24-1 PowerPoint Notes
advertisement

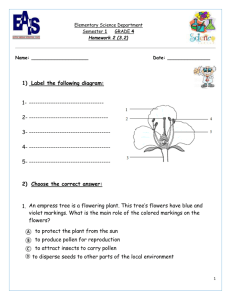
Biologist ___________________________ Date ______________ 24.1 Reproduction in Flowering Plants – PowerPoint Notes The Structure of Flowers Flowers are reproductive organs that are composed of ___________ different kinds of specialized leaves: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. This diagram shows the parts of a typical ___________ flower. Sepals and Petals The outermost circle of floral parts contains the ___________. Sepals enclose the bud before it opens, and they protect the flower while it is ___________. Petals, which are often ___________ colored, are found just inside the sepals. The colors, number, and shapes of such petals ___________ insects and other pollinators to the flower. Stamens The stamens are the ___________ parts of the flower—each stamen consists of a stalk called a filament with an anther at its tip. Anthers are the structures in which pollen grains—the male gametophytes—are ___________. Carpels The innermost floral parts are the carpels, which produce and shelter the ___________ gametophytes and, later, seeds. Each carpel has a broad base forming an ovary, which contains one or more ___________ where female gametophytes are produced. The diameter of the carpel narrows into a stalk called the style. At the top of the ___________ is a sticky or feathery portion known as the stigma, which is specialized to capture pollen. Botanists sometimes call a single carpel or several fused carpels a ___________. The Angiosperm Life Cycle Angiosperms have a life cycle that shows an alternation of generations between a ___________ sporophyte phase and a haploid gametophyte stage. Male and female gametophytes live within the tissues of the ___________. Development of Male Gametophytes The male gametophytes—the pollen grains—develop inside ___________. First, meiosis produces four haploid ___________ cells. Each spore undergoes one mitotic division to produce the two haploid nuclei of a single ___________ grain. The two nuclei are surrounded by a thick wall that protects the ___________ gametophyte. Development of Female Gametophytes Female gametophytes develop inside each ___________ of a flower. The ovules—the future seeds—are enveloped in a protective ovary—the future ___________. A single diploid cell goes through meiosis to produce four haploid cells, three of which ___________. The remaining cell undergoes mitosis, producing eight nuclei. These eight nuclei and the surrounding membrane are called the ___________ sac. The embryo sac, contained within the ovule, makes up the female gametophyte of a ___________ plant. Cell walls form around six of the ___________ nuclei. One of the eight nuclei, near the base of the gametophyte, is the nucleus of the egg—the female gamete. If fertilization takes place, this egg cell will fuse with the male gamete to become the ___________ that grows into a new sporophyte plant. Pollination Pollination is the transfer of pollen to the female portions of the ___________. Some angiosperms are wind pollinated, but ___________ are pollinated by animals. Because wind pollination is ___________ efficient than animal pollination, wind-pollinated plants, such as oak trees, rely on favorable weather and sheer numbers of pollen grains to get pollen from one plant to another. Animal-pollinated plants have a variety of ___________, such as bright colors and sweet nectar, to attract and reward animals. Animals have evolved ___________ shapes that enable them to reach nectar deep within certain flowers. Insect pollination is beneficial to insects and other animals because it provides a dependable source of ___________ —pollen and nectar. Plants benefit because the insects take the ___________ directly from flower to flower. Insect pollination is more efficient than wind pollination, giving insect-pollinated plants a ___________ chance of reproductive success. Fertilization If a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a flower of the same species, it begins to grow a pollen ___________. Of the pollen grain’s two cells, one cell—the “generative” cell—divides and forms two ___________ cells. The other cell becomes the pollen tube. The pollen tube contains a tube nucleus and the two sperm cells. The pollen tube grows into the style, where it eventually reaches the ovary and enters an ___________. Inside the embryo sac, two distinct fertilizations take place—a process called double ___________. First, one of the sperm nuclei fuses with the egg nucleus to produce a diploid ___________, which will grow into the new plant embryo. Second, the other sperm nucleus fuses with two polar nuclei in the embryo sac to form a ___________ (3N) cell. This cell will grow into a food-rich tissue known as endosperm, which ___________ the seedling as it grows. By using endosperm to store food, the flowering plant spends very little in the way of ___________ resources on producing seeds from ovules until double fertilization has actually taken place. The resources saved can be used to make ___________ more seeds. Vegetative Reproduction Many flowering plants can reproduce ___________. This process, known as vegetative reproduction, enables a single plant to produce offspring genetically identical to itself by mitosis. It does not require gametes, flowers, or fertilization. This process takes place ___________ in many plants. Types of Vegetative Reproduction New plants may grow from roots, leaves, stems, or ___________. A ___________ is an underground stem that can grow whole new plants from buds, called “eyes.” Because vegetative reproduction does not involve pollination or seed formation, a single plant can reproduce ______. Asexual reproduction allows a single plant to produce genetically ___________ offspring, enabling well-adapted individuals to rapidly fill a favorable environment. One drawback of asexual reproduction is that it does not produce ___________ combinations of genetic traits, which may be valuable if conditions in the physical environment change. Plant Propagation To propagate plants with desirable characteristics, horticulturists use cuttings or grafting (shown) to make many identical copies of a plant or to produce offspring from ___________ plants. One of the simplest ways to reproduce plants vegetatively is by ___________. A grower cuts from the plant a length of stem that includes a number of buds containing ___________ tissue. That stem is then partially buried in soil or in a special mixture of nutrients that encourages root formation. ___________ is a method of propagation used to reproduce seedless plants and varieties of woody plants that cannot be propagated from cuttings. To graft, a piece of stem or a lateral bud is cut from the parent plant and attached to another plant, as shown. Grafting works only when the two plants are ___________ related, such as when a bud from a lemon tree is grafted onto an orange tree. Grafting usually works best when plants are ___________, which allows the wounds created by the cut to heal before new growth starts.