POROSITY and PERMEABILITY lab
advertisement
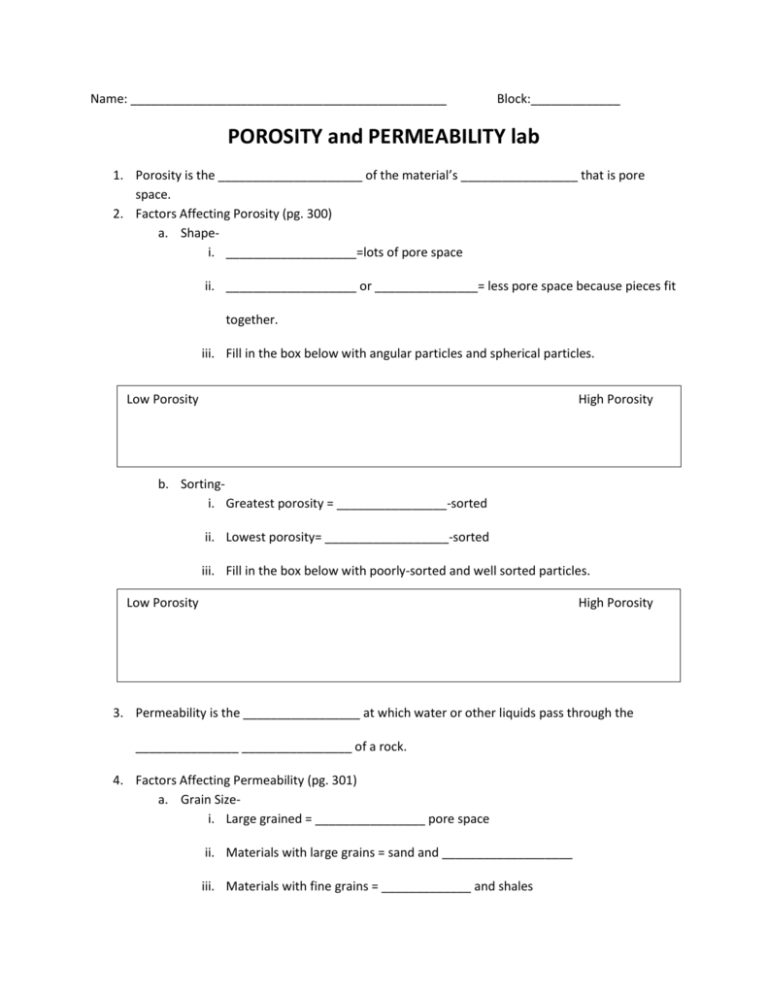
Name: ______________________________________________ Block:_____________ POROSITY and PERMEABILITY lab 1. Porosity is the _____________________ of the material’s _________________ that is pore space. 2. Factors Affecting Porosity (pg. 300) a. Shapei. ___________________=lots of pore space ii. ___________________ or _______________= less pore space because pieces fit together. iii. Fill in the box below with angular particles and spherical particles. Low Porosity High Porosity b. Sortingi. Greatest porosity = ________________-sorted ii. Lowest porosity= __________________-sorted iii. Fill in the box below with poorly-sorted and well sorted particles. Low Porosity High Porosity 3. Permeability is the _________________ at which water or other liquids pass through the _______________ ________________ of a rock. 4. Factors Affecting Permeability (pg. 301) a. Grain Sizei. Large grained = ________________ pore space ii. Materials with large grains = sand and ___________________ iii. Materials with fine grains = _____________ and shales 5. Impermeable = water _____________________ pass through rock. 6. True or false? A material can have high porosity with low permeability 7. True or false? A material can be impermeable but porous. Use the graduated cylinders with beads and water to answer the following questions. 8. Hypothesis: The cylinder with all large beads will have a (higher/lower) porosity than the cylinder with mixed beads. 9. Fill the graduated cylinder with 100 ml of water. Pour water into the graduated cylinder with large beads just until the beads are covered. 10. Record the volume of the water left in the graduated cylinder. 11. To determine the volume of water in the pour spaces, subtract the volume of water after pouring from 100 ml. 12. Repeat for the graduated cylinder with the mixed beads. Graduated Cylinder Volume of water in Volume of water in Volume of water in graduated cylinder graduated cylinder the pore spaces. after pouring Large Beads 100 ml Mixed Beads 100 ml 13. Calculate the porosity as follows: Porosity= volume of water in pore space 100ml a. Large Bead Porosity- X100 b. Mixed Bead Porosity14. Which cylinder has the greatest porosity? Explain why. 15. Use the terms rounded, angular, well-sorted, poorly-sorted, high porosity, low porosity to write a conclusion describing each container of beads.