Genetics
advertisement

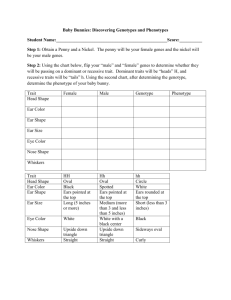
Genetics Homozygous or Heterozygous? III. Gentics Terms A. A _____________ is a long molecule of DNA. B. Two connected copies of a chromosome are ______________. C. A ___________ is a part of the DNA that has instructions for a specific trait, like eye color or hair color. D. An _____________is one form of a gene that has instructions for a particular characteristic like blue eyes or brown eyes. E. Some traits are _______________. They can hide other traits. 1. We use capital letters to represent _____________ alleles. TT Tt tt IV. Predicting Genetic Outcomes A. Punnet squares are a tool to help us determine what genotypes the offspring of certain parents might have. B. Sample Cross: Key: T = Tall pea plants, t = Short pea plants 2. Brown hair and brown eyes are _____________ traits. F. Some traits can be hidden by dominant traits. These traits are ________________. 1. We use lower case letters to represent _____________ alleles. 2. Blue eyes and blonde hair are ______________ traits. G. If an organism has two alleles that are the same, we call that organism ___________________. (Ex: TT, tt) H. If an organism has two different alleles of the same gene, we call that organism ________________. (Ex: Tt) ***A heterozygous organism shows the dominant trait.*** Phenotype? % Dominant Phenotype (Tall): ________ % Recessive Phenotype (Short): ________ Ratio of Dominant to Recessive: ________ Key: P = purple flowers p = white flowers Key: R = round seeds r = wrinkled seeds P = purple flowers p = white flowers R = round seeds r = wrinkled seeds Parent 1: ____________________ Parent 2:____________________ Parent 1: ____________________ Parent 2:____________________ % Dominant Phenotype: ________ % Dominant Phenotype: ________ % Recessive Phenotype: ________ % Recessive Phenotype: ________ Ratio of Dominant to Recessive: ________ Ratio of Dominant to Recessive: ________ Parent 1: ____________________ Parent 2:____________________ Parent 1: ____________________ Parent 2:____________________ % Dominant Phenotype: ________ % Dominant Phenotype: ________ % Recessive Phenotype: ________ % Recessive Phenotype: ________ Ratio of Dominant to Recessive: ________ Ratio of Dominant to Recessive: ________