3-5 Purifying and Analyzing Proteins
advertisement

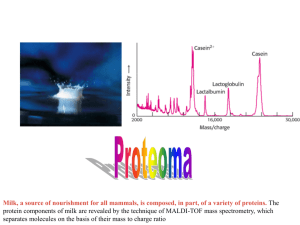
3-5 PURIFYING ANDANALYZING PROTEINS Purifying Proteins Concerns with purifying proteins… o _______________ it from all other cell components and other similar proteins o Methods are _______________ for each protein o Want proteins to remain biologically _______________ o Must be done between _____°C and _____°C to avoid protein degradation and denaturation Purification uses differences in… o _______________ o _____ _______________ o __________ o _______________ _______________ Purification follows a series of general steps: 1. Prepare a solution of proteins from a cell. 2. Separate the mixture of proteins using ammonium sulfate as a _______________ agent, and then _______________ to isolate a fraction containing the desired protein. 3. Separation by _______________ works by washing the fraction containing the desired protein through an insoluble material (matrix) using a specific solvent. This divides the mixture into finer fractions, then those fractions must be assayed (tested) for biological activity or other properties. a. Chromatographic techniques include… i. high-performance liquid chromatography (__________) ii. ion-exchange chromatography iii. gel-filtration chromatography, and iv. affinity chromatography * Read pages 68 and 69 to learn more about these different types of chromatography. Analytical Techniques _______________ – separates proteins based on their migration in an electric field. o Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (__________) uses a slightly basic gel matrix with an electric field passed through it. The gel matrix retards the migration of large molecules, thus the proteins are fractionated on the basis of _______________ and _______________. The fractions of proteins can be visualized by _______________. o Sodium dodecyl suflate is sometimes added (__________) to overwhelm the native charge on proteins so that the technique separates the proteins based on __________ only. It can be used to assess the purity and the molecular weight of the protein. The “bands” of proteins can be cut out of the gel and isolated for structural analysis, preparation of antibodies, or other purposes. __________ _______________ - determines the __________ of a molecule by measuring the __________ it takes for a charged gas phase molecule to travel from the injection point to a detector. The time depends on the __________and__________ of the molecule. This technique was not applicable to biochemists until the late 1980s when electrospray MS was developed to disperse charged protein molecules into a gaseous stream of particles. Another new technique is matrix-assisted desorption ionization (MALDI), which you can read about on page 71 of your book. o This technique can determine the mass of a protein from _______________ quantities isolated from SDS-PAGE gel, and the correct mass can be determined with an accuracy of less than the mass of a single _______________! Mass Spectrometer Diagram