Metric Conversions - St. Anne Catholic School
advertisement

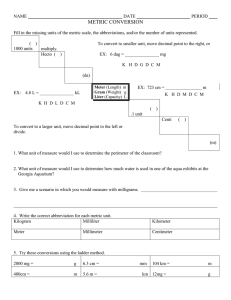
Metric Unit Conversions There are times when you will need to convert metric measurements to a smaller or larger unit. Since the metric system is a base 10 system, converting metric measurements boils down to multiplying or dividing by powers of 10 (10, 100, 1000, .1, …). The shortcut to multiplying and dividing by powers of 10 is moving the decimal point in a number to either the right or left. To begin, you need to understand the prefixes used in the metric system. Prefix Symbol Value Kilo k 1000 Hecto h 100 Deca da 10 Deci d .1 or 1/10 Centi c .01 or 1/100 Milli m .001 or 1/1000 There is a fun acronym you can learn to remember the order of the prefixes – King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk The B in By represents the base unit such as meter, gram, or liter. So here is a complete example of the King Henry breakdown using meters. km (kilometer = 1000 meters) hm (hectometer = 100 meters) dam (decameter = 10 meters) m (meter) dm (decimeter = 1/10 of a meter) cm (centimeter = 1/100 of a meter) mm (millimeter = 1/1000 of a meter) Example Problem: 1. How many centimeters are in 3 kilometers? 3 km = _____ cm First, you want to write the prefixes for metric measurements in order from left to right. k h da B d c m To go from kilometers to centimeters, you have to jump 5 places to the right (the Base unit counts as one jump). The shortcut here is to move the decimal 5 places to the right. 3. = 300,000 3 km = 300,000 cm 2. How many kilometers are in 5 meters? 5 m =________ km Again, write the prefixes for metric measurements in order from left to right. k h da B d c m This time you have to move left from B (base unit of meters) to kilometers a total of 3 spaces. The shortcut is to move the decimal 3 places to the left. 5. = .005 5 m = .005 km Practice Problems 1. 7.4 km = _________ m 2. 8.7 cL = _________ kL 3. 4 mg = __________ cg 4. 30 mL = __________ L 5. 1600 kg = __________ g 6. 38 dm = __________ hm