1-5 ch2
advertisement

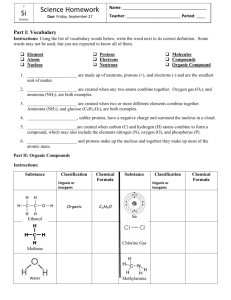
Warm-up: (9-4-15) *Tragedy of the Commons and packet rubric out for stamp! 1. What is the basic building block of matter? 2. N2 and O2 are examples of _____ consisting of two ____ of the same _____. 3. Why is sustainably caught fish more expensive? 4. Give one example of a time delay. 5. Sweating to cool down after exercising is an example of ______________. 6. If a solution has a pH of 9, it is (acidic, basic) and has a proton concentration of _____ moles per liter. *Continue working on HW for next week. Ch.2-pt 2 Mrs. Boyd What does “organic” mean in food production? What does “organic” mean in chemistry? Organic Compounds: Carbon Rules Organic compounds contain carbon atoms combined with one another and with various other atoms such as H+, N+, or Cl-. Contain at least two carbon atoms combined with each other and with atoms. Methane (CH4) is the only exception. All other compounds are inorganic. Organic or inorganic? N2O CO2 CH4 C14H9Cl5 (DDT) CO C6H12O6 Organic or inorganic? Organic or inorganic? Living things are made of basically 4 types of macronutrients. Carbohydrates (C, H, O) Lipids (C, H, O) Nucleic Acids (C, H, O, N, P) Proteins (C, H, O, N, sometimes S) Are these considered to be organic or inorganic molecules? Matter Quality Matter can be classified as having high or low quality depending on how useful it is to us as a resource. High quality matter: concentrated and easily extracted. low quality matter: more widely dispersed and more difficult to extract. Low or high quality matter? Low or high quality matter? Low or high quality matter? Low or high quality matter? Low or high quality matter? Low or high quality matter? Low or high quality matter? CHANGES IN MATTER Matter can change from one physical form to another or change its chemical composition. When a physical or chemical change occurs, no atoms are created or destroyed. What law states this? Earth is a closed system for matter What does this mean? Physical change maintains original chemical composition. (ice to water, water to water vapor) Chemical change involves a chemical reaction which changes the arrangement of the elements or compounds involved. Chemical equations are used to represent the reaction. Chemical Change Energy is given off during the reaction as a product. Types of Pollutants Factors that determine the severity of a pollutant’s effects: chemical nature, concentration, and persistence. Pollutants are classified based on their persistence (how long they stick around): Degradable pollutants- can be broken down completely Biodegradable pollutantsbiological action to break down biological things Slowly degradable pollutants- takes decades or longer to degrade (plastics, DDT) Nondegradable pollutants- chemicals that cannot be broken down by natural processes. (mercury, lead, arsenic) Concentration ppm = 1 part per million parts of gas, liquid, or solid mixture. Now we can measure in ppt What does the t stand for? Check for Understanding: 1. Give one example of a nondegradable chemical. 2. Describe the law of conservation of matter. 3. Give one example of high quality matter.