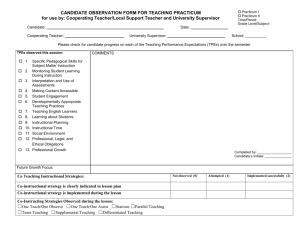
Candidate Proficiency Alignment
advertisement

4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment Calumet College of St. Joseph Education Department Candidate Proficiencies Alignment The Education unit presents the alignment of standards from three educational entities: 1) The Indiana Department of Education (IDOE) Essential Pedagogy, 2) The Interstate New Teacher Assessment and Support Consortium (INTASC), 3) The National Board for Professional Teacher Standards (NBPTS) and 4) The Association for Childhood Education International (ACEI) for elementary. The following table combines the standards from the first three entities and aligns them with the unit’s Candidate Outcomes. To assure a high level of pedagogical and content knowledge for all teacher candidates, the unit program has defined five major objectives corresponding to the academic, developmental, and social needs of PK-12 students. These are aligned with the three pillars of the conceptual framework: Preparation, Reflection and Transformation. All teacher candidates are required to demonstrate: Preparation 1. Understanding How Students Learn and How They Differ 2. Knowledge of What to Teach Reflection 3. Continuous Personal and Professional Growth Transformation 4. Demonstration of How to Teach Effectively 5. Effective Implementation of Technology The unit’s alignment of its Candidate Outcomes with the standards of the IDOE, INTASC and NBPTS demonstrates a comprehensive approach to the achieving consistency professional performance. 1 4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment Alignment of Unit’s Candidate Outcomes with the Standards of the IDOE, INTASC and NBPTS Education Unit Candidate Outcomes IDOE INTASC NBPTS CORE Preparation: #1. Understanding How Students Learn and How They Differ Teacher candidates: design curriculum to motivate students through active learning in supportive environments. monitor and manage student learning using appropriate assessments as an integral part of instruction. plan lessons that reflect an understanding of students’ developmental characteristics and needs, using a variety of pedagogical techniques to convey information and teach skills. establish classroom rules and procedures: to promote an organized and productive learning environment, to set appropriate behavior standards that communicate high and realistic expectations for students’ behavior, and to ensure that students understand both expectations and consequences of misbehavior. promote student learning by providing responsive instruction that makes use of effective communication techniques; instructional strategies that actively engage students in the learning process; and timely, high-quality feedback. Essential Pedagogy Teacher candidates: exhibit a strong working knowledge of subject matter that enables students to better understand patterns of thinking specific to a discipline. stay abreast of current knowledge and practice within the content areas, related disciplines, and Developmentally appropriate literacy standards based on scientifically-based reading research and developed and approved by the board Understanding of historical and contemporary development of early childhood education Psychology of child development, including, but not limited to the development of exceptional needs students Competence in multicultural education Essential Pedagogy Preparation: #2. Knowledge of What to Teach Principle #2 Teaching across the content areas of: English/Language Arts, Math, Science, Social, P.E./Health, Music Visual Art (See content standards) 2 The candidate understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle #3: The candidate understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle #1: The candidate understands Core #1 Teachers are committed to students and their learning Core #2 the central concepts, tools of inquiry, and the structures of the discipline(s) he or she Teachers know the subjects they teach Core #5 Teachers are members of 4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment technology. design instruction appropriate for all students that reflects an understanding of relevant content and is based on continuous and appropriate assessment. know and understand the importance of the state content and performance standards as outlined in the Indiana Teacher Content Standards and Essential Pedagogy for Teachers. know and understand the relevant content of the discipline being taught, including concepts, principles, relationships, methods of inquiry, and key issues. know how to plan lesson content and skills and implement instructional strategies that make connections within the discipline and across disciplines. know how to use varied activities and instructional groupings to engage students in instructional content and to meet instructional goals and objectives. know and understand how to engage students intellectually by teaching content in relevant and meaningful ways that promote all students’ active and invested participation in the learning process. know how to develop and use a variety of formative and summative assessment tools, consistently applied to instructional goals and outcomes, fairly administered, accurately measured, carefully interpreted, and effectively communicated. plan instructional experiences that progress sequentially and support stated instructional goals; are aligned with the Indiana Academic/Core Standards are clear, relevant, meaningful, age appropriate, and able to be assessed. Curriculum Development, lesson planning assessment and data used in informing instruction teaches and can create learning experiences that make these aspects of subject matter meaningful for students. Principle #4: The candidate understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage student’s development of critical thinking, problem solving and performance skills Principle #7 The candidate plans instruction based upon knowledge of subject matter, the community and curriculum goals. Principle #8 The teacher understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continuous intellectual, social and physical development of the learner. 3 learning communities 4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment Reflection: #3 Continuous Personal and Professional Growth Teacher candidates: respect individual and cultural differences of students and their families. model and encourage appreciation for students’ cultural heritage, unique endowments, learning styles, interests, and needs. design learning experiences that show consideration for student culture and heritage in appropriate classroom, school, and social contexts. collaborate with diverse families, professionals, and communities. integrate and adapt instructional strategies and assessments that are appropriate for and responsive to diverse student’s needs, abilities, and interests including the needs of English language learners. acknowledge and address concerns that affect learners by using community diversity, strengths, and resources. create a learning environment in which diversity and individual differences are valued and respected. recognize and support the efforts of families to engage in the education of their children. commit to grow professionally, benefiting from the use of self-assessment. serve as advocates for students and the profession. participate in mentoring opportunities and in beginning teacher support systems. think critically, solve problems, reflect on teaching practice, demonstrating success through a variety of roles when teaching. demonstrate a commitment to learn, improve the profession, maintain professional ethics and personal integrity, and share responsibility for the result of student learning with the members of the learning community. identify and use group processes to make decisions Essential Pedagogy Classroom and behavioral management, including but not limited to the legal rights and responsibilities of teachers, students and families Reflection on and evaluation of professional practices, professional conduct and leadership Collaboration and consultation with team members including colleagues, families, primary caregivers, agency personnel, and other service personnel to design and implement experiences and instruction Principle #5: The candidate uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning and self-motivation Principle #9: The candidate is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (students, parents and other professionals in the learning community) and who actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally. Core #3 Teachers are responsible for managing and monitoring student learning Core #4 Teachers think systematically about their practice and learn from experience Core #5 4 Principle #10: The candidate fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and wellbeing. Teachers are members of learning communities 4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment and solve problems, as a member of a collaborative educational team. enhance content and pedagogical knowledge and skills through a variety of professional development activities. Transformation: #4 Demonstration of How to Teach Effectively Essential Pedagogy Teacher candidates: demonstrate a belief that children can learn by being respectful and sensitive to learners and enabling learners to use their skills and talents. are dedicated to teaching life-long learning by engaging students in active learning to promote critical thinking, creativity, and problem solving focused on future learning. are committed to professional and ethical standards reflected in daily decisions. work to create an environment in which taking risks, sharing new ideas, and innovative problem solving are encouraged and supported. engage in an active exchange of ideas with teaching colleagues; observe peers; and encourage feedback from students to establish a successful learning community. know and understand the importance of communicating enthusiasm for learning, of interacting with students in ways that reflect support and show respect for all students, and of using effective interpersonal skills (including both verbal and nonverbal skills) to reach students and communicate a sincere commitment to student success. create an environment in which learners work cooperatively and purposefully using a variety of resources to understand themselves, their immediate community, and the global society in which they live. manage and monitor student learning using appropriate assessments and adjusting instruction Application of effective teaching practices for teaching young children through a variety of early and ongoing clinical experiences with infant and toddler, preprimary-aged and primary-aged children within a range of educational programming models Differentiation of instruction and teaching methods, including methods for teaching English as a new language and students with exceptional needs, designed to maximize student engagement Use of informal and formal assessment and evaluation strategies in collaboration with others to plan individualized curriculum and teaching practices 5 Principle #2: The candidate understands how children learn and develop, and can provide learning opportunities that support their intellectual, social and personal development. Principle #3: The candidate understands how students differ in their approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are adapted to diverse learners. Principle #4: The candidate understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage student’s development of critical thinking, problem solving and performance skills. Principle #8 The teacher understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continuous Core #1 Teachers are committed to students and their learning Core #3 Teachers are responsible for managing and monitoring student learning Core #4 Teachers think systematically about their practice and learn from experience Core #5 Teachers are members of learning communities 4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment accordingly. encourage learners to work independently and cooperatively in a positive and stimulating learning climate fueled by self-discipline and motivation. manage the learning environment effectively so that optimal learning occurs. Transformation: #5 Effective Implementation of Technology Teacher candidates: integrate technology in teaching and learning. adapt instruction to respond to diverse students’ abilities, needs, and interests. select materials, technology, activities, and space that are developmentally appropriate and designed to engage students' interest in Essential Pedagogy Use of technology to support instruction, access and manipulate data, enhance professional growth and productivity; communicate and collaborate with colleagues, families, and community agencies and conduct research. 6 intellectual, social and physical development of the learner. Principle #9: The candidate is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his/her choices and actions on others (students, parents and other professionals in the learning community) and who actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally. Principle #10: The candidate fosters relationships with school colleagues, parents and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and wellbeing. Principle #6: The candidate uses knowledge of effective verbal, nonverbal and media communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration and supportive interaction in the classroom. Principle #10: The candidate fosters Core #2 Teachers know the subjects they teach Core #3 Teachers are responsible for managing and monitoring student 4.4 Candidate Proficiencies Alignment relationships with school colleagues, parents and agencies in the larger community to support students’ learning and wellbeing. learning. select and organize topics recognizing the dynamic nature of knowledge so students make clear connections between what is taught in the classroom and what they experience outside the classroom. select and use materials, technology, activities, space, and other resources that are developmentally appropriate, that support instructional goals and objectives, and that are designed to engage student interest in meaningful learning. use verbal, nonverbal, and media techniques so that students explore ideas collaboratively, pose questions, and support one another in their learning. Principle #4: The candidate understands and uses a variety of instructional strategies to encourage student’s development of critical thinking, problem solving and performance skills 7 learning Core #5 Teachers are members of learning communities