Hydrogen Trainer
advertisement

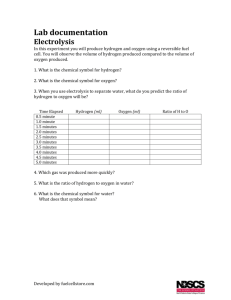
Hydrogen Trainer Background: Electrolysis - The process by which we generate hydrogen (and oxygen) from water is called electrolysis. The word "lysis" means to dissolve or break apart, so the word "electrolysis" literally means to break something apart (in this case water) using electricity. Electrolyser – used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen Note: The water level should be at the mark and fill before beginning if necessary. Always keep capped when not in use to prevent evaporation. Gas Storage – Used for the storage of the hydrogen and oxygen produced by the electrolyser. Gas Storage – fill with water to the 0 ml mark Fuel Cell - Converts the chemicals hydrogen and oxygen into water, and in the process it produces electricity. There are two connecting sleeves (the red capped things) on each side. The upper sleeves are the feed lines of the gases and connect to the hydrogen and oxygen gas storage. The lower sleeves vent the exhaust gases and water from the reaction. Lab 1: Objective: To examine the ratio between the produced gas volumes. During electrolysis, the gases (oxygen and hydrogen) are produced from water. Set up the Windtrainer kit using the diagram below: Connect the appropriate tubes from the hydrogen and oxygen electrolyser to the appropriate hydrogen and oxygen connective sleeves on the gas storage as shown above. Note: the hydrogen side of the electrolyser connects to the hydrogen side of the gas storage and the oxygen side of the electrolyser connects to the oxygen side of the gas storage. Directions: 1. Fill the gas storage with distilled water to the 0 ml mark if not already done. 2. Close the right connective sleeves of the gas storage with fitting caps to prevent the gas from leaking out. 3. Set the regulator to the maximum. Wait until approximately 20 mls of hydrogen gas have been produced and read the gas volumes produced by both the hydrogen and oxygen. Fill in the table. Gas volumes produced in ml (V) Hydrogen Oxygen Next, setup the windtrainer kit using the diagram below: 1. Set the regulator to the maximum. Wait until approximately 20 mls of hydrogen gas have been produced and read the gas volumes produced by both the hydrogen and oxygen. Set the multimeter to 20 DC V to measure voltage. What do you notice about the voltage? Questions: 1. What is the ratio between the gas volumes produced? 2. How can this ratio be explained? 3. How is the voltage related to the amount of gas produced? Lab 2: Setup the windtrainer as in the picture below: Directions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Vent the air from the fuel cell before beginning. Close the lower connecting sleeves of the fuel cell with the red fitting caps. Set the regulator to maximum. Wait until the gas storage is filled with 50 ml of hydrogen, and 25 ml of oxygen. Remove the fitting caps from the lower connecting sleeves of the fuel cell unit all of the gas is emitted and put on the fitting caps again. 6. The motor turns as proof for the energy conversion by the fuel cell. 7. Remove the motor and replace with the multimeter. a. Turn the dial to 20 DC V. How much voltage is generated? b. Turn the dial to 200 AC V. How much current is generated? c. If you multiply the voltage by current (VxI), you can calculate Power (W). How much power did you generate? d. Is this enough power to light up the lightbulb on the load (the piece with the motor and lightbulb)? 8. Using the equipment provided, design your own experiment.