Earth Systems Vocabulary
advertisement

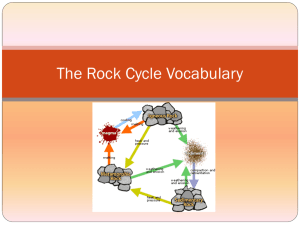
Earth Systems Vocabulary earth the third planet from the sun in the solar system minerals a solid substance found in nature that has never been alive Examples: copper, sulfur, gold rock cycle an ongoing process when rocks are changed from one type into another magma molten (melted) rock below the surface of the earth; on the surface, we call it lava igneous rock rock formed when magma/lava cools and hardens volcano An opening in earth’s surface through which lava, gases, and ash pour out weathering the breaking down of rocks into smaller pieces erosion the third planet from the sun the planet where we live sediment material that settles at the bottom of a liquid deposition the wearing and carrying away of rocks and soil sedimentary rock rock formed when layers of sediment are pressed together pressure force produced by pushing or pressing on something metamorphic rock new rock formed when a rock deep in the earth is changed by heat and pressure water cycle ongoing movement of water between the atmosphere and earth’s surface evaporation change from a liquid to a gas transpiration plant leaves giving off water vapor condensation gas changes to a liquid as it cools; Example: forming a cloud precipitation water in the atmosphere that falls to earth Examples: rain, snow, sleet, hail runoff water that flows over earth’s surface (does not evaporate or soak into ground) biogeochemical cycles the cycling of matter through earth’s water, air, land, and living things carbon cycle oxygen cycle nitrogen cycle