english grammar punctuation and spelling grid jan 2015
advertisement

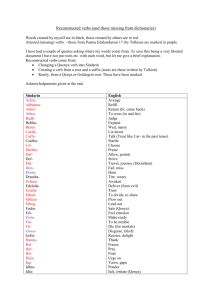
English Grammar, Punctuation and Spelling (EGPS) Progression Grid - January 2015 Guidance Children should be able to use the terminology for their year group. Children will be expected to apply the terminology in their writing. Terminology and content for previous years should be constantly revised, as the objectives are progressive. If children are ready for progression into the next year group’s terminology, allow for this within differentiation. Foundation/ Year 1 -letter (consonants and vowels) -capital letter -word -noun -adjective -verb -statement -question -singular -plural -sentence (subject / verb) -punctuation -full stop -question mark -headings/ sub headings to aid presentation -identify joining words (conjunctions) and joining clauses using and, but and or -exclamation mark -suffixes that can be added to verbs when no change is need e.g. helping, helped and helper) -the prefix un e.g. unkind -separation of words with spaces Note – in the Foundation Stage content will be delivered verbally and revisited in Year 1. Year 2 -noun phrase -command -exclamation -bullet points -headings/ sub headings to aid presentation -compound words (whiteboard, Superman, playground and football) -sentence (subject / verb) -adverb -progressive form of verbs in the present and past tense to mark actions in progress e.g. she is drumming. -subordination (using when, if, that, because) and co-ordination (using or, and, but) -formation of nouns using suffixes (-ness, -er, -ful and -less) -formation of adjectives using suffixes (-ful and – less) -use of the suffixes –er/ -est in adjectives (comparative and superlative) -use of –ly to turn adjectives into adverbs -tense (past and present) -apostrophe of omission (to form contractions) -comma to separate items in a list Year 3 -word family e.g. solve, solution, solver, dissolve, soluble -conjunctions to express time, place and cause (e.g. when, before, after, while, so, because) -adverb (e.g. then, next, soon, therefore) -preposition (before, after, during, in, because of) -direct speech -inverted commas (or speech marks) -prefix (super-, anti-, auto-) -use of a / an -sentence (subject / verb) -clause -subordinate clause -paragraphs used as a way to group related material -headings and subheadings to aid presentation -use of the past progressive instead of the simple past e.g. he has gone out to play instead of he went out to play. Year 4 -determiner -pronoun -sentence (subject / verb) -possessive pronoun -adverbial -inverted commas and other punctuation needed for speech (before speech opens / closes) -apostrophes to mark singular and plural possession e.g. the girl’s name -difference between plural and possessive s -commas used after fronted adverbials (e.g. Later that day, I heard the bad news) -paragraphs used to organise ideas around a theme -use of pronouns to avoid repetition e.g. he -expanded noun phrases e.g. ‘the teacher’ expanded to ‘the strict maths teacher with curly hair’ -Standard English instead of spoken verbs e.g. We were instead of we was. Year 5 Year 6 -modal verb -sentence (subject / verb) -sentence (subject / verb) -object -relative pronouns (who, which, where, when, -active whose, that) and omitted relative pronouns -passive -relative clause -differences between formal and informal speech -converting nouns or adjectives into verbs using -subjunctive forms e.g. If I were suffixes e.g. –ate, -ise, -ify). -synonym -verb prefixes (e.g. dis-, de-, mis-, over-, and re-) -antonym -indicating degrees of possibility using adverbs -ellipsis e.g. perhaps/ surely or modal verbs e.g. might, -cohesive devices – repetition of a word, phrase, should, will, must) grammatical connections e.g. the use of -parenthesis adverbials such as on the other hand, in contrast -bracket or as a consequence) and ellipsis -dash -layout devices e.g. headings, sub-headings, -cohesion columns, bullets, or tables, to structure text) -ambiguity -hyphen used to avoid ambiguity e.g. man eating -brackets, dashes and commas to indicate shark/ man-eating shark parenthesis -colon -commas to clarify meaning and avoid ambiguity -semi-colon -devices to build cohesion within a paragraph e.g. -bullet points then, after that, this, firstly -semi-colon, colon and dash to mark the -linking ideas across paragraphs using adverbials boundary between independent clauses e.g. It’s of time (e.g. later), place (e.g. nearby) and raining; I’m fed up. number (e.g. secondly) -use of colon to introduce a list