Body Orientation & Tissue Types Unit Structural Levels of
advertisement

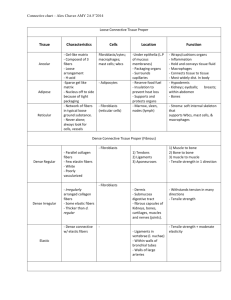
Body Orientation & Tissue Types Unit Structural Levels of Organization Chemical Level Different kinds of atoms join together to form molecules which make up all living matter Ex. Molecules, organelles Cellular Level Cell is structural & functional unit of all living things; fundamental unit of life Ex. Red blood cell Tissue Level Cells with common origin, appearance & function Each tissue has one or more specialized function Ex. Connective tissue Cell differentiation- groups of cells having common origin become specialized for certain physiological functions at an early embryonic stage Organ Level Different tissues joined together & adapted for a special (vital) function Ex. Stomach System Level Groups of organs acting together to perform a complex but specialized function Ex. Digestive system Organism Level Group of systems that can live on its own Ex. Human Body systems Responsible for maintaining & adjusting its activities to provide the proper internal environment (homeostasis) for each cell Major body systems & their main job Integumentary- external support & protection of body Skeletal- internal support & flexible framework for body movements Muscular- body movement Nervous- control & regulation of other systems in body Endocrine- secretion of hormones for chemical regulation Circulatory- transport of nutrients & removal of wastes from cells Lymphatic—body immunity Respiratory- gaseous exchange between external environment & blood Digestive- breakdown & absorption of food materials Urinary- filtration of blood & removal of metabolic wastes Reproductive- production of sex cells, union of sex cells & development of fetus Intro to Anatomical Language Bilateral symmetry Found in humans & other vertebrates Body can be dissected vertically into equal left & right segments One cut down midline will result in identical (exterior) mirror image halves Sagittal plane Runs vertically & divides the body into two portions Midsagittal plane divides the body into two identical halves Frontal (Coronal) plane At right angle to midsagittal plane Divides body into ventral (anterior, front) and dorsal (posterior, back) portions Transverse plane At right angle to sagittal plane Divides body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions Body Cavities Dorsal (posterior) cavity- found within skull & vertebral column Cranial cavity- contains brain Spinal cavity- contains spinal cord Ventral (anterior) cavity- larger of two & divided by diaphragm Thoracic cavity- above diaphragm; contains lungs & air passages, esophagus, heart & major blood vessels Abdominal cavity- below diaphragm; organs here are known as viscera & include the digestive system, kidneys & spleen Pelvic cavity- lowest part of abdominal cavity; contains urinary bladder, rectum & reproductive system Histology- Study of tissues Four primary tissue types classified based on cellular composition, function & appearance Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous Tissues made of cells surrounded & bound together by nonliving intercellular matrix Matrix is secreted by the cells & can be liquid, semisolid, or solid Some tissues also contain intercellular fibers Epithelial tissue Main job: protect, absorb, secrete, regulate movement of materials in/out by passive & active transport Cover surfaces & lines all internal structures/cavities of body Structure: cells are close together & usually arranged in one or more layers; cells held together by basement membrane & intercellular fibers; little matrix present No blood vessels in layers so nutrients must be transported by diffusion Can replace at a high rate; cells divide more often than other tissue types Two main categories: membranous & glandular Membranous epithelial Found throughout body; forms linings, coverings, etc. Always has one free surface exposed; may be one or several cell layers thick but always supported by basement membrane Cells tightly packed with little matrix Regenerate (reproduce) quickly since often exposed to friction & harmful substances Classified by the number of layers & cell shape Simple- single cell layer thick; absorb, filter, diffuse & secrete; surface often covered by mucus to keep tissue from drying out Simple squamous- flat scale-like cells forming very thin tissue; found lining blood vessels (called endothelium), heart & lungs; secrete fluid to help reduce friction; allows for rapid movement of molecules by filtration/diffusion Simple cuboidal- square shaped cells; found lining ducts & tube portions of glands, kidney tubules & tissue around ovary; line glands & digestive tract; absorb/secrete Simple columnar- column shaped; tightly packed to form protective covering for inner surface of organ; can produce secretions (such as goblet cells in stomach); used for absorption in intestine (microvilli on free surface); can replace itself every 2-3 days Simple ciliated columnar- has cilia on free surface used to transport materials through tubes such as in uterine tubes, sperm tubes or trachea Stratified- 2 or more layers of cells; primarily protective function found in areas subject to abrasion or stress Stratified squamous- basement membrane is cuboidal or columnar & cells flatten as they reach free surface; outermost cells may contain keratin to protect delicate layers below; main job is to cover/protect Cheek cells are non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelial Skin is keratinized stratified squamous epithelial Stratified cuboidal- 2-3 layers of cuboidal cells; found lining large ducts; mainly for protection/strength Glandular epithelial Specialized tissues that form the secretory portion of glands; either unicellular or multicellular Connective Tissue Main job: support the body by connecting tissues; connect, support, bind together, protect, storage, transport Most widespread & abundant tissue in body Structure: tightly packed cells, fibers & intercellular matrix (lots of matrix); fewer cells than matrix & cells normally do not touch each other; matrix made of proteins, carbohydrates & water; three types of protein fibers (collagen, elastin & reticular) Highly vascular tissue; well nourished; can replicate (reproduce) Different types classified based on matrix that binds the cells together Connective Tissue Proper Contain many types of cells- both resident & wandering Loose flexible matrix Contains all types of fibers Collagen fibers are white fibers; flexible & have great strength; long unbranched fibers Elastin fibers are yellow fibers; thinner in size but are elastic; branched Reticular fibers form a reinforcing lattice structure; tough but flexible fibers; thinnest branched Loose Connective Tissue Areolar tissue- few cells in semi-fluid matrix; fibers are loosely arranged; found in dermis of skin where it provides nutrients; also found between/around organs to support/cushion, binding/packing material; provides flexibility & strength in any direction (permits skin to move when part of body is rubbed); major part of subcutaneous layer Reticular tissue- jellylike matrix with network of interwoven reticular fibers; some cells are phagocytic & can eat foreign materials; found in liver, spleen, lymph nodes & bone marrow Adipose tissue- fat storage tissue; large cells with single vacuole containing fat droplet; serves as reserve energy supply, padding to absorb jolts & insulation to keep in heat; found on surface of viscera, in membranes, bone marrow; makes up 18% of body weight Dense Connective Tissue- more protein fibers & less matrix Dense regular tissue- white fibrous tissue with large amounts of densely packed collagenous fibers running parallel to the direction of force placed on tissues; contain few blood vessels so takes long time to heal; ex. Tendons & ligaments Dense irregular tissue- large amounts of densely packed collagenous fibers that are interwoven in all directions; form fibrous capsules around organs & joints Elastic- composed primarily of irregularly arranged yellowish elastic fibers; found in artery walls, larynx, trachea, vocal cords Supporting Connective Tissue Cartilage- consists of cartilage cells & semisolid matrix; supportive/protective functions; mature tissue has no blood vessels so must get nutrients from surrounding tissue; heals slowly; some types ossify to become bone Hyaline- “gristle”; fine collagenous fibers with clear glassy appearance; most abundant type of cartilage; covers bone surface, supports trachea, reinforces nose, larynx, rib connections; stiff but flexible support Fibrocartilage- matrix reinforced with collagenous fibers; part of knee (meniscus) & intervertebral discs; allows for shock absorption & resists compression Elastic- contains more elastin fibers; very flexible but otherwise similar to hyaline tissue; found in outer ear, larynx, epiglottis & auditory canal Bone- osseous tissue; most rigid connective tissue; hardness due to calcium phosphate deposited in matrix; some collagen fibers for flexibility; cells are called osteocytes Blood- vascular tissue; fluid connective tissue made of cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes) suspended in liquid matrix (plasma); protein fibers are dissolved in plasma & then become modified to be insoluble & helpful in clotting Nervous Tissue Main job: responds to certain changes in external/internal environments; controls body Vary in structure & function but all adapted to collect/transmit nerve impulses; specialized to respond to physical/chemical stimuli, convert stimuli into nerve impulses & conduct them Basic unit of structure is neuron Neurons are excitable, have a high metabolic rate, exhibit extreme longevity, but are non-mitotic (non-dividing) 3 parts: cell body that contains nucleus & other organelles; dendrites that receive nerve impulses & send them to cell body; axons carry nerve impulses away from cell body Types of neurons: sensory neurons receive impulses from environment; motor neurons carry impulses to muscles/glands; associative (interneurons) neurons relay impulses between sensory & motor neurons Besides neurons there are also glial cells Glial cells are 5 times more abundant but are non-excitable (can’t carry impulses) but are mitotic Muscle Tissue Main job: produce movement of body parts with respect to each other or for movement of materials through the body Composed of lots of cells that contract & change shape; very little matrix Very vascular due to heavy demand for oxygen Can shorten by about 1/3 of resting length Make up 40-50% of body mass Rate & control of movement depends on kind of cells in muscle tissue Types of muscle tissue Skeletal- voluntary muscle that requires conscious effort to move; relatively large/very active cells so contain more than one nuclei/cell; also known as striated muscle; long cylindrical cells called fibers; require nerve-bone impulse Smooth- involuntary muscles which are not consciously controlled; lack striations; only one nuclei/cell; found in walls of digestive organs, arteries/veins; long spindle shaped cells; help to propel materials along cavities Cardiac- only found in heart (forms the myocardial layer); branched cells forming a network; nuclei in middle of cells; can contract without being stimulated by nerve-bone impulse so considered involuntary; don’t regenerate (reproduce) well