CSTPs –Essential Standards Evidence Ideas Ideas created by
advertisement

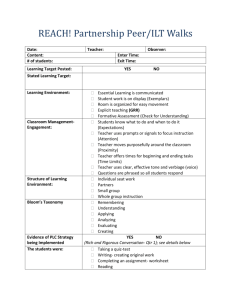
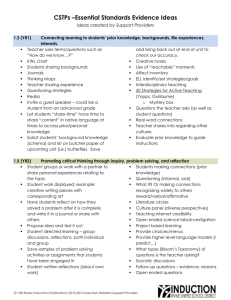
CSTPs –Essential Standards Evidence Ideas Ideas created by Support Providers 1.2 1.4 Connecting learning to students’ prior knowledge, backgrounds, life experiences, interests. Teacher uses terms/questions such as “How bring back out at end of unit to check our do we know…?” accuracy. KWL chart Creative hooks Students sharing backgrounds Use of “teachable” moments Journals Affect inventory Thinking Maps ELL identify/set strategies/goals Teacher sharing experience Interdisciplinary teaching Questioning strategies 50 Strategies for Active Teaching (Yopps, Realia Guillaume) Invite a guest speaker – could be a student o Mystery box from an advanced grade Questions the teacher asks (as well as Let students “share-time” have time to share student questions) “content” in native language at times to Real word connections access prior/personal knowledge Teacher shares info regarding other cultures Solicit students’ background knowledge Evaluate prior knowledge to guide (schema) and list on butcher paper of instructions upcoming unit (i.e.) butterflies. Save and Using a variety of instructional strategies, resources, and technologies to meet students’ diverse learning need Books on tape Flexible grouping Utilize a variety of sensory strategies that Skits help with students that might have Jigsaw challenging or difficult behaviors (i.e. carry Popcorn item to office, way to ask for help, etc.) True/False and Yes/No cards Discovery lessons White board (individual) Groups: differentiated instruction Use of technology – computers, iPads ELD strategies Critiques (self) using LAN school Thinking Maps Did the activities in class address multiple Student-driven activities intelligences? Nook/Kindle/iPad under document camera Balance of student and teacher use of Group work technology Teach-show model Open ended projects that show mastery of Differentiate self-evaluation material in a creative way Give one, get one Authentic learning – Edmodo Visuals/audios/hands-on PowerPoint/video recording G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT 1.5 2.3 Promoting critical thinking through inquiry, problem solving, and reflection Student groups or work with a partner to What if? Or making connections share personal experiences relating to the recognizing widely to others topic reward/verbal/affirmative Student work displayed; example: creative Literature circles writing pieces with corresponding art Culture panel (diverse perspectives) Have students reflect on how they solved a Teaching internet credibility problem after it is complete and write it in a Open ended science labs/investigation journal or share with others Project based learning Propose idea and test it out Provide choices/menus Student directed learning – group Provide higher level language models (I discussions, reflections, both individual and predict…) group What types (Bloom’s Taxonomy) of Save samples of problem solving activities questions is the teacher asking? or assignments that students have been Socratic discussions engaged in Follow-up questions – evidence, reasons Student written reflections (about own Open ended questions work) Evaluate point of view & perspective on Students making connections (prior primary sources knowledge) Debates Questioning (informal, oral) Analyzing Establishing and maintaining learning environments that are physically, intellectually, and emotionally safe 100% participation activities Peer share Avoids negative responses to student Emergency rules/directions posted incorrect answers Safe space posters “May I suggest, may I recommend” instead Students sharing opinions of “you need, you should be…” Think – pair – share Review classroom/school core values – i.e. Name/number sticks to randomly call on “integrity” - then students explain what student integrity looks like in a classroom setting, Flow pattern for teacher movement noted on i.e. doing your own work seating chart Modeling Student inventories to encourage teachers Be open to and embrace PBIS strategies that get to know students better are being implemented (common core Using sticks to call on students language for positive behaviors throughout Call on multiple students for different school really does work) perspectives Ask for student ideas Positive reward system, especially for Time to think/respond student participation Positive reinforcement Sharing student work under doc camera Class discussions Students in charge of class discussions Impromptu reviews Rick Morris “Who’s Next” app on iPhone G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT 2.6 Are classroom norms established with student feedback? Body language of teacher towards students Small group activities Evaluating “the process” during group work Set up of the classroom – does it encourage students’ sharing ideas Modeling behavior Employing classroom routines, procedures, norms, and supports positive behavior to ensure a climate in which all students can learn Transitions - for example: noise signals, Classroom expectations posted gestures Assigned roles to help kids with special Be aware of which students you’re calling needs on; develop a system that easily documents Transitional songs/routines who you have called upon Class constitution Agenda/schedule/changes posted Morning meeting Rewards – both class wide and individual Multiple activities available to students to Beginning of class procedure established: minimize down time always have instructions on board – hand in Plan lesson to reduce transitions homework, take out notebook, response to Procedures established for activities, i.e.: journal entry, etc. Students begin at the bell. setting up a lab/get supplies etc. PBIS strategies: incentive cards, acronyms Behavioral expectations are posted Classroom success plan posted Enforces behavior expectations Using and adapting resources, technologies, and standards-aligned instructional materials, including adopted materials, to make subject matter accessible to all students Books on tape Brain pop iPads Online resources Student computer access Rick Morris class cards Electronic response technology Call dojo United streaming Kids using interactive resources Photo stories Student teaching other students/shared Edmodo learning Blackboard Freedom to propose own learning method to Wiki teacher and fellow students (video/art etc.) Class websites Language labs Prezi Student – generated culture learning PowerPoint (holiday reports, etc.) iPods LCD projector, doc camera Document camera SMART board Response clickers (Quizdom) Supplementary and/or auxiliary materials CD Player/MP3 provided in adoption of texts Videos United streaming 3.5 G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT 3.6 4.1 4.5 Addressing the needs of English learners and students with special needs to provide equitable access to the content Give them more time Use of picture cards Provide hard copy of PowerPoint or lesson Acting out vocabulary for student to use & follow along Using EL support books provided with Make sure you have materials & teacher T.E.S. manuals for your SPEC ED grade level so Review 504 plan to guarantee that you can spend time “modifying” and implementation of all requirements making accommodations rather than time & Look at student cumulative folders and energy finding materials for instruction discuss/gather facts from previous teachers (equal access) Discussion with case carrier Vocabulary lists on walls Internet “virtual” field trips Realia Picture walk through book as preview “cloze” copy of notes technique IEPs – review and be knowledgeable Vocabulary “box” Hands-on activities Student activities to preview vocabulary SDAIE strategies digital translators Preview/review of content Using knowledge of students’ academic readiness, language proficiency, cultural background, and individual development to plan instruction KWL charts Graphic organizers Journaling Check profile on ABI PPE Assessments Ask open-ended questions at beginning of Parent info surveys (Google Docs) – family, lesson to learn about student experiences background, educational history, languages Listen to your students Kids surveys Pre-assessments based on prior classes Multiple intelligence inventory Use strategies for all types of learners – CELDT/CST scores visual, auditory, etc. Schoolnet Use developmental knowledge, example: Students introduce self/selves through letter “change it up” every 15 minutes for K, of introduction (directed/narrative essay) attention span limited Students interview each other – create Allow for movement. wordlist – shows family, background, Use examples from the neighborhood interests, strengths, etc. Anticipation Activities Culture Day Differentiate instructions Parent/grandparent interview Adapting instructional plans and curricular materials to meet the assessed learning needs of all students Review IEP goals before planning lessons & Check for understanding modify Small groups Use visuals Peer tutoring (i.e. math all stars) Pre-assessments Pair sharing G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT 5.4 6.3 “Ask Three Before Me” Differentiated instruction Group activities (small) Launchpoint strategies: wait-time, equity strategies, etc. Use the resources for EL learners and get materials that are at instructional level Gen. Ed. teacher reviews all student IEPs Use ELP standards Informal assessments made during learning: thumps up, show your white board, etc. RTI/PLC planning (elementary/secondary) Reflective – formal, informal assessment to guide instruction Using assessment data to establish learning goals and to plan, differentiate, and modify instruction Department PLC’s → formative assessment Post-its Item analysis from multiple choice questions Class discussion/evaluate assessment or on a test activity and suggestions for Schoolnet assessment information improvements/what to keep/what did not Include SPEC ED staff in planning (e.g. work SPEC ED teacher, resource teacher, o Butcher paper group discussion, list speech/language, O.T., P.T., etc.) & share out Review LPA scores at the instructional level RTI – grouping/homogenous Use of Exit Cards Pre, ongoing, post, and summative Teacher-made check list assessment to guide instruction Use of hands-on assessment Interpret data/scores Anecdotal notes Collaborating with colleagues and the broader professional community to support teacher and student learning PLC meetings Grade level meetings: planning, new ideas, Professional development align to common core, PLC Vertical teams & grade-level teams for Goal setting meetings sharing and articulating IEPs and SSTs for concerns, mainstreaming Informal conversations with IAs and and implementation of goals Support Staff (SAI) Professional develops: teach & implement Eat lunch together new teaching strategies, share ideas, gain Attend committee meetings knowledge Attend different department or grade level Talk/email IA’s to explain lesson plans, meeting to learn new goals classroom management, modeling Conversations w/BTSA Support Provider Meet and collaborate with anyone that is Staff meeting “share out” knowledgeable about my subject matter Teacher conventions Meet daily to give progress reports to S.I.P days appropriate staff members Staff development Go back to previous teachers to learn about Peer observation my students Seek professional assistance Constant collaboration with colleagues Talking with colleagues Get students involved with culture of the Staff meetings: collaborate & share school G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT Compare assessment data with fellow staff New teachers interact with veteran teachers RTI teacher drops in on staff meetings and inquires about students with homeroom teacher Communicate by email with administrator Approach your administrator to help solve/resolve concerns and issues Member of PBIS team PLC meetings with ELD teachers Collaborate with co-teachers, speech therapists, and psychologists to enhance student learning 6.6 Managing professional responsibilities to maintain motivation and commitment to all students. Teacher collaboration (PLC) Teaching magazines Utilizing personal necessity days Professional development – furthering your Workshops continuing education, knowledge & toolbox development PLC with teaching teams – share ideas Read books on content or teaching strategies Pinterest/online searches/Ted Talks – help Exercise/pedometer with specific content area – Get Upbeat attitude creative…collaborate Setting limits for yourself Goal setting – sets direction Prioritizing → focus on 1-2 important things Collaborating w/other schools teaching Letting go of “old” curriculum teams Visiting other classrooms to observe best City programs – interact with community practices Technology – CUE conference (implement Looking for new ways to teach the lesson new strategies , creative) (Google, other internet, Pinterest) Adjunct duties – get involved, interact with Edmodo – professional learning students outside schools (PTA) – communities community Attending concerts/conferences Grants, Donors Choose – bring new things Teaching Channel into classroom enhance teaching Sharing a favorite part of the week Explore resources like Scholastic – Getting to know your colleagues Common Core materials (non-fiction texts, Taking risks etc.) Trying new things → technology (Skype) Constantly seeking information – PD, and storing the experience pictures using idea CGI Training Seek out best practice & adapt to student Common Core needs Primary Literacy Project Set goal, progress notes GATE Weekly collaboration sessions – notes Differential instruction Consult with veteran teachers Teachers Pay Teachers Developing inquiry question Technology Professional reading – describe how it was Real life examples applied, journaling, summary Mentor Technology – photos Observing other teachers G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT Bring you and your interests into the classroom Getting involved in software opportunities: Edmodo, Raz Kids, First in Math, Lexi, Prezi, English in a Flash Create a 3-year Science Curriculum for SAI – Moderate/Severe Students Using Reading A-Z software to enhance HM curriculum in nonfiction texts to be implemented in RTI Became school site TAC in order to facilitate my own learning and challenge my knowledge of technology G:\HR-Share\BTSA\FACT