Problem Solving Flow Chart
advertisement
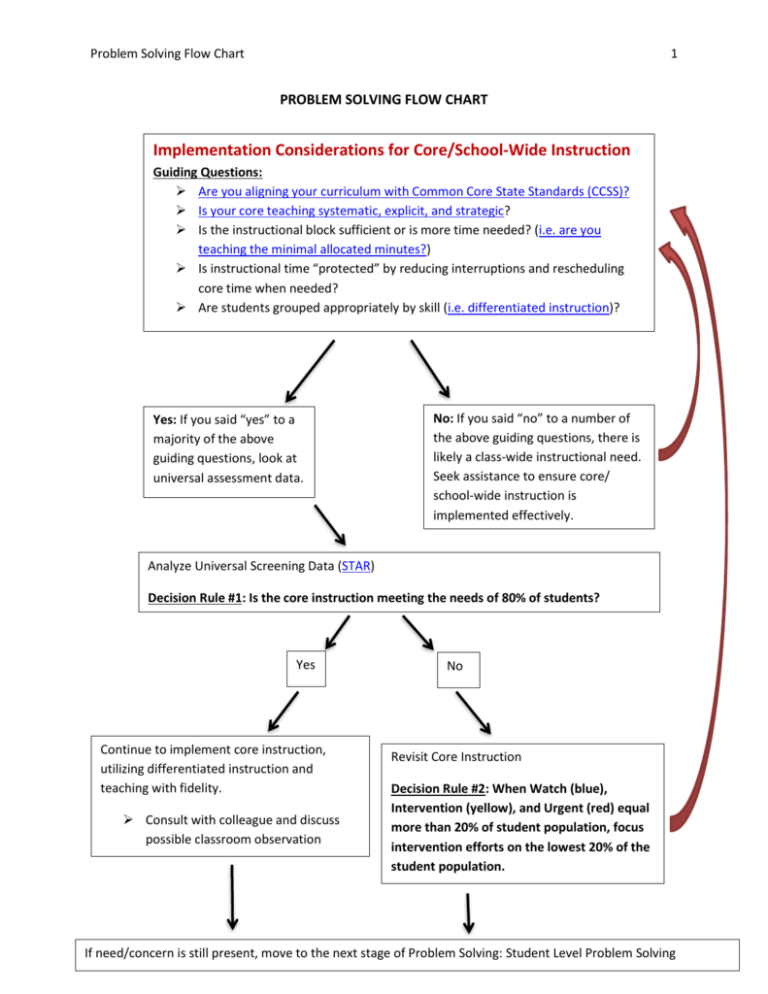
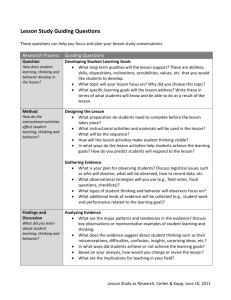
Problem Solving Flow Chart 1 PROBLEM SOLVING FLOW CHART Implementation Considerations for Core/School-Wide Instruction Guiding Questions: Are you aligning your curriculum with Common Core State Standards (CCSS)? Is your core teaching systematic, explicit, and strategic? Is the instructional block sufficient or is more time needed? (i.e. are you teaching the minimal allocated minutes?) Is instructional time “protected” by reducing interruptions and rescheduling core time when needed? Are students grouped appropriately by skill (i.e. differentiated instruction)? Yes: If you said “yes” to a majority of the above guiding questions, look at universal assessment data. No: If you said “no” to a number of the above guiding questions, there is likely a class-wide instructional need. Seek assistance to ensure core/ school-wide instruction is implemented effectively. Analyze Universal Screening Data (STAR) Decision Rule #1: Is the core instruction meeting the needs of 80% of students? Yes Continue to implement core instruction, utilizing differentiated instruction and teaching with fidelity. Consult with colleague and discuss possible classroom observation No Revisit Core Instruction Decision Rule #2: When Watch (blue), Intervention (yellow), and Urgent (red) equal more than 20% of student population, focus intervention efforts on the lowest 20% of the student population. If need/concern is still present, move to the next stage of Problem Solving: Student Level Problem Solving Problem Solving Flow Chart 2 STUDENT LEVEL PROBLEM SOLVING Beginning Stages: Problem Identification and Problem Analysis. Determine if it is a “can’t do” (skill deficit) or “won’t do” (performance deficit) need. Can’t Do Won’t Do Analyze current data using a balanced assessment approach to determine skill deficit. Options: Employ motivational and engagement strategies. Options: STAR FAST (coming soon) PALS, WKCE Classroom Samples Teacher Input (i.e., grade-level team, At-Risk Grid) Historical Information (i.e., cumulative file) Data from Reading Specialists (when requested) Parent Input Skill Deficit Identified Final Stages of Student Level Problem Solving: Intervention Development, Intervention Implementation, Intervention Evaluation Group for Intervention (menu of interventions: work-in-progress) Set up Progress Monitoring Set up Fidelity Checks Schedule an Intervention Evaluation meeting to analyze progress monitoring data (minimum of 4 intervention data points required) Analyze what it is that the student won’t do (i.e., tests, homework, projects, seat work, class participation) Develop rapport with student (ask student why they aren’t doing work) Focus on strengths Increase reinforcement of desired behavior (see Intervention Ideas on Google Drive) Model appropriate behavior (don’t forget what it can be like to be a student) Parent Input Teacher Input (i.e., grade-level team, At-Risk Grid) Skill Deficit Not Identified: Options: Consult with Reading/Math Specialists Complete the Request for Assistance Form (RAF) If problem persists despite employing motivational and engagement strategies, complete the Request for Assistance Form (RAF). Review Progress of Intervention Decision Rule #3: 1.) Continue 2.) Change 3.) Intensify and continue to monitor progress If progress is not made, intervention ideas have been exhausted, and additional assistance is needed, complete the Request for Assistance Form (RAF)