Electrolyser model designing for HIL test setup
advertisement

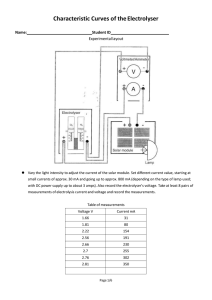
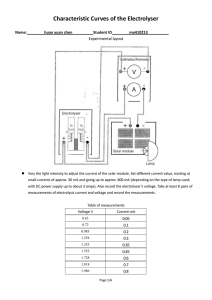
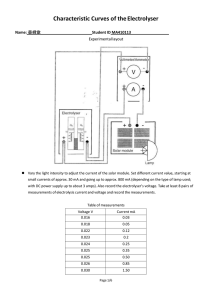
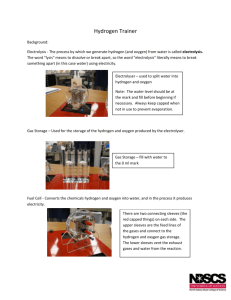
Water electrolyser model designing for hardware-inloop test setup Joonas Koponen, Antti Kosonen / Topics of the presentation • Electric conditioning of water electrolyser systems • Specific energy consumption of water electrolyser systems • Faraday efficiency • Model designing for the HIL setup / Power-to-Hydrogen research focus at LUT • Power electronics, control, and dynamics – Electrical behavior of water electrolysers – Influence of different current waveforms • System energy efficiency in conversion • Operation with renewable energy systems / Conversion structures based on natural commutation Source: Ursúa, A, Sanchis, P, & Marroyo, L 2013, “Chapter 14 - Electric conditioning and efficiency of hydrogen production systems and their integration with renewable energies”, in: Gandia, L, Arzamendi, G, & Diéguez, P (eds.), Renewable hydrogen technologies, Elsevier, Amsterdam. / Three-phase, full-wave rectifier • Based on thyristors, and diodes in half-controlled rectifiers, which switch according to the line-frequency Source: Mohan, N, Undeland, T, & Robbins, W 2003, Power electronics: converters, applications, and design, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey. / DC-current and voltage waveforms (1/2) / DC-current and voltage waveforms (2/2) . / Current component amplitudes as a function of load . / Influence of power supply, literature review Source: Ursúa, A, Sanchis, P, & Marroyo, L 2013, “Chapter 14 - Electric conditioning and efficiency of hydrogen production systems and their integration with renewable energies”, in: Gandia, L, Arzamendi, G, & Diéguez, P (eds.), Renewable hydrogen technologies, Elsevier, Amsterdam. / Efficiency of water electrolyser systems = • Specific energy consumption: • Efficiency, HHV: • Possible error from the assumption that all electrons effectively contribute to the water splitting = reaction Definition of Faraday efficiency, the ratio between the actual and theoretical amount of hydrogen produced / Faraday efficiency, literature review Source: Ulleberg, Ø 2003, “Modeling of advanced alkaline electrolyzers: a system simulation approach”, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 21–33. / Electrical behaviour of an alkaline electrolyser cell / Model design for the HIL setup (1/2) • Enable the emulation of main water electrolysis technologies • Model the electrical characteristics of a cell stack • • – Current and voltage waveforms, phase-shift impedance – Calculate the voltage level according to the input current – Mimic the impedance of a water electrolyser Structure of the HIL setup: 1. AC/DC rectifier 2. DC/DC buck converter 3. DC/DC boost converter, the modelled water electrolyser 4. DC/AC inverter The effect of different waveforms on the cell – Communication to the converters in the HIL setup t = 10 ms – Limitation on the electrolyser’s voltage level update rate / Model design for the HIL setup (2/2) Thank you! Questions? Comments?