Water & pH Notes
advertisement

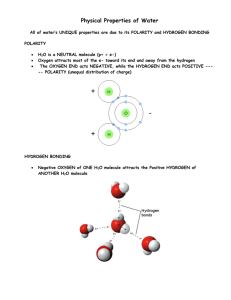
Unit 2 BioChemistry Section 2 Water Most abundant compound, exists in 3 phases 70% of earth is covered with water & 60% of body is made of water. H2O : Molecule – more than one atom Compound – more than one type of element O has 1 covalent bond with each H Polarity : Oxygen and hydrogen are held together by a strong covalent bond O (8 protons) has a stronger electronegativity than H electrons are shared unequally the electrons surround oxygen more makes oxygen side of the molecule partially negative makes the hydrogen side of the molecule partly positive Polar molecule is a molecule where charges are unevenly distributed. Hydrogen Bonds: Weak bond between molecules (Not between atoms to create a molecule, that’s covalent and ionic) Hydrogen is often partially positively charged and makes weak bonds with partially negatively charged Oxygen of other molecules. H2O molecules sticking together; H+ area of one atom attracting the O- areas of a different atom. 1 H2O molecule can form hydrogen bonds with 4 other H2O molecules Draw 5 Water Polarity of water molecules molecules here Allows them to form hydrogen bonds with each other Contributes to the various properties water exhibits Properties of Water Cohesion : Same type of molecule attracted to each other Ex: H2O molecules stick together and form droplets Surface tension: Due to cohesion surface of water appears & act as membrane (invisible skin) Ex. Insects walk on water surface. Adhesion Different types of molecules attracted to each other Water molecules stick to other polar molecules Ex: H2O sticks to the glass forming meniscus Capillary Action – Cohesion and adhesion lead to capillarity H2O rises in a narrow tube against gravity. This is how water gets from the roots of a plant to the leaves. Water Expands upon freezing and ice is less dense than water Ice floats on the top prevents entire pond or lake from freezing acts as blanket to moderate temperatures below life allows more organisms to survive winter High specific heat: takes a long time to heat up takes a long time to cool down (doesn’t transfer heat quickly) High heat of vaopization phase change from liquid water to gas (water vapor) requires heat that heat is pulled from your body as sweat evaporates Universal solvent dissolves polar substances by making hydration shell does not dissolve nonpolar molecules Mixture : 2 or more substances physically mixed, but NOT chemically combined (so NOT H2O, H is chemically bonded to the O) Ex. Earth’s atmosphere is a mixture of gases 1.Solution – Homogeneous mixture (one sub is dissolved in another) mixture where solute (ex: salt) is dissolved in the solvent (ex: water) Particles are evenly distributed H2O is the greatest solvent in the world 2. Suspension -Mixture that is not dissolved but remains suspended Ex. Sand in water, blood with cells pH : The concentration of H+ ions (parts hydrogen or percent hydrogen) neutral pH Scale Acids 1 Bases 7 more H+ions less OH- ions 14 less H+ ions more OH- ions Each step is 10X more or less concentrated than the previous step. EX: pH 4 has pH 3 has pH 2 has pH 5 has pH 6 has 10 _____ _____ _____ _____ H+ ions H+ ions H+ ions H+ ions H+ ions Acid is a compound that forms H+ ions in solution Base is a compound that forms OH- ions in solution Buffers – weak acids or bases that help maintain homeostasis. They react with strong acids or bases to prevent sharp sudden changes in pH.