Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
advertisement

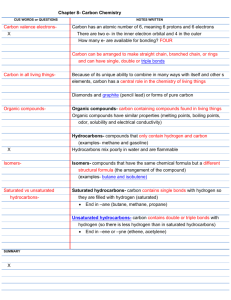
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry If you can do all the things listed below, you are ready for the Unit 13 test. Place a checkmark next to each item that you can do! If a sample problem is given, complete it as evidence. _____1. I can still do everything from Unit 1. _____2. I can still do everything from Unit 2. _____3. I can still do everything from Unit 3. _____4. I can still do everything from Unit 4. _____5. I can still do everything from Unit 5. _____6. I can still do everything from Unit 6. _____7. I can still do everything from Unit 7. _____8. I can still do everything from Unit 8. _____9. I can still do everything from Unit 10. _____10. I can still do everything from Unit 11. _____11. I can still do everything from Unit 12. Definitions: organic compound – all carbonate containing compounds except CO, CO2, and carbonates saturated hydrocarbon – a compound containing only C and H in which each carbon atom has 4 single bonds _____12. I can define organic compound, saturated hydrocarbon, unsaturated hydrocarbon, and isomer. unsaturated hydrocarbon - a compound containing only C and H in which there is at least one double bond (possibly triple) between C atoms isomer –two organic compounds that have the same molecular formula, but different structural formula and therefore different physical and chemical properties Draw the complete structural formula for CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3. _____13. I can expand a condensed structural formula to show the structural formula of an organic compound. (Sorry. This will take WAAY too long on the computer.) Draw the complete structural formula for CH3CHCHCH3. (This one too.) _____14. I can state the name and symbol of the element that is capable of forming rings, chains, and networks. The element that is capable of forming rings, chains, and networks is ____carbon______. Its symbol is_______C_______. HONC1234 tells me that Hydrogen forms 1 bond. Oxygen forms 2 bonds. Nitrogen forms 3 bonds. Carbon forms 4 bonds. _____15. I can explain the meaning of and apply HONC1234. _____16. Given the formula, I can determine if a compound is a hydrocarbon or not. Determine how many carbon atoms are in each of the following compounds: _____17. Given the name, I can use Reference Table P to determine how many carbons atoms are in a compound. _____18. Given the name, I can use Reference Table Q to determine to which class of hydrocarbons a compound belongs. decane_______10________________ ethene_________2_________________ 3-nonene______9_______________ 1-pentyne________5_________________ Determine the homologous series of hydrocarbons to which each of the following belongs: decane____alkane_______________ 2-decene______alkene____________ 3-nonene___alkene_____________ 1-pentyne_______alkyne____________ Determine if each of the following is a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon. _____19. Given the name, I can determine if the hydrocarbon is saturated or unsaturated. decane_______sat_________ ethene_________unsat________________ 3-nonene_____unsat____________ 1-pentyne_____unsat_______________ Determine the homologous series of hydrocarbons to which each of the following belongs: belongs to the ____alkane____________ series. _____20. Given the formula, I can determine to which homologous series a hydrocarbon belongs. belongs to the ________alkyne__________ series. belongs to the _____alkene____________ series. Determine if each of the following is a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon. _____21. Given the formula, I can determine if a hydrocarbon is saturated or unsaturated. CH3CH2CH2CH3_______sat_________ CH3CHCHCH3________nsat_______________ Determine the number of hydrogen atoms in each of the following. _____22.Given the name, I can use Reference Table Q to determine how many hydrogen atoms the hydrocarbon contains. _____23. Given a list of compounds, I can determine which ones are isomers. decane______22_________ 1-butene_____8_______________ 3-nonene___18________________ 1-pentyne_______18_______________ _____24. Given a structural formula, I can use Reference Table R to identify to which class of organic compounds a substance belongs. Name the following hydrocarbons. 2-pentene _____25. I can use Reference Tables P & Q and IUPAC nomenclature to name simple hydrocarbons. 3-heptyne nonane 2-hexene Name the following organic compounds. _____26. I can use Reference Tables P & R and IUPAC nomenclature to name simple compounds in any of the classes of organic compounds. butane butanone butanoic acid 2-butene 1-butanol 1-butanamine 2-butyne butanal butanamide 1bromobutane methylpropanoate methylpropyl ether F stands for____fermentation______________. This type of organic reaction results from a reaction of __a sugar_______ to form ____carbon dioxide______________ and ______ethanol____________. It typically requires a catalyst, in the form of an enzyme to occur. S stands for ____substitution________________. This type of organic reaction happens when ___saturated____________ hydrocarbons _____27. I can use F-SCAPES to list and describe the 7 types of organic reactions. replace one of the ___hydrogens________ for some other element (often a halide). C stands for ______combustion___________. In this type of organic reaction a _______hydrocarbon______________ reacts with ___oxygen_________ to form ___carbon dioxide_________ and _______water_________. It is an exothermic reaction. A stands for _______addition____________. In this type of organic reaction an _______unsaturated hydrocarbon___________________ becomes a ________saturated_____________________ when the double bond breaks and two atoms of another element (often a halide) are added. P stands for _____polymerization___________. In this type of organic reaction many ___monomers________ are linked together to form a _______polymer__________. A generalized form of this reaction looks like this….. _____27. I can use F-SCAPES to list and describe the 7 types of organic reactions. (continued) E stands for ___esterification________________. In this type of organic reaction an __alcohol_____ reacts with a __organic acid______________ to form an ____ester______ and _____water____________. The products of this reaction are typically fragrant. S stands for _______saponification_______________. In this type of organic reaction a __fat____ reacts with a __base___________ to form _____soap__________. You can really “clean up” if you remember this organic reaction. _____28. Given an equation, I can identify the type of organic reaction that is occurring.