Notes Document

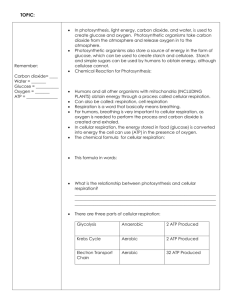
Name: Date: Per.
Power Point Notes Cell Energy
Energy
Energy for living things comes from food. Originally, the energy in food comes from the _________.
Organisms that use light energy from the sun to produce food are __________________(auto = self)
Ex: plants and _____________microorganisms (some bacteria and protists)
Organisms that cannot use the sun’s energy to make food are ____________________. Ex.: animals and most microorganisms.
Cell Energy
Cells _________________ source of energy is called ATP
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate
Label the parts of the ATP molecule and memorize them.
All energy is stored in the _______________ of compounds, breaking the bond releases the energy
When the cell has energy available it can _____________ this energy by adding a phosphate group to
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate), producing ___________
ATP is converted into ADP by breaking the bond between the second and third phosphate groups and
______________________ energy for cellular processes. Label the ADP – ATP Cycle.
Photosynthesis
The process by which the energy of sunlight is _____________ into the energy of glucose.
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plants and in the cytoplasm of some bacteria.
Name: Date:
Label the structures of the chloroplast
Per.
The light absorbing compound is a pigment – pigments absorb some wavelengths of light and
_______________ others
The color our eyes see is the color that the ________________ reflects
Chlorophyll is the pigment inside the chloroplast that absorbs the wavelengths of light used in photosynthesis. What wavelength color does it reflect? _______________
General formula for photosynthesis (memorize this)
Carbon dioxide + water + light yields glucose + oxygen
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
0 + light C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Diagram the process of photosynthesis
Summary: Light Dependent Reaction – H
2
O is _________ (photolysis), oxygen is released as a waste
product. Energized electrons move down an electron transport chain (ETC). Light energy is
stored temporarily in inorganic energy carriers, ATP and NADPH. The oxygen in the
atmosphere comes from what molecule? ____________
Light Independent Reaction = The Calvin Cycle – energy is transferred from ________ and
NADPH to build ________ from Carbon Dioxide. Six CO2 are converted to one glucose by an
Enzyme called rubisco. All plant tissues are made from which gas? ______________
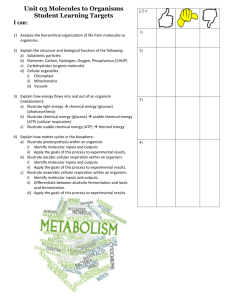
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which the energy between the _________ bonds in glucose is released in the cell to be converted for use for life processes.
Cells require a constant source of energy for life processes but keeps only a _____ amount of ATP on hand. Cells can regenerate ATP as needed by using the energy ________ in foods, particularly glucose.
Name: Date: Per.
The energy stored in glucose by photosynthesis is ____________ by cellular respiration and repackaged into the energy of ATP, particularly the bond between the second and third phosphate.
Diagram the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Respiration occurs in ______ cells and can take place aerobically or anaerobically.
Cellular Respiration is aerobic: _____________oxygen and occurs in the mitochondria of cells.
A total of ________ ATP molecules are produced for each glucose molecule!
The formula for aerobic respiration (memorize this). glucose + oxygen yields carbon dioxide + water + energy
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
0 + 36 ATP
Diagram the two locations of Cellular Respiration
Summary of Cellular Respiration:
Steps: 1._____________– glucose is split in to two pyruvates, uses 2 ATP, makes 4 ATP, net 2 ATP
2. _____________ – Citric Acid Cycle – pyruvate is broken down into Carbon dioxide, 2 ATP
3._____________________________ (ETC) – 34 ATP produced
Name: Date:
Diagram the steps of Cellular Respiration
Per.
Anaerobic Respiration occurs when ____ oxygen is available to the cell. Also called Fermentation.
Two kinds: Alcoholic fermentation and Lactic Acid fermentation – based upon waste product released
Much _______ ATP produced (only 2 ATP per glucose) than in cellular respiration (aerobic).
Alcoholic fermentation occurs in bacteria and yeast. Process used in the baking and brewing industryyeast produces _______ gas during fermentation to make dough rise before baking.
Glucose -> ethyl alcohol + carbon dioxide + 2 ATP
Lactic acid fermentation – occurs in ______________ cells. Lactic acid is produced in the muscles during rapid ______________ when the body cannot supply enough oxygen to the tissues. This causes a burning sensation in muscles and soreness later due to lactic acid build-up in muscle cells.
Glucose -> lactic acid + carbon dioxide + 2 ATP
In anaerobic respiration only glycolysis occurs. Where does glycolysis occur? _______________
Diagram of Cellular energy: Respiration and Fermentation
Note: All of this will be on the semester exam in December. Understanding both processes is essential. Memorizing one of the equations (photosynthesis or cellular respiration) is necessary.