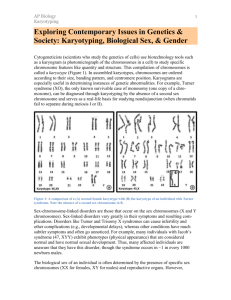
VI. Alterations of Chromosome Number A. Nondisjunction: Accident
advertisement

VI. Alterations of Chromosome Number A. Nondisjunction: Accident, in which members of a pair of homologous chromosomes do not move apart properly during meiosis I 1. Or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II 2. One gamete receives two of the same type of chromosome 3. Another gamete receives no copy B. Aneuploidy: Having an abnormal chromosome number 1. Trisomic: Chromosome in triplicate in fertilized egg (2n +1) 2. Monosomic: If a chromosome is missing (2n - 1) a. Mitosis will transmit the condition to all embryonic cells b. Symptoms caused by abnormal dosage of genes located on the extra or missing chromosome C. Polyploidy: Having more than two complete chromosome sets 1. Triploidy: (3n) haploid sets 1. Fertilization of an abnormal diploid egg 2. Tetraploidy: (4n) haploid sets 1. Failure of 2n zygote to divide after replicating its chromosomes 2. Mitosis would produce a 4n embryo a. Common in plant kingdom b. Rare in animals 1. Researchers in Chile identified 1st mammalian candidate for polyploidy 2. Tympanoctomys barrerae a. Tetraploid rodent 3. One extra or missing disrupts genetic balance more than an entire set a. Sperm head is large b. Does it have 4 homologous sets? VII. Alterations of Chromosome Structure A. Deletion: Original chromosome is missing certain genes 1. Fragments without centromeres are usually lost when cell divides B. Duplication: Fragment attaches to homologous chromosome C. Inversion: Fragment reattaches to original chromosome but in the reverse orientation D. Translocation: Fragment may join a nonhomologous chromosome 1. Reciprocal: Nonhomologous chromosomes exchange fragments a. Most common 2.Nonreciprocal: A chromosome transfers a fragment without receiving one in return a. Error during crossing over E. Lethal Alterations in chromosome structure 1. Diploid embryo homozygous for a large deletion 2. Male who inherits an X chromosome with a deletion missing a number of essential genes F. Duplications and translocations have harmful effects G. Reciprocal translocations and inversions 1. Balance of genes is not abnormal 2. Can alter phenotype 3. Gene’s expression can be influenced by its location among neighboring genes 1 VIII Human Autosomal Non-Disjunction Disorders A. Down Syndrome 1. Most common serious birth defect in US: 1/700 2. Extra 21st chromosome (Trisomy 21) a. Each body cell has 47 b. Characteristic facial features c. Short stature d. Heart defects e. Susceptibility to respiratory infection f. Mental retardation 1. Most common form of severe mental retardation g. Prone to developing 1. Leukemia and Alzheimer’s disease a. Associated genes found on chromosome 21 h. Shorter than normal life span i. Sexually underdeveloped and sterile j. Correlates with age of mother 1. Higher chance in older mothers B. Patau syndrome: Trisomy for chromosome 13 1. Serious eye, brain, circulatory defects, harelip and cleft palate 2. 1/5000 births C. Edwards syndrome: Trisomy 18 1. Affects almost every organ system in the body 2. 1/10,000 3. Survive less than a year IX Nondisjunction Disorders of sex chromosomes A. Klinefelter syndrome: XXY 1. 1/2000 2. Male sex organs: Testes abnormally small, sterile 3. Breast enlargement and other feminine body characteristics 4. Normal intelligence B. XYY: Not characterized by any well-defined syndrome 1.Tend to be taller C. Metafemales: XXX, Healthy 1. Cannot be distinguished from XX females except by karyotype D. Turner syndrome: XO 1. 1/5000 2. Only known viable human monosomy 3. Phenotypically female 4. Secondary sex characteristics fail to develop 5. Sterile 6. Normal intelligence X. Structural alterations of chromosomes associated with disorders A. Cri du chat (cry of the cat): Deletion in chromosome 5 1. Mentally retarded 2 2. Small head with unusual facial features 3. Cry that sounds like the mewing of a distressed cat 4. Death in infancy or early childhood B. Translocations; Certain cancers 1. Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): Reciprocal translocation a. Portion of 22 has switches places with the tip of 9 XI. Parental Imprinting of Genes: Some traits depend on which parent passed along the alleles for those traits (not sex linkage, may be on an autosome) A. Prader-Willi syndrome 1. Mental retardation 2. Obesity 3. Short stature 4. Unusually small hands and feet B. Angelman syndrome 1. Spontaneous uncontrollable laughter 2. Jerky movements C. Both conditions: Deletion of chromosome 15 1. Prader-Willi: Defective chromosome from father 2. Angelman syndrome: Defective chromosome from mother D. Genomic imprinting: A gene on one chromosome is silenced, while its allele on the homologous chromosome is left free to be expressed 1. In the new generation: Maternal and paternal imprints are erased in gameteproducing cells 2. Recoded according to the sex of the individual in which they now reside 3.(-CH3) groups added to cytosine of one of the alleles a. Silences 4. Animal uses allele that is not imprinted 5. 20 mammalian genes subject to imprinting a. Mice embryos engineered to inherit both copies of certain chromosomes 1. Die before birth 2. Normal development requires that certain genes have one active copy 6. Fragile-X syndrome: Abnormal appearance of X chromosome in which the tip hangs on to the rest by a thin thread of DNA a. 1/1500 males b. 1/2500 females c. Mental retardation (most common form) d. Not every one with the fragile X-chromosome shows the symptoms e. More likely to occur, if inherited from the mother 1. More common in males a. Males inherit from Mom b. Females from Dad or Mom f. Imprinting (methylation) of abnormal allele by mother causes rather than silences syndrome XII. Extra-nuclear Inheritance: Genes located on DNA outside the nucleus A. Small circles of DNA: Plastids B. Mitochondria and plastids in plants including chloroplasts 3 1. Replicate and transmit genes to daughter organelles 2. Do not display Mendelian inheritance 3. Not distributed to offspring by meiosis 4. First observed in plants in 1909 (Karl Correns) a. Inheritance of yellow or white patches on leaves b. Zygote receives all plastids from the cytoplasm of ovum c. None from pollen 5. Maternal inheritance is also the rule for mitochondrial genes in mammals 1. Passed on by zygote comes from cytoplasm of ovum 2. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA cause a number of rare human disorders a. Protein complexes of electron transport chain b. ATP synthase c. Body parts most susceptible to energy deprivation 1. Nervous system 2. Muscles d. Mitochondrial myopathy: 1. Weakness, intolerance of exercise, muscle deterioration 4