Unit Review
advertisement

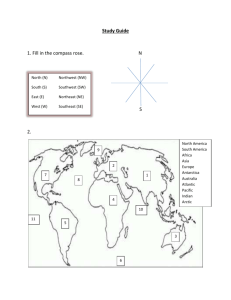
Unit 2 Review Unit Test Friday March 22, 2013 Learning Goals: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. I can identify the requirements for a map I can identify and use various types of maps, including general purpose, topographic, thematic and digital maps. I can determine locations on a map using directions and compass bearings I can locate places on using alphanumeric grid system I can locate places on a map using military grid system I can locate places on a map using latitude and longitude. I can use the three types of map scales (direct statement, representative fraction and linear scale) 2.1 What is a Map? 1. What is a map? 2. List and explain the 6 features of a map. 3. Identify and provide an example of the 4 types of maps covered in class. 4. Power point “Geographer’s Toolkit” 5. Define key terms (page 20) 6. Questions page 29 # 1-8 2.2 Chapter 4: Using map Scales a) Power point b) Chapter 4, Questions page 48 and 49 #1-10, 13, 14, 15. 2.3 Chapter 3: Locating Places on Maps a) Label direction and compass bearings using the compass rose. b) Power Point c) Pilots test d) Define key terms (chapter 3) e) Chapter 3, Answer, page 43 #1-5, 8 2.3B a) b) c) Alphanumeric Grid Systems Introduce Road maps – see pages 32-33 Note Chapter 3, Activity page 32 #1-10 2.3C Topographic Maps a) Introduce topographic maps on blackboard b) Power point c) Cambridge maps 2.3D Latitude and Longitude a) Power point b) Note c) Practice handout 2.3E a) b) c) Time Zones Map the 6 time zones Power point Handout Unit Practice Problems 1. Complete the following chart. Convert each scale. Direct statement a) 1 cm = 250 km Representative fraction Linear scale b) 1 cm = 30 km c) 1: 30 000 000 d) 1: 250 000 e) 0 35km f) 0 55 km 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What does 1 : 250 000 mean? Explain. Explain why it is important to be able to convert scales Define scale. What are the six features required on all maps? List the 4 types of maps. Provide an example of each type of map. What direction is opposite each of the following compass points? a) N _________________ b) E _________________ c) E _________________ d) W _________________ e) SW _________________ f) SW _________________ What is the direction for the following angular bearings? a) 22.5 _________________ b) 202.5 _________________ c) 112.5 _________________ d) 135 _________________ e) 292.5 _________________ f) 337.5 _________________ 9. What is the angular bearings for the following direction? a) N _________________ b) ESE c) S _________________ d) WSW e) NNE _________________ f) NNW _________________ _________________ _________________ 10. List the following points. a) cardinal points b) ordinal points c) third level points 11. What government level and ministry is responsible for producing road maps? 12. When was the first Ontario road map produced? 13. List and identify the 4 parts of a legend on an Ontario road map. 14. What is the scale on a topographic map. 15. On a topographic map, what is a(n) a) easting b) northing 16. Latitude. What line of latitude is: a) 80 ° south of the north pole ___________ b) 20° north of the equator c) 35 ° north of the south pole ___________ d) 55° north of 15° south 17. Longitude. What line of longitude is: ___________ ___________ a) 60° west of the prime meridian ___________ b) 50° east of 180° ___________ c) 30° west of 10° east ___________ d) 110° east of 170° west ___________ 18. Using pages 112 -113 of the Pearson School Atlas, find the latitude and longitude of the following locations: a) Timmins, Ont. ___________ b) Montreal, Que. ___________ c) Norfolk, Virginia ___________ d) Moose Jaw, Saskatchewan ___________ e) Billings, Montana ___________ f) Mobile, Alabama ___________ 19. Using pages 128 -129 of the Pearson School Atlas, find the latitude and longitude of the following locations: a) Tripoli, Libya ___________ b) Timbuktu, Mali ___________ c) Mogadishu, , Somalia ___________ d) Athens, Greece ___________ 20. Using page 120 of the Pearson School Atlas, identify the city located at the following coordinates: a) 0° , 78°W _______________________ b) 30°S, 51° W _______________________ c) 53° S, 71° W _______________________ d) 7°N, 58°W _______________________ 21. Label and list the 7 major lines of latitude. 22. What is another name for: a) latitude? b) longitude? 23. How far apart is each line of latitude? 24. Mick and Keith leave on a plane at 12:00 p.m. from the Toronto airport. Their flight to Vancouver B.C. will take 3 hours and 30 minutes. What time will it be in Vancouver when they land? 25. Paul and John leave Montreal airport at 7:00 am, en route to Vancouver B.C. Their flight takes 5 hours and 40 minutes. What time will it be in Vancouver when they land? 26. Bob and Doug’s plane leaves Toronto at 8:30 a.m. They are bound for Antigonish, N.S. Their flight takes 2 hours and 45 minutes. What will the clocks read in Antigonish when they land? 27. Using a topographic map of Cambridge, answer the following questions; a)