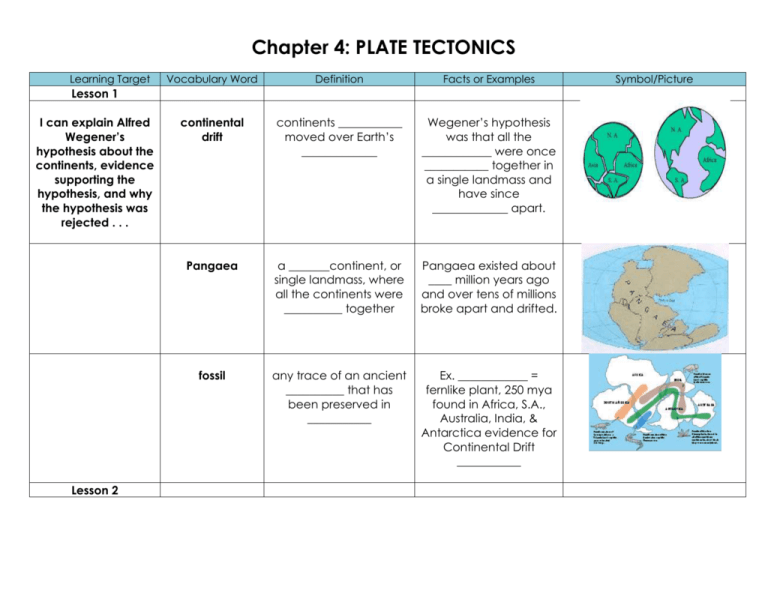
Chapter 4: PLATE TECTONICS Learning Target Vocabulary Word Definition Facts or Examples continental drift continents ___________ moved over Earth’s _____________ Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the ____________ were once ___________ together in a single landmass and have since _____________ apart. Pangaea a _______continent, or single landmass, where all the continents were __________ together Pangaea existed about ____ million years ago and over tens of millions broke apart and drifted. fossil any trace of an ancient __________ that has been preserved in ___________ Ex. ____________ = fernlike plant, 250 mya found in Africa, S.A., Australia, India, & Antarctica evidence for Continental Drift ___________ Lesson 1 I can explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents, evidence supporting the hypothesis, and why the hypothesis was rejected . . . Lesson 2 Symbol/Picture I can define and describe mid-ocean ridges . . . mid-ocean ridge long chains of ________________ that rise up from the ocean _____________ mid-ocean ridges are mapped using __________ (sound waves) I can explain how sea-floor spreading affects Earth’s crust . . . sea-floor spreading at mid-ocean ridges, new material is continually ___________ to the ocean floor As sea-floor spreading adds new more crust to the ocean floor, older strips of rock move _____________ from either side of the ridge. I can explain deepocean trenches and the process of subduction . . . deep ocean trenches the oceanic crust bends _________________ In a process that takes tens of _________ of years, part of the ocean floor _______ back into the mantle at deep ocean trenches. subduction the process by which the ocean floor ________ beneath a deep ocean trench and back into the ___________ again As subduction occurs, crust closer to the midocean ridge moves _________ from the ridge and ____________ a deep-ocean trench. Lesson 3 I can explain the theory of plate tectonics . . . plate pieces of Earth’s _______sphere The major tectonic plates are: North American, South American, Pacific, African, Eurasian, Antarctic, IndoAustralian, Nazca, Scotia, Phillippine, Cocos, Arabian, Caribbean, & the Juan de Fuca plates. divergent boundary where _____ plates move __________ from each other Most occur along midocean ridge, can also cause ________ valleys. convergent boundary where ______ tectonic plates _____________________ Two continental plates, two ocean plates or one continental and one oceanic that collide can cause _______________ or ________________. transform boundary where two _________ slip __________ each other North Amerian – Pacific plates (by California), many _____________ can occur at this boundary. plate tectonics theory that states that Earth’s plates are in _________, ___________ motion, driven by convection currents in the _____________. This theory incorporates sea-floor spreading, continental drift and ______________ as evidence. faults breaks in Earth’s __________ where rocks have ____________ past each other Occurs at plate boundaries. Plates can collide, pull apart or ______________ past each other. rift valley d ______ valley that forms when plates _______ apart or diverge on land. Ex, East African rift system Learning Targets Chapter 4 Lesson 1 I can explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents, evidence supporting the hypothesis, and why the hypothesis was rejected . . . Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the ___________________ were once joined together in a _______________ landmass, called __________________ and have since __________ apart. Lesson 2 Mid-ocean _______________ form long chains of __________________ that rise up from the ocean floor. I can explain how sea-floor spreading affects Earth’s crust . . . Sea-floor spreading adds more ____________ to the ocean floor. At the same time, older strips of rock move _________________ from either side of the _____________. I can explain deep-ocean trenches and the process of subduction . . . In a process taking tens of millions of years, part of the ocean floor _______________ back into the _______________ at deepocean ridges. Lesson 3 I can explain the theory of plate tectonics . . . The Theory of Plate Tectonics states that Earth’s _____________ are in slow, ________________ motion, driven by ____________ currents in the ____________________.