Chemistry: Chapter 6
advertisement

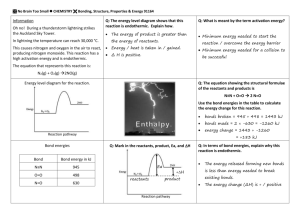
Chapter 6 – Chemical Change Key Concepts Lesson 6.1 What is a Chemical Reaction? Key Concepts: • A physical change, such as a state change or dissolving, does not create a new substance, but a chemical change does. • In a chemical reaction, the atoms and molecules that interact with each other are called reactants. • In a chemical reaction, the atoms and molecules produced by the reaction are called products. • In a chemical reaction, only the atoms present in the reactants can end up in the products. No new atoms are created, and no atoms are destroyed. • In a chemical reaction, reactants contact each other, bonds between atoms in the reactants are broken, and atoms rearrange and form new bonds to make the products. Lesson 6.2 Controlling the Amount of Products in a Chemical Reaction Key Concepts • Changing the amount of reactants affects the amount of products produced in a chemical reaction. • In a chemical reaction, only the atoms present in the reactants can end up in the products. • Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction. Lesson 6.3 Forming a Precipitate Key Concepts The ions or molecules in two solutions can react to form a solid. A solid formed from two solutions is called a precipitate. Lesson 6.5 A Catalyst and the Rate of Reaction Key Concepts A catalyst is a substance that can help the reactants in a chemical reaction react with each other faster. A catalyst does not actually become part of the products of the reaction. Lesson 6.7 Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Key Concepts If two substances react and the temperature of the mixture decreases, the reaction is endothermic. If two substances react and the temperature of the mixture increases, the reaction is exothermic. A chemical reaction involves the breaking of bonds in the reactants and the forming of bonds in the products. It takes energy to break bonds. Energy is released when bonds are formed. If a reaction is endothermic, it takes more energy to break the bonds of the reactants than is released when the bonds of the products are formed. If a reaction is exothermic, more energy is released when the bonds of the products are formed than it takes to break the bonds of the reactants. Lesson 6.8 pH and Color Change Key Concepts Whether a solution is acidic or basic can be measured on the pH scale. When universal indicator is added to a solution, the color change can indicate the approximate pH of the solution. Acids cause universal indicator solution to change from green toward red. Bases cause universal indicator to change from green toward purple. Water molecules (H2O) can interact with one another to form H3O+ ions and OH− ions. At a pH of 7, there are equal numbers of H3O+ ions and OH− ions in water, and this is called a neutral solution. Acidic solutions have a pH below 7 on the pH scale. Basic solutions have a pH above 7 on the pH scale. Lesson 6.9 Neutralizing Acids and Bases Key Concepts pH is a measure of the concentration of H3O+ ions in a solution. Adding an acid increases the concentration of H3O+ ions in the solution. Adding a base decreases the concentration of H3O+ ions in the solution. An acid and a base are like chemical opposites. If a base is added to an acidic solution, the solution becomes less acidic and moves toward the middle of the pH scale. This is called neutralizing the acid. If an acid is added to a basic solution, the solution becomes less basic and moves toward the middle of the pH scale. This is called neutralizing the base.