C4 Vocabulary packet ANSWERS
advertisement
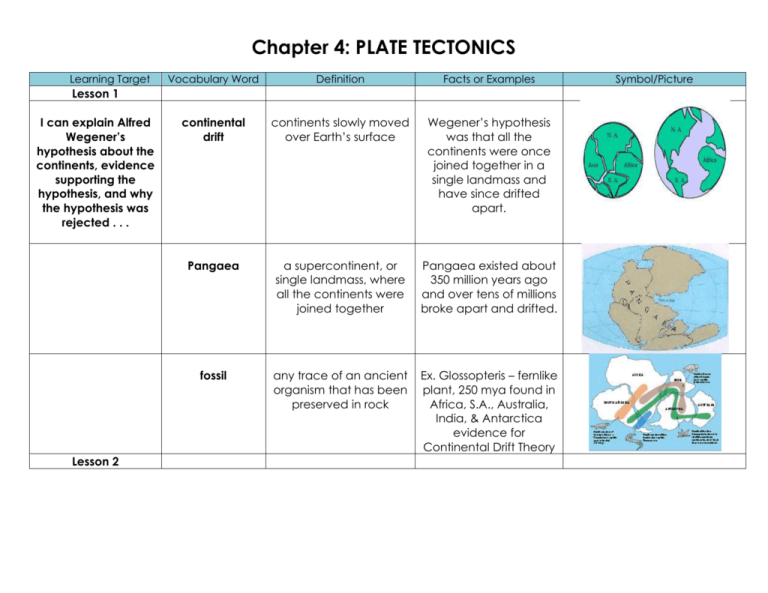
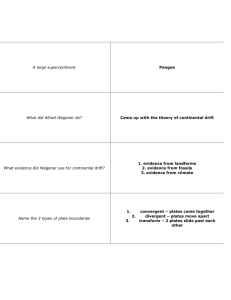
Chapter 4: PLATE TECTONICS Learning Target Vocabulary Word Definition Facts or Examples continental drift continents slowly moved over Earth’s surface Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the continents were once joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart. Pangaea a supercontinent, or single landmass, where all the continents were joined together Pangaea existed about 350 million years ago and over tens of millions broke apart and drifted. fossil any trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock Ex. Glossopteris – fernlike plant, 250 mya found in Africa, S.A., Australia, India, & Antarctica evidence for Continental Drift Theory Lesson 1 I can explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents, evidence supporting the hypothesis, and why the hypothesis was rejected . . . Lesson 2 Symbol/Picture I can define and describe mid-ocean ridges . . . mid-ocean ridge long chains of mountains that rise up from the ocean floor Mid-ocean ridges are mapped using sonar (sound waves). I can explain how sea-floor spreading affects Earth’s crust . . . sea-floor spreading at mid-ocean ridges, new material is continually added to the ocean floor As sea-floor spreading adds new more crust to the ocean floor, older strips of rock move outward from either side of the ridge. I can explain deepocean trenches and the process of subduction . . . deep ocean trenches the oceanic crust bends downward In a process that takes tens of millions of years, part of the ocean floor sinks back into the mantle at deep ocean trenches. subduction the process by which the ocean floor sinks beneath a deep ocean trench and back into the mantle again As subduction occurs, crust closer to the midocean ridge moves away from the ridge and toward a deepocean trench. Lesson 3 I can explain the theory of plate tectonics . . . The major tectonic plates are: North American, South American, Pacific, African, Eurasian, Antarctic, IndoAustralian, Nazca, Scotia, Phillippine, Cocos, Arabian, Caribbean, & the Juan de Fuca plates. plate pieces of Earth’s Lithosphere divergent boundary where two plates move apart from each other Most occur along midocean ridge, can also cause rift valleys. where two tectonic plates come together Two continental plates, two ocean plates or one continental and one oceanic that collide can cause mountains or subduction. convergent boundary transform boundary where two plates slip past each other North Amerian – Pacific plates (by California), many earthquakes can occur at this boundary. plate tectonics theory that states that Earth’s plates are in slow, constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle This theory incorporates sea-floor spreading, continental drift and fossils as evidence. faults breaks in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other Occurs at plate boundaries. Plates can collide, pull apart or grind past each other. rift valley a deep valley that forms when plates pull apart or diverge on land Ex, East African rift system Learning Targets Chapter 4 Lesson 1 I can explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents, evidence supporting the hypothesis, and why the hypothesis was rejected . . . Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the ___________________ were once joined together in a _______________ landmass, called __________________ and have since __________ apart. Lesson 2 Mid-ocean _______________ form long chains of __________________ that rise up from the ocean floor. I can explain how sea-floor spreading affects Earth’s crust . . . Sea-floor spreading adds more ____________ to the ocean floor. At the same time, older strips of rock move _________________ from either side of the _____________. I can explain deep-ocean trenches and the process of subduction . . . In a process taking tens of millions of years, part of the ocean floor _______________ back into the _______________ at deepocean ridges. Lesson 3 I can explain the theory of plate tectonics . . . The Theory of Plate Tectonics states that Earth’s _____________ are in slow, ________________ motion, driven by ____________ currents in the ____________________.