Give the IUPAC name for the following compound
advertisement

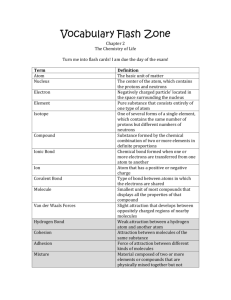
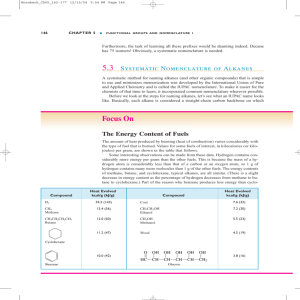
CH221 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I QUIZ 1 2 MARCH 2009 Time allowed: 50 minutes Attempt all 40 questions on the grid answer sheet provided 1. Which of the following is (are) a Lewis structure(s) for the anion (CH2NO2)-? Assume the atoms are arranged as drawn.E 7. Which of the following species has (have) a trigonal planar structure with 120 bond angles around the labeled carbon atom? D 2 Convert the following compound from a condensed formula to a skeletal formula. D CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2CH(CH2CH3)CH2CH(CH3)2 8. Of the molecules listed, which does not have a dipole moment? D A. HCl B. NCl3 C. CO D. BF3 E. All molecules have a dipole moment. 3. How are the molecules in the following pair related? B A. They are isomers. B. They are resonance structures. C. Neither of the choices is correct. 4. Indicate the hybridization at the carbon ion in each compound below. D A. a - sp2; b - sp2 B. a - sp2; b - sp3 C. a - sp3; b - sp3 D. a - sp3; b - sp2 E. None of the choices are correct. 5. Which of the labeled carbon atoms is (are) sp2 hybridized? D 6. Which of the following species contains a carbon atom with a +1 formal charge? (All nonbonded electron pairs have been drawn in.) A 9. From the list below, pick the one species that cannot act as both a Bronsted-Lowry acid and base. D A. HCO3B. HSO4C. H2PO4D. OHE. HPO4210. Rank the acidity of the labeled protons in the following molecule from lowest to highest acidity. Hc > Ha > Hb 11. Which of the following compounds is the strongest Bronsted Lowry acid? B A. CH3CH2OH B. ClCH2OH C. CH3OCH2F D. ClCH2NH2 E. CH3CH3 12. Which of the following species is the strongest base? A A. NH2B. OHC. ClD. NH3 E. I13. Which of the following statements is true? C A. CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base. B. BBr3 can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid. C. CH3Cl can be a Lewis base. D. CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base, and BBr3 can be a BronstedLowry acid. E. CH3CH3 can be a Lewis base, BBr3 can be a Bronsted-Lowry acid, and CH3Cl can be a Lewis base. 1 14. What is the nucleophilic site in each of the following molecules? C A. B. C. D. E. A: hydrogen; B: nitrogen; C: electrons in bond A: oxygen; B: nitrogen; C: carbon A: oxygen; B: nitrogen; C: electrons in bond A: oxygen; B: carbon; C: electrons in bond A: carbon; B: nitrogen; C: hydrogen 15. Estimate the pKa of the hydrogen to the nearest multiple of 5. D A. B. C. D. E. 10 20 30 40 50 16. Which is the strongest base? B A. B. C. D. NH3 NH2OHH- 17. Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point? E A. B. C. D. E. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH CH3CH2OCH2CH3 CH3OCH(CH3)2 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH(CH3)2 21. A thiol should have properties most similar to A A. B. C. D. E. an alcohol. an amine. an ether. a sulfide. an alkyl halide. 22. Hydrogen bonding E A. requires at least one lone pair of electrons. B. is a common intermolecular bonding force in alkanes. C. can occur between a compound and water even if the compound cannot hydrogen bond with itself. D. is the weakest of the intermolecular forces. E. requires at least one lone pair of electrons and can occur between a compound and water even if the compound cannot hydrogen bond with itself. 23. Polarizability of molecules such as Br2 leads to E A. B. C. D. E. an inability to interact with polar or non-polar solvents. an induced dipole moment. a molecule that can act as a nucleophile or an electrophile. an inert molecule. an induced dipole moment and a molecule that can act as a nucleophile or an electrophile. 24. The compound shown below is penicillin G. This was a "wonder" drug for killing bacterial infections after World War II. Identify the functional groups a, b, and c listed in that order. A : Phenyl, Benzyl or Arene B: Carbonyl or amide C: Carboxylic acid 18. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?E 25. From the list below, which compound would you predict to have the lowest boiling point? A 19. Which of the following compounds is (are) the most water soluble? A A. B. C. D. E. CH3CH2CH2OH CH3CH2OCH3 CH3CH2CH2Cl Both (CH3CH2CH2OH) and (CH3CH2OCH3) are H2O soluble. Compounds (CH3CH2CH2OH), (CH3CH2OCH3), and (CH3CH2CH2Cl) are all H2O soluble. 20. Which of the following molecules can hydrogen bond to another molecule like itself? D A. B. C. D. E. CH3CH2NH2 CH3COOH CH3OCH2CH3 (CH3CH2NH2) and (CH3COOH) can hydrogen bond. (CH3CH2NH2), (CH3COOH), and (CH3OCH2CH3) can all hydrogen bond. A. CH4 B. SiH4 C. AsH4 D. PH3 E. NH3 26. What is the IUPAC name for the following compound? 7,7-diethyl -2,3,7-dimethyl-5-isopropyl decane 27. Give the IUPAC name for the following compound. 4-tert-butyl-2,5-dimethylheptane 2 28. Give the IUPAC name for the following compound. 5-sec-butyl-7,7-diethyl-2,3-dimethyldecane 34. Which of the following statements is (are) true about the following compound? E 29. Draw the ring-flipped conformer of this compound? CH2CH3 A. B. C. D. E. H3 C H3CH2C 30. Draw the most stable conformer of 1, 3-dimethylcyclohexane. Ca and Cd are 1 carbons. Cb and Cc are 3 carbons. Ce and Ca are 2 carbons. (Ca and Cd are 1 carbons) and (Cb and Cc are 3 carbons). (Cb and Cc are 3 carbons) and (Ce and Ca are 2 carbons). 35. Which of the following Newman Projections represents the most stable conformation of 2,3-dimethylbutane? C 31. Given the three Newman projections drawn below, rank them in order of increasing stability. B<C<A 36. Which of the following curved arrows account for the differences between the two structures? 3 O H2C 32. Assuming that the size of substituents is H<CH3<I, which of the following conformations is the most stable? C O C 1 C H H 2C O 2 C H2C C H H 2C O H2C C H H 2C O 4 H O C H2C H O C 3 H O C H H 2C H 37. How many constitutional isomers are there with the molecular formula C6H14? C a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 8 33. How are the molecules below related to each other? C 38. Which of the following compounds can adopt a chair conformation in which there are no axial methyl groups? C or D a. 1,1-dimethylcyclohexane b. cis-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane c. trans-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane d. cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane 39. Which of the following cycloalkanes has the smallest heat of combustion per carbon atom? C a. cyclopropane b. cyclopentane c. cyclohexane d. cycloheptane A. B. C. D. E. They are constitutional isomers. They are identical. They are resonance structures. They are not isomers; they are different compounds. They are stereoisomers. 40. Which of the following substituted cyclohexanes has the most negative value of ΔG° for ring flipping from the conformation in which the substituent is axial to the one where it is equatorial? D a. fluorocyclohexane b. methylcyclohexane c. ethylcyclohexane d. tert-butylcyclohexane 3 CH221 QUIZ 1 ANSWER GRID Write in each box the answer you think corresponds to the correct answer to that question. Name…………………………………………….. 1 2 E 6 3 D 7 A 11 8 12 16 21 22 25 A 14 18 26 7,7-diethyl-5isopropyl-2,3dimethyldecane C E E E 27 4-tert-butyl-2,5dimethylheptane Hc>Ha>Hb 15 19 23 D 10 D C E A 9 13 17 5 D D A B 4 B D B Student Number…………………….…………… D 20 A D 24 A : Phenyl or Benzyl B: Carbonyl or amide C: Carboxylic acid 28 5-sec-butyl-7,7-diethyl-2,3-dimethyldecan 30 31 B<C<A 29 32 33 34 35 36 C C E C 3 37 38 39 40 C C or D C D Total score 4