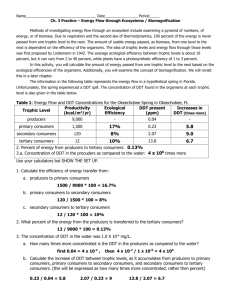
Unit I- Study Materials
advertisement

Unit I- Toxicity and Environmental Justice Videos Story of Stuff Canada’s Toxic Chemical Valley The Story of Electronics The Slow Poisoning of India 210 Million Tons Maquilapolis The Story of Make Up Terra Blight Vanishing of the Bees Erin Brockovich Readings Wakernargel and Rees and the ecological footprint (P. 6) Population and consumption drive environmental impact (P. 16) Consumption from affluence creates environmental impact (P. 226) Toxicants may accumulate and move up the food chain (P. 396) Silent Spring began the public debate over synthetic chemicals + Weighing the Issues (P. 389) Synthetic chemicals are ubiquitous in our environment (P. 388) Endocrine disruption may be widespread (P. 390) Toxicants come in different forms (P. 389) E-waste is a new and growing problem (P. 648) We have developed thousands of chemical pesticides (P. 268) We depend on insects to pollinate crops (P. 271) We have three disposal methods for hazardous waste (P. 650) Contaminated sites are being cleaned up slowly (P. 652) Facts on Environmental Racism Environmental Justice seeks equal treatment for all races and classes + Weighing Issues (P. 35) Environmental Justice is an international issue (P. 36) Is there a trade-off between economics and the environment? (P. 36) Labs LD50 UV beads lab Decomposition Lab Unit I Exam Content 20 multiple choice 2 Short Answer 1 Laboratory short answer 30 matching Skills Extract evidence for 4 lenses of ES. Write a high-level COSTA question Vocabulary 1. PPM 2. Anthropogenic 3. Ecocentrism 4. Biocentrism 5. Anthropocentrism 6. Endocrine disruptors 7. Environmental justice 8. Toxins 9. Superfund 10. Toxicology 11. Toxicity 12. Heavy metals 13. Bioaccumulation 14. Biomagnification 15. Developing country 16. Developed country 17. Underdeveloped country 18. Mutagens 19. Teratogens carcinogens 20. Pesticides 21. Pollinators 22. Deep-well injection 23. Surface impoundment 24. Landfill 25. Leachate. 26. Lead 27. Fire Retardants 28. Dioxin 29. DDT 30. Rachel Carson 31. BPA Bisphenol A 32. Carbon Footprint 33. Food Footprint 34. Housing Footprint 35. Goods Footprint 36. Ecological Footprint 37. Global Hectare 38. Atrazine 39. Environmental Health 40. Chemical Hazard 41. Physical Hazard 42. Cultural Hazard 43. Natural Hazard 44. Mutagen 45. Carcinogen 46. Teratogen 47. Ozone 48. Ozone-depleting substance 49. Chlorofluorocarbon CFC 50. Antarctic Ozone Hole 51. Montreal Protocol 52. Perfluorinated chemicals (PFCs) 53. Mercury 54. LD-50 Curve 55. E-waste 56. Decomposition 57. Chromium-6 58. Colony-Collapse Disorder Study Questions: 1. Explain the mechanism of biomagnification. Identify and describe the characteristics that cause some pollutants to pose a greater threat than others. 2. The use of the pesticide DDT is an example of the conflict between benefit to humans and ecological damage. List some of the benefits and some of the damage that result from the use of DDT. Identify and describe the properties of DDT that led to unexpected damage. Write one argument in favor of a worldwide ban of DDT. Write one argument opposed to a worldwide ban of DDT. 3. List three chemicals in your home, which would have an LD50. Research to find if there is a substitute chemical that could be used that does not have an LD50. 4. Be able to correctly graph/label and interpret an LD-50 graph. 5. Be able to correct identify and apply the vocabulary in the box on the previous page. 6. Know the health/environmental affects of a major toxin (Lead, Mercury, Pesticide, etc.) and be able to explain how it gets into the environment/bodies and why it is so harmful. 7. Explain the role of pollinators through the 4 lenses of ES. 8. Be able to define Colony Collapse Disorder and explain some alternate explanations on the cause. 9. Explain the role of Rachel Carson in the case against DDT. 10. Distinguish between developed, underdeveloped and developing countries as well as provide some examples and be able to connect this information to their ecological footprint. 11. Explain the different types of footprints and some solutions to reducing each one of them. 12. Be able to identify some examples of environmental justice/injustice and discuss in depth. 13. Be able to explain what e-waste is, where it goes, some solutions. 14. Why is the Montreal Protocol a model for global solution collaboration? 15. What causes ozone depletion? What causes it? Solutions? 16. Remember the main issues in each of the films that you watched, both in and out of class. 17. Give examples of synthetic materials as well as some of the effects on humans. 18. Explain how superfund sites demonstrate environmental injustice. 19. The importance of decomposition, role in an ecosystem, role in reducing waste. 20. Explain the circle of poison, in relation to pesticides and food production.