Wordfile
advertisement

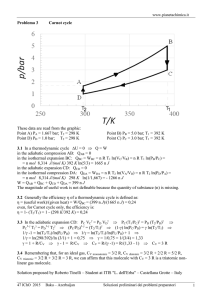
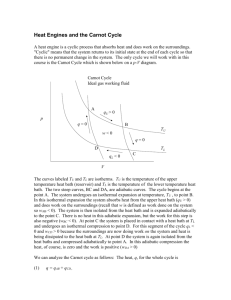
CHE 3190 Survey of Physical Chemistry (Fall 2015) G.Lind STUDY GUIDE FOR EXAM 3 Fenn CH 4 : Back to Work Study the lecture notes Calculate work for different paths, including geometrically (area under curve) Work going different ways on path (forward, backward) Fenn CH 5 : More in re Heat q = mc(Tf – Ti) = C D T c = specific heat C = cm = (specific) heat capacity C = molar heat capacity (units : Jmol-1 ) ; n m ; n = amount of substance (mol) ; n= M C = n C = m C ; C = MC C= C= C = specific heat capacity (units : Jg-1) m m = mass (g) ; M = molar mass (gmol -1) 1.0000 cal = 4.1845 J C increases with the complexity of the molecule : Equipartition Theorem : 1 1 1 Cu = Rftrans + Rfrot + 2 Rfvib = molar heat capacity at constant volume at high T 2 2 2 1 1 Cu = Rftrans + Rfrot = molar heat capacity at constant volume at low T 2 2 Total degrees of freedom (f) = 3N with N = number of atoms in molecule linear molecule : fvib = 3N - 5 ; nonlinear molecule : fvib = 3N - 6 C p = Cu + R Fenn CH 6 : The Origin of Cycle Analysis Carnot Cycle : Step I : isothermal , Step II : adiabatic : Step III : isothermal , Step IV : adiabatic ; Know how to calculate Pf , Vf , Tf , q , w , D U , D H for : (a) Isothermal change (b) Isochoric change (c) Isobaric change (d) Adiabatic change e= -w general qadd ; e(Carnot) = TH - TC TH only for Carnot cycle Fenn CH 7 : Heat is Work and Work is Heat. But Energy's the Difference First Law : dU = dq + dw DU = q + w Sign convention ( + is in, - is out) w = won , q = qadd 1 D Ucycle = 0 Fenn CH 8 : Two Laws from One Dilemma dU = dq - PdV H = U + PV dqv = D U ; dqp = D H U = U(T) and H = H(T) for ideal gas dU = Cv dT and dH = Cp dT for ideal gas DU = n C u (Tf - Ti ) adiabatic change : DH ; = n C p (Tf g PV = const - Ti ) and TV g -1 = const Fenn CH 9 :All in a Nutshell Good summary Fenn CH 10 : HER Has Much to say Pages 166 - 175 Thermal Pollution by Power Plants TC qc general ; c(Carnot) = only for Carnot cycle TH - TC w TH -qH Heat pump : coefficient of performance b = general ; b (Carnot) = only for Carnot cycle TH - TC w Refrigerator : coefficient of performance c= Fenn CH 12 : Enter Entropy Pages 210 -226 Definition of Entropy Computation of Entropy changes : reversible phase change Processes : isothermal, isochoric, isobaric, adiabatic, general Reversible, irreversible changes CHEAT SHEET: (8.5x11 in), both sides, everything handwritten (no copies), no answers to end of chapter problems or PEs or DQs. Your name must be on the sheet. Sheets has to be handed in with the exam. 2