Kindergarten Math Standards Rubric - Midland ISD
advertisement
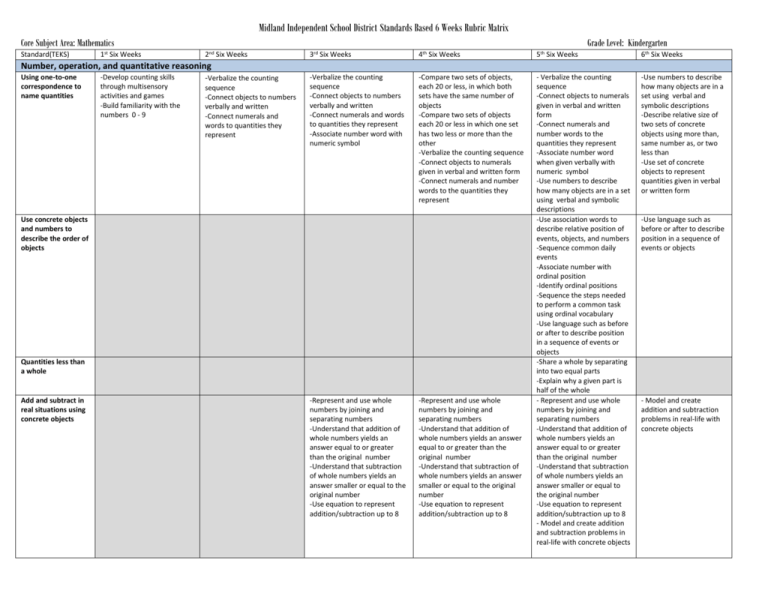
Midland Independent School District Standards Based 6 Weeks Rubric Matrix Core Subject Area: Mathematics Standard(TEKS) 1st Six Weeks Grade Level: Kindergarten 2nd Six Weeks 3rd Six Weeks 4th Six Weeks 5th Six Weeks 6th Six Weeks -Verbalize the counting sequence -Connect objects to numbers verbally and written -Connect numerals and words to quantities they represent -Associate number word with numeric symbol -Compare two sets of objects, each 20 or less, in which both sets have the same number of objects -Compare two sets of objects each 20 or less in which one set has two less or more than the other -Verbalize the counting sequence -Connect objects to numerals given in verbal and written form -Connect numerals and number words to the quantities they represent - Verbalize the counting sequence -Connect objects to numerals given in verbal and written form -Connect numerals and number words to the quantities they represent -Associate number word when given verbally with numeric symbol -Use numbers to describe how many objects are in a set using verbal and symbolic descriptions -Use association words to describe relative position of events, objects, and numbers -Sequence common daily events -Associate number with ordinal position -Identify ordinal positions -Sequence the steps needed to perform a common task using ordinal vocabulary -Use language such as before or after to describe position in a sequence of events or objects -Share a whole by separating into two equal parts -Explain why a given part is half of the whole - Represent and use whole numbers by joining and separating numbers -Understand that addition of whole numbers yields an answer equal to or greater than the original number -Understand that subtraction of whole numbers yields an answer smaller or equal to the original number -Use equation to represent addition/subtraction up to 8 - Model and create addition and subtraction problems in real-life with concrete objects -Use numbers to describe how many objects are in a set using verbal and symbolic descriptions -Describe relative size of two sets of concrete objects using more than, same number as, or two less than -Use set of concrete objects to represent quantities given in verbal or written form Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning Using one-to-one correspondence to name quantities -Develop counting skills through multisensory activities and games -Build familiarity with the numbers 0 - 9 -Verbalize the counting sequence -Connect objects to numbers verbally and written -Connect numerals and words to quantities they represent Use concrete objects and numbers to describe the order of objects Quantities less than a whole Add and subtract in real situations using concrete objects -Represent and use whole numbers by joining and separating numbers -Understand that addition of whole numbers yields an answer equal to or greater than the original number -Understand that subtraction of whole numbers yields an answer smaller or equal to the original number -Use equation to represent addition/subtraction up to 8 -Represent and use whole numbers by joining and separating numbers -Understand that addition of whole numbers yields an answer equal to or greater than the original number -Understand that subtraction of whole numbers yields an answer smaller or equal to the original number -Use equation to represent addition/subtraction up to 8 -Use language such as before or after to describe position in a sequence of events or objects - Model and create addition and subtraction problems in real-life with concrete objects Midland Independent School District Standards Based 6 Weeks Rubric Matrix Core Subject Area: Mathematics Grade Level: Kindergarten Patterns, relationships, and algebraic thinking Identifies, extends, and creates patterns -Introduce patterning through multisensory activities - Order three sounds/ physical movements/objects according to attributes -Identify and replicate patterns using concrete objects -Extend horizontal and vertical patterns using concrete objects and describes how the pattern was extended -Create patterns using sounds, movement, and concrete ideas. -Describe what is missing in a pattern or sequence - Order three sounds/ physical movements/objects according to attributes -Identify and replicate patterns using concrete objects -Extend horizontal and vertical patterns using concrete objects and describes how the pattern was extended -Create patterns using sounds, movement, and concrete ideas. - Order three sounds/ physical movements/objects according to attributes -Identify and replicate patterns using concrete objects -Extend horizontal and vertical patterns using concrete objects and describes how the pattern was extended -Create patterns using sounds, movement, and concrete ideas. Counts to 100 by 1’s 10 20 30 50 70 100 - Order three sounds/ physical movements/objects according to attributes -Identify and replicate patterns using concrete objects -Extend horizontal and vertical patterns using concrete objects and describes how the pattern was extended -Create patterns using sounds, movement, and concrete ideas. -Describe what is missing in a pattern or sequence -Predict what comes next -Count by ones to 100 -Count by twos to 100 -Predict what comes next -Identify, extend, and create patterns of sounds, physical movement, and concrete objects -Identify and describe where an object is located -Name and demonstrate the relative position of objects -Describe one object in relation to another using over, under, above and below -Place an object in a specified position -Select all shapes or objects of one attribute from a group -Describe common objects by shape, size, color, texture, or use -Sort or classify two- and three-dimensional geometric figures into groups based on student/teacher defined categories -Describe how objects are alike or different using appropriate vocabulary based on size, shape, color, texture, or use - Identify and define shapes based on characteristics -Describe one object in relation to another using over, under, above and below -Count by ones to 100 -Count by twos to 100 -Count by tens to 100 Geometry and spatial reasoning Describe relative positions Uses attributes to determine how objects are alike/different -Identify and describe where an object is located -Introduce sorting by attributes -Identify how objects are alike and different based on defined categories -Describe common objects by shape, size, color, texture or use -Identify and define shapes based on characteristics. -Select all shapes or objects of one attribute from a group -Describe common objects by shape, size, color, texture, or use -Identify and define shapes based on characteristics -Sort or classify two- and threedimensional geometric figures into groups based on student/teacher defined categories -Describe how two- and threedimensional geometric figures are alike or different using appropriate vocabulary based on size, shape, color, texture, or use -Describe and identify an object by its attributes Midland Independent School District Standards Based 6 Weeks Rubric Matrix Core Subject Area: Mathematics Recognized attributes of 2D and 3D figures Grade Level: Kindergarten -Draw and verbally describe attributes of specified shapes -Draw and verbally describe attributes of specified shapes -Describe and compare the attributes of real-life objects such as balls, boxes, cans, and cones, or models of three-dimensional figures -Recognize shapes in real-life figures or models of threedimensional geometric figures -Recognize shapes in reallife figures or models of three-dimensional geometric figures -Describe, identify, and compare circles, triangles, rectangles, and squares Estimate length before comparing objects -Identify objects that are longer, shorter, or equal in length -Use a benchmark length to decide if one object is longer than another -Use math language to describe lengths such as “longer than” or “shorter than” -Compare the areas of two flat surfaces of twodimensional figures (covers more, covers less, or covers the same) Measurement Directly compares attributes of length and area -Explore measurement by comparing lengths Directly compares the attributes of weight/mass/capacity -Introduce capacity through sand and water play Directly compares the attributes of relative temperature -Compare and discuss situations that are hotter, colder, and about the same temperature -Estimate length before comparing objects -Identify objects that are longer, shorter, or equal in length -Use a benchmark length to decide if one object is longer than another -Use math language to describe lengths such as “longer than” or “shorter than” -Estimate weight/mass before measuring Use objects to measure weight/mass -Use a benchmark weight/mass to decide if another object is heavier, lighter, or equal weight/mass -Compare two objects according to weight/mass (heavier than, lighter than, or equal to) Use time to describe, compare and order events and situations -Order up to three events according to duration -Order everyday events according to occurrence -Compare events according to duration such as more time or less time Probability Constructs and uses graphs of real objects or pictures -Create age and birthday graphs -Arrange objects in a floor or table graph according to attributes -Label graphs appropriately -Construct both horizontal and vertical graphs -Gather, sort, and interpret data in response to questions posed by the teacher/student -Arrange objects in a floor or table graph according to attributes -Label graphs appropriately -Construct both horizontal and vertical graphs -Gather, sort, and interpret data in response to questions posed by the teacher/student -Arrange objects in a floor or table graph according to attributes -Label graphs appropriately -Construct both horizontal and vertical graphs -Gather, sort, and interpret data in response to questions posed by the teacher/student -Construct graphs using real -Compare events according to duration such as more time or less time Midland Independent School District Standards Based 6 Weeks Rubric Matrix Core Subject Area: Mathematics Grade Level: Kindergarten objects or pictures in order to answer questions -Use information from a graph of real objects or pictures in order to answer questions. Underlying Processed and Mathematical Tools Applies kindergarten math to solve problems, to communicate, and to use logical reasoning -Identify mathematics in everyday situations -Solve problems with guidance that incorporates the processes of understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness -Select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, or acting it out in order to solve a problem -Use tool such as real objects, manipulatives, and technology to solve problems -Communicate mathematical ideas using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Relate everyday language to mathematical language -Justify his or her thinking using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Identify mathematics in everyday situations -Solve problems with guidance that incorporates the processes of understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness -Select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, or acting it out in order to solve a problem -Use tool such as real objects, manipulatives, and technology to solve problems -Communicate mathematical ideas using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Relate everyday language to mathematical language -Justify his or her thinking using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Identify mathematics in everyday situations -Solve problems with guidance that incorporates the processes of understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness -Select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, or acting it out in order to solve a problem -Use tool such as real objects, manipulatives, and technology to solve problems -Communicate mathematical ideas using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Relate everyday language to mathematical language -Justify his or her thinking using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Identify mathematics in everyday situations -Solve problems with guidance that incorporates the processes of understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness -Select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, or acting it out in order to solve a problem -Use tool such as real objects, manipulatives, and technology to solve problems -Communicate mathematical ideas using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Relate everyday language to mathematical language -Justify his or her thinking using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Identify mathematics in everyday situations -Solve problems with guidance that incorporates the processes of understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness -Select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, or acting it out in order to solve a problem -Use tool such as real objects, manipulatives, and technology to solve problems -Communicate mathematical ideas using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Relate everyday language to mathematical language -Justify his or her thinking using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Identify mathematics in everyday situations -Solve problems with guidance that incorporates the processes of understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness -Select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, or acting it out in order to solve a problem -Use tool such as real objects, manipulatives, and technology to solve problems -Communicate mathematical ideas using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology -Relate everyday language to mathematical language -Justify his or her thinking using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology