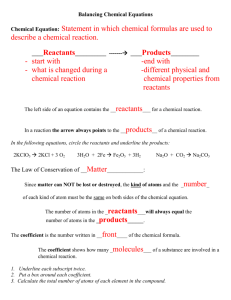
CHEMICAL REACTIONS - Page 201 Reactants and Products A
advertisement

CHEMICAL REACTIONS - Page 201 Reactants and Products A chemical reaction has two sides: o The reactants (what you start with) o The products (what you end with The Law of Conservation of Matter The Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass) states that Matter can neither be created nor destroyed This means that the number of atoms in the reactants for each element and the number of atoms in the products for each element must remain the same in a chemical reaction (but not in a nuclear reaction) A chemical equation is a way to show a chemical reaction. To make sure the equation is balanced, we use two kinds of numbers o A subscript is a little number in a chemical formula like the 2 in H2O. It tells you how many atoms of an element are in one molecule of that compound. If there is no subscript, the number is automatically one. o A coefficient is a normal sized number placed in front of a chemical formula like the 3 in 3H2O. It tells how many molecules of a compound are needed for the reaction. Again, if there is no coefficient that means the number is one. o To get the total number of atoms of an element for the reactants or products, you multiply the coefficient by the subscript (2H2O has a total of 2*2=4 Hydrogen atoms and 2*1=2 Oxygen atoms) Because the number of grams you have is dependent on the number of atoms you have, the mass of the reactants in an equation (measured in grams) is equal to the mass of the products, just like the total number of atoms are. Energy in Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions always involve the exchange of energy Usually, but not always, the energy involved is heat In exothermic reactions, heat is released by the reaction, so the temperature gets hotter In endothermic reactions, heat is absorbed by the reaction, so the temperature gets colder Acids and Bases Compounds can be classified as acids or bases An acid releases Hydronium (H3O+) ions when in solution A base releases Hydroxide (OH-) ions when in solution. To measure the acidity of a solution, we use a number called pH Acids have a pH less than 7. The lower the number, the stronger the acid Bases have a pH more than 7. The higher the number, the stronger the base Scientists use litmus paper to test the acidity of a solution. Acids turn blue litmus paper red. Bases turn red litmus paper blue Pure Distilled Water has a pH of exactly 7. Compounds like these are considered neutral