Appendix Appendix 1 ICD-9 and CPT codes for clinical outcomes
advertisement

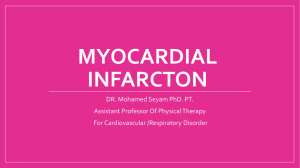
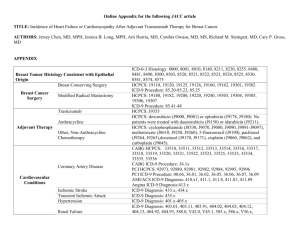
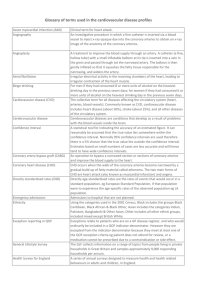
Appendix Appendix 1 ICD-9 and CPT codes for clinical outcomes Cardiovascular-related endpoint (ICD-9 codes) 430-438 Cerebrovascular disease (Stroke) 410 Acute myocardial infarction Cardiovascular death Coronary artery disease [410-414] or cerebrovascular disease [430-438] on the day of death Acute coronary syndromes (ICD-9 codes) 410 Acute myocardial infarction 411.1 Unstable angina Microvascular complications (ICD-9 codes) 249.5, 250.5, 362.0, 362.1, 379.23 Retinopathy 249.4, 250.4, 791.0 Nephropathy 249.6, 250.6, 353.5, 356.9, 536.3, 713.5, Neuropathy 337.1, 357.2, 354, 355 Cardiovascular surgical procedures (ICD-9 procedure codes; CPT codes) Coronary artery bypass 36.10-36.19; 33510-33536 graft Percutaneous coronary 00.66, 36.01, 36.02, 36.05, 36.06, 36.07; 92982, 92984, 92980,92981 intervention Appendix 2 Analysis of Baseline Characteristics Based on Dual-Goal Achievement in the 7-12 Months Following the Index Date Dual-goal Non–dual-goal (n=7,432) (n=9,397) 65.5 ± 10.2 61.5 ± 10.6 18-44 160 (2.2) 506 (5.4%) 45-54 798 (10.7) 1,781 (19.0%) 55-64 2,933 (39.5) 4,063 (43.2%) 65-69 992 (13.4) 1,003 (10.7%) 70-74 1,018 (13.7) 869 (9.3%) Characteristics P value Demographics Age as of the index date, yearsA Age groups, n (%) < .001 75-79 874 (11.8) 660 (7.0%) 80+ 657 (8.8) 515 (5.5%) 7,243 (97.5) 9,050 (96.3%) < .001 5,154 (69.4) 6,115 (65.1%) < .001 31.6 ± 4.9 32. ± 5.4 < .001 Male, n (%) White, n (%) Body mass index, kg/m2B Index year, n (%) < .001 2004 1,237 (16.6) 1,579 (16.8) 2005 1,625 (21.9) 2,259 (24.0) 2006 1,230 (16.6) 1,669 (17.8) 2007 1,297 (17.5) 1,535 (16.3) 2008 1,340 (18.0) 1,524 (16.2) 703 (9.5) 831 (8.8) HbA1c<7% 6,581 (88.6) 5,391 (57.4) < .001 LDL-C<100 mg/dl 5,982 (80.5) 3,008 (32.0) < .001 Dual-goal Achievers 3,900 (52.5) 1,380 (14.7) < .001 Retinopathy 241 (3.2) 517 (5.5) < .001 Nephropathy 189 (2.5) 230 (2.5) .693 Neuropathy 799 (10.8) 1,174 (12.5) < .001 Atherosclerosis, aneurysm, or embolism 230 (3.1) 213 (2.3) .001 Peripheral vascular disease 417 (5.6) 465 (5.0) .055 Cerebrovascular disease 595 (8.0) 626 (6.7) .001 Coronary artery disease 2,448 (32.9) 2,259 (24.0) < .001 Angina 294 (4.0) 349 (3.7) .416 Myocardial infarction 60 (0.8) 79 (0.8) .812 717 (9.7) 901 (9.6) .897 2,028 (27.3) 2,377 (25.3) .004 119 (1.6) 134 (1.4) .354 hyperosmolarity 20 (0.3) 38 (0.4) .137 Hypoglycemia 197 (2.7) 278 (3.0) .231 Congestive heart failure 489 (6.6) 539 (5.7) .023 Valvular heart disease 158 (2.1) 145 (1.5) .005 7,026 (94.5) 8,781 (93.4) .003 2009 Baseline goal achievement, n (%)C Diabetes-related complications, n (%) Microvascular Macrovascular Other InfectionD Ocular problemsE UlcerationF Ketoacidosis (without coma) and Comorbidities, n (%) Cardiovascular diseaseG Hypertension Other 1,479 (19.9) 1,528 (16.3) < .001 Obesity 2,086 (28.1) 2,861 (30.5) .001 Hyperlipidemia 5,500 (74.0) 6,732 (71.6) .001 Depression 2,713 (36.5) 3,907 (41.6) < .001 Renal disease 701 (9.4) 730 (7.8) < .001 Tobacco use 1,329 (17.9) 1,962 (20.9) < .001 3,610 (48.6) 5,365 (57.1) < .001 480 (6.5) 1,269 (13.5) < .001 Anti-hypertensive 5,257 (70.7) 6,514 (69.3) .047 Lipid lowering 5,539 (74.5) 6,467 (68.8) < .001 Lower extremity amputation 10 (0.1) 24 (0.3) .083 Coronary artery bypass graft 28 (0.4) 31 (0.3) .610 Percutaneous coronary intervention 68 (0.9) 85 (0.9) .944 Outpatient visit 7,337 (98.7) 9,268 (98.6) .595 Urgent care visit 1,168 (15.7) 1,669 (17.8) < .001 903 (12.2) 1,221 (13.0) .102 400 (5.4) 606 (6.5) .004 0.3 ± 0.8 0.3 ± 0.7 < .001 CCI = 0, n (%) 5,955 (80.1) 7,882 (83.9) < .001 1 ≤ CCI <3, n (%) 1,270 (17.1) 1,316 (14.0) < .001 207 (2.8) 199 (2.1) .005 Diabetic medications, n (%) Oral anti-diabetic Insulin Surgical Procedures, n (%) Resource Utilization, n (%) Inpatient Emergency room Charlson comorbidity CCI ≥ 3, n (%) indexA Unless otherwise specified, all characteristics were measured in the 1-year period around the index date (i.e., six months before and six months after). AData are means ± SD. BEstimated using the height and weight information closest to the index date. For patients with no height and weight information, the average body mass index calculated from all other patients was used. CCalculated using the area under the curve method for the first six months following the index date. DIncludes skin, urinary tract, and kidney infections. EIncludes glaucoma, macular edema, retinal edema, vitreous hemorrhage, and blindness. F'Includes foot ulcer, bone changes, amputation, and other ulcerations. GExcludes macrovascular complications. Statistical significance is indicated with bolded text. Abbreviations: CCI indicates Charlson comorbidity index; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.