Semester 1 Review: NAME
advertisement

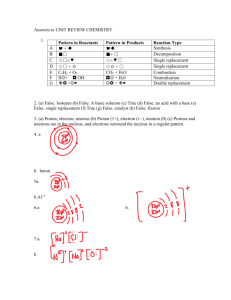
Semester 1 Review: NAME:___________________ Lab equipment and safety Define the following terms: hand lens- Used to magnify something small for better view. stereoscopes-gives 3D image of items, usually for samples during dissection microscopes-used to view microscopic items on a slide-cells beakers-holding container for liquid that gives approximate volume Petri dishes-used for grow plates, sampling and experiments holding dish microscope slides- a small flat rectangular piece of glass on which specimens canbe mounted for microscopic study graduated cylinders-used for accurate measurement of liquids test tubes-used for chemicals designed for heating chemicals meter sticks-used for measuring long distances in meters timing devices-for timing hot plates-used to warm liquids and other items during labs triple beam balances-used for accurate measurement of mass thermometers-used to determine the temperature temperature and pH probes- used to determine the internal temperature of specimens aprons-to protect clothes and body from chemical spills/splashes eye/face wash-used to wash out eyes in case chemicals or other objects get in/on your eyes fire blanket-used to extinguish small fires fire extinguisher-for putting out fire Physical change- limited to changes that result in a difference in display without changing the composition Chemical change-occurs when the substance’s composition is changed. When bonds are broken and new ones are formed a chemical change occurs. Endothermic-chemical reaction that absorbs heat energy. The reactions usually feels cool to the touch or decrease in temperature. Exothermic-chemical reactions that release heat energy. These reactions usually feel hot to the touch or increase in temperature Dependent variable-what you measure in the experiment. The effect. The response Independent variable-manipulated variable. What you test or change in the experiment. You observe what happens Constant-something that scientist makes sure is the same throughout the experiment Control-stays the same in the experiment Answer the following: What piece of equipment is best to use when measuring the volume of a liquid? Graduated cylinder What piece of equipment is best to use when measuring the mass of a rock? Triple beam balance What piece of equipment is best to use when measuring the length of the courtyard? Meter stick Organic/ Inorganic Compounds What is the difference between an element and a compound? An element cannot be broken down by chemical or physical means. A compound is a substance made of two or more different elements that are chemically bound. _______Element_____________ - substances that cannot be broken down into any other substance by chemical or physical means. The ______Periodic___________ ______Table______ is an organized collection of all of the known elements. _____Compound_____ is a substance made of 2 or more different elements that are chemically bound. Of the 90+ naturally occurring elements on Earth, about _40_ are required by living organisms. The key elements that compose __99.8%_ of ALL living things are: __S__ ( Sulfur ) __P__ ( Phosporus ) __O__ ( ) Oxygen __N__ ( Nitrogen ) __C__ ( ) Carbon __H__ ( Hydrogen ) __Ca__ ( Calcium ) __Fe__ ( Iron ) __K__ ( Potassium ) For a compound to be considered ____organic___, it must contain both: __C__ ( Carbon ) & __H__ ( Hydrogen ). What are some ways carbon can be recycled? 1. Plants take in carbon dioxide to create glucose. 2. When humans exhale, carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere. 3. Plants and animals decompose and return carbon dioxide to the air and carbon into the soil Physical/ Chemical Changes Common examples of physical changes: Change in states of matter (boiling point versus melting point) Texture Shape Temperature Size Common examples of chemical changes: Change in temperature Change in color Noticeable odor Formation of bubbles Formation of precipitate (solid) What is the difference between physical and chemical changes? Physical changes do not result in a change to the composition of the chemical. A chemical change will change the bonds of the composition of the chemical What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic? Endothermic reactions absorb heat and feel cold. Exothermic reactions release energy and feel hot. Circle whether the following are organic or inorganic. C27H46O ORGANIC INORGANIC H2O ORGANIC INORGANIC CO2 ORGANIC INORGANIC CH3COCH3 ORGANIC INORGANIC C12H22O11 ORGANIC INORGANIC NaCl ORGANIC INORGANIC BrCH3 ORGANIC INORGANIC CCl2F2 ORGANIC INORGANIC CaH2 ORGANIC INORGANIC CHBr3 ORGANIC INORGANIC Ca(OH)2 ORGANIC INORGANIC Plants Plants give off the gas _Oxygen___ and take in the gas _Carbon Dioxide__. What is the function of a chlorophyll? To absorb light energy. Label the process shown in the picture below. 1.Oxygen is released 2.Carbon dioxide is absorbed 3.Light energy is absorbed in the chlorophyll 4.water & nutrients are absorbed in the roots 5.Glucose is formed in the leaves Decide whether each is an internal or external stimulus (circle) and write what response might be reasonable. A. Hunger Internal or External Stimuli Response: stomach growls B. Sunburn Internal or External Stimuli Response: skin peels, painful C. Sunlight for a plant Internal or External Stimuli Response: photosynthesis Define: Phototropism- plants response to light (plant leans towards the light energy source) Geotropism-plants response to gravity (Plant tipped on its side will still grow up and down) Thigmotropism- plants response to touch (vines grow along the side of a building) Hydrotropism- Plants response to water (roots grow towards an underground water source) Turgor Pressure- The pressure within the cells of a plant due to water storage in the vacuoles. (with no water, plant will wilt) Chemical Energy – Breaking apart of chemical bonds. Glucose is Chemical Energy in Plants!!! When humans eat that energy we break the molecules apart and use them for energy in our body. C6H12O6 Chemical Energy – Breaking apart of chemical bonds. Glucose is Chemical Energy in Plants!!! When humans eat that energy we break the molecules apart and use them for energy in our body. C6H12O6 Radiant Energy – Radiant energy is energy from the ___sun_____. respiration- The process of taking in and releasing gases transpiration- The process of a plant releasing water via the roots, leaves, stem. Pollination- The process of moving pollen from plant to plant. What is the reproductive part of the plant? flower How might a plant respond if the turgor pressure in its cells was low? wilt CELLS What is the basic unit of life? cells Who are the three men that designed the cell theory? Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow What are the three parts of the cell theory? 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from preexisting cells. Eukaryotic cell- a cell with an organized nucleus. Prokaryotic cell- a cell with NO nucleus. What are the four main macromolecules found in all cells? Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleic acids Give the LOCATION and FUNCTION of each organelle listed below: Cell wall- stiff structure outside of the cell membrane (only on plant, fungi, bacteria, and some protozoans) made mainly of carbohydrates. Cell membrane- flexible covering that protects the inside of all cells from the environment. Made mostly of proteins and lipids. Nucleus- (Eukaryotic) directs cell activities and contains genetic information stored in DNA (Chromosomes). Also contains proteins and nucleolus. Nucleolus- large dark spot in the nucleus of a cell that makes ribosomes. Ribosomes- protein factory of the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum- network of passageways that carry materials from one part of the cell to another. Mitochondria- produces most of the cell’s energy. Chloroplast- found in plant and some protozoan cells. Membrane-bound organelles that use light energy and make food (sugar called glucose) from water and carbon dioxide in a process known as photosynthesis. Chlorophyll- collects the light energy in a plant cell. Found in the chloroplast. Cytoplasm- Fluid inside all cells that contain the water, salts, and enzymes. Golgi apparatus- prepares proteins for their jobs/ functions then packages proteins into vesicles. Vacuoles- store food, water, and waste material (plants have one large, animals have many small) Which two organelles above are found ONLY in plant cells? Chloroplast, cell wall List the five levels of organization starting with the smallest unit of life and define each: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. cells- smallest unit of life tissue- many cells with the same function together. organ- many tissues of the same function together. organ system- several organs with similar functions combined. organism- network of organs working together to keep an INDEPENDENTLY functioning organism alive. Nervous System 2 Types of Neuronsa. sensory neurons- receive signals from the environment utilizing the five senses. b. motor neurons- receive specific responses back from the brain and spinal cord on how to react. What are the functions of the nervous system? 1. Receive and respond to stimuli 2. Transmit impulses to the body Skeletal System 4 types of bones1. 2. 3. 4. Flat-protects and support organs (ribs, shoulder) Long-support weight and movement (leg, arm) Short-support weight (feet, wrist) Irregular- Irregular shape (vertebrae, ear) Joint – Where two bones meet. 1. 2. 3. 4. Ball & socket- shoulder and hip hinge- elbow and knee Pivot- Neck and arm Gliding- wrist What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Shape and support Allows movement Protects tissues and organs Stores minerals Produces blood cells Muscular System Involuntary Muscles – muscles you CANNOT control. Voluntary Muscles – muscles you are able to control. Three Types of Muscle Cardiac Smooth Skeletal Where are they found in the body? Only found in your heart, never stops contracting and relaxing your entire life. Found in internal organs and blood vessels. Thin layer surrounding intestines, arteries, and veins that help keep things moving. Most common muscle that moves bones. When one muscle contracts, the opposite relaxes. What are the functions of the muscular system? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pumps blood Enables breathing Holds you up right Allows you to move Some temperature control Voluntary or Involuntary involuntary involuntary voluntary Digestion Digestion – Breaking down food into smaller molecules Mechanical Digestion – Physical digestion(change)- material is broken down without adding additional substances. EX: chewing muscles mixing in stomach Chemical Digestion –material is broken down with substances creating a chemical reaction. EX: saliva mixing in mouth When nutrients are absorbed in small intestine Villi – fingerlike projections that cover the inside of the intestine Peristalsis – the waves of muscle contractions that move the food down the esophagus. The organs of the digestive system List the Digestive System Organs in the correct order that food passes through them, earliest to latest: Mouth Esophagus Function – What is the main job of this organ? chews food and breaks it down for swallowing Both hollow tube that connects the mouth to the stomach None Small Intestine flexible baglike organ that contains enzymes (stomach acid) that help to break down food molecules further through the action of Churning long wound-up tube that helps digest food and absorbs the nutrients from the food through the Villi Large Intestine long wound-up tube that collects what is not absorbed in the small intestine. Also absorbs the water from the remaining waste. Rectum/Anus Rectum- Where waste is stored, Anus releases it. Stomach Chemical or Mechanical Digestion or Both or None What are the functions of the digestive system? Chemical Both Mechanical None 1. Breaking down food into smaller molecules 2. Absorbing nutrients into our blood for energy 3. Preparing food for waste LABEL EACH OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Respiratory System Where in the respiratory system is oxygen exchanged with carbon dioxide? alveoli What are the functions of the respiratory system? 1. Take in oxygen to send throughout the body. 2. Release carbon dioxide as a waste product. LABEL EACH ORGAN OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Circulatory System All animals need _______oxygen______ to make___ _energy________ from food. The body then gives off _________carbon dioxide________ as a waste product. What are the functions of the circulatory system? 1. Transport oxygen, nutrients, and substances to the body’s cells. 2. Transports carbon dioxide and other waste away from cells. 3. Fights infection 4. Regulates body temperature What are the 3 main organs of the circulatory system? 1. Heart- major organ and major muscle 2. Blood 3. Blood vessles Excretory System What are the functions of the excretory system? 1. Eliminates/ removes cellular waste from the body (including liquids, solids, and gases) What do the following organs do for the excretory system? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Lungs- remove carbon dioxide (CO2) and excess water vapors Skin- removes water and salt when you sweat Liver- removes waste from the blood, breaks down proteins creating urea Kidneys- remove urea from the body by making urine Ureter- tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder (transports urine) Bladder- flexible sac that stores urine Urethra- Where urine is removed from the body Rectum- stores feces until it is removed from the body Integumentary System What are the functions of the Integumentary system? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. First line of defense (protection from environment and pathogens) Formation of vitamin D Regulates body temperature Gets rid of waste in your body (through sweat glands) Sensory response (nerve endings in skin relay messages to the brain) What are the 3 main organs of the Integumentary system? 1. hair 2. nails 3. skin Endocrine System What are the functions of the endocrine system? 1. To produce required hormones. 2. To control long term body functions. Which gland controls the following hormones? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Pituitary gland- Master controller, controls growth and sexual development. Thyroid gland- Controls metabolism. Parathyroid gland- Controls calcium levels in the blood. Thymus gland- Controls white blood cells developed. Adrenal gland- Controls fight or flight reflexes in danger. Pancreas- Regulates blood sugar. Ovaries/ Testes- Controls reproduction female/ male (respectively). Reproductive System What are the functions of the reproductive system? 1. The continuation of life. What organs are vital to the reproductive system (female and male)? Male system: Testes- main organ that makes the sperm. Female system: Ovaries- organ where the eggs are made. Fallopian tubes- tube that connects the ovaries to the uterus. Uterus- Where the baby grows.