maitland/5231/P6The Periodic Table
advertisement

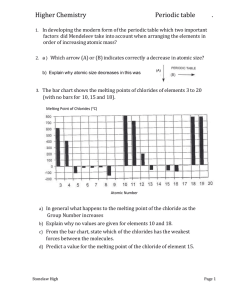
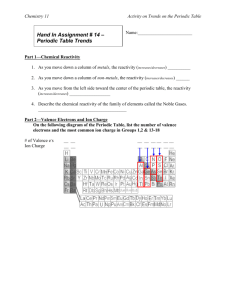
P6 The Periodic Table The Periodic Table is an important tool that chemists use to summarise the physical and chemical properties of elements. The strength of the Periodic Table lies in its ability to predict the properties of elements that have not yet been discovered. Historical development of the Periodic Table Periodic law Properties of elements varied periodically with their atomic weights Atomic number Henry Mosley (1914) determined the atomic number of the elements Modified Periodic law Properties of the elements vary periodically with their atomic numbers Trend in atomic radius Decreases from left to right across any period of the table Increases down each group of the table Ionisation energies First ionisation energy M(g) Second ionisation energy M+(g) Third ionisation energy M2+(g) Trend in ionisation energies The first ionisation energy increases from left to right across each period of the table The first ionisation energy decreases down each group of the table The lower its ionisation energy the more readily an element forms positive ions Trend in melting points across a period Trend in melting points down groups Dobereiner described the triads of elements (1829) Newlands described the law of octaves (1864) Mendeleev and Meyer described the periodic law (1869) M+(g) + eM2+(g) + eM3+(g) + e- Each period begins with a low melting point element Melting points tend to increase until a maximum is reached (group 4 elements in the second and third periods) After the maximum melting points in any period decrease The lowest melting point for any element in a period is the melting point for the group 8 element Melting points decrease down groups 2 and 3 Melting points increase down groups 7 and 8 Trend in metallic character Valency and the periodic table Metallic character decreases across each period Metallic character increases down each group The most metallic elements are found in the bottom left hand side of the periodic table The most non-metallic elements are found in the top right hand side of the periodic table The most common valency of elements from groups 1 to 4 is equal to the group number The most common valency of elements from groups 5 to 8 is 8 minus the group number Electronegativity A measure of the ability of an atom of that element to attract bonding electrons towards itself when it forms compounds Trend in electronegativities Ionic compounds Covalent compounds Electronegativities increase from left to right across each period Electronegativities decrease down each group Electronegativities range from 0.7 (francium) to 4.0 (fluorine) When the difference between the electronegativities of two elements is greater than 1.5 an ionic compound is formed An ionic compound is formed between the atoms of a metal and the atoms of a non-metal When the difference between the electronegativities of two elements is less than 1.5 a covalent compound is formed Covalent compounds are formed between the atoms of different non-metallic elements