Earth Science Study Guide crust lithosphere Outermost layer. Made
advertisement
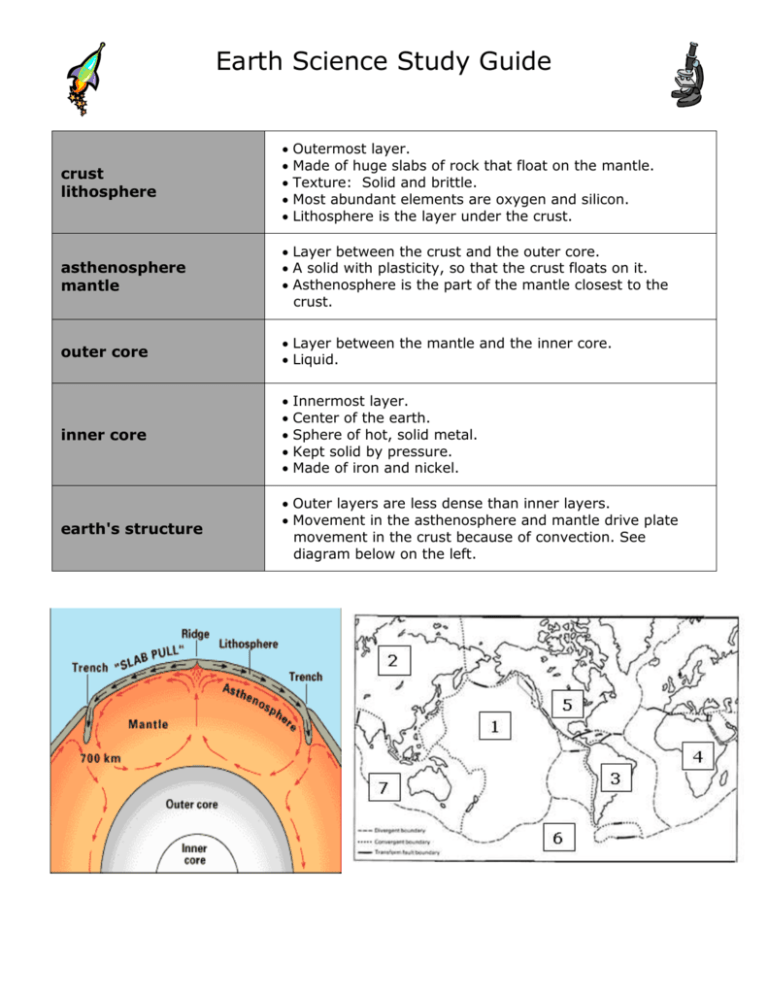
Earth Science Study Guide crust lithosphere Outermost layer. Made of huge slabs of rock that float on the mantle. Texture: Solid and brittle. Most abundant elements are oxygen and silicon. Lithosphere is the layer under the crust. asthenosphere mantle Layer between the crust and the outer core. A solid with plasticity, so that the crust floats on it. Asthenosphere is the part of the mantle closest to the crust. outer core Layer between the mantle and the inner core. Liquid. inner core earth's structure Outer layers are less dense than inner layers. Movement in the asthenosphere and mantle drive plate movement in the crust because of convection. See diagram below on the left. Innermost layer. Center of the earth. Sphere of hot, solid metal. Kept solid by pressure. Made of iron and nickel. major plates Geologic Events Ocean basins are created when oceanic plates diverge (move apart) and new crust is formed when magma rises and cools. Earthquakes are when movement of the plates or rock happens so quickly that it sends out vibrations moving the nearby rock. This mostly happens at transform (side by side) boundaries. Volcanic eruptions occur mostly when one plate is being subducted beneath another as the two plates converge(move towards each other.) Melting occurs that rises to the surface creating the Volcano. Mountains are built when plates converge and neither gives way to the other. Rock Cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 7. Pacific Plate. Eurasian Plate: largest plate. South American Plate. African Plate. North American Plate. Australian Plate. Process by which rock is broken down, formed, and / or changed into other kinds of rock. Rock: formed from minerals. Three kinds of rock: o Igneous, Sedimentary. Metamorphic. Igneous Rock Sedimentary Rock Metamorphic Rock Formed from melted rock: o Magma: melted rock underground. o Lava: melted rock at earth's surface. Likely shows evidence of volcanoes nearby. Examples: o Obsidian. o Granite. o Pumice. o Basalt: forms ocean floor. Rock formed from sediment by weathering and erosion. Sediment: small pieces of rocks, minerals, or shells. Formed by: o Compaction: pressure from rocks on layers below. o Cementation: minerals form a "glue" that holds sediments together. Examples: o Limestone. o Sandstone. Rock changes form, deep underground (at C in picture). Formed by: o Heat. o Pressure. "Morph" means change. Examples: o Marble. o Slate.







