7 th GradeCore Connections 2Chapter 2
advertisement
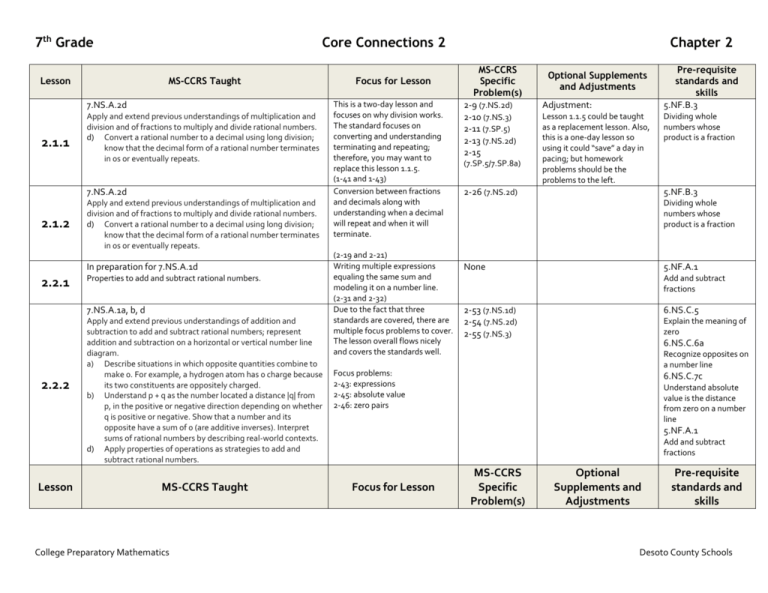
7th Grade Lesson Core Connections 2 MS-CCRS Taught 7.NS.A.2d 2.1.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. d) Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. 7.NS.A.2d 2.1.2 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. d) Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. In preparation for 7.NS.A.1d 2.2.1 Properties to add and subtract rational numbers. 7.NS.A.1a, b, d 2.2.2 Lesson Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. a) Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged. b) Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. d) Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. MS-CCRS Taught College Preparatory Mathematics Focus for Lesson This is a two-day lesson and focuses on why division works. The standard focuses on converting and understanding terminating and repeating; therefore, you may want to replace this lesson 1.1.5. (1-41 and 1-43) Conversion between fractions and decimals along with understanding when a decimal will repeat and when it will terminate. (2-19 and 2-21) Writing multiple expressions equaling the same sum and modeling it on a number line. (2-31 and 2-32) Due to the fact that three standards are covered, there are multiple focus problems to cover. The lesson overall flows nicely and covers the standards well. Chapter 2 MS-CCRS Specific Problem(s) 2-9 (7.NS.2d) 2-10 (7.NS.3) 2-11 (7.SP.5) 2-13 (7.NS.2d) 2-15 (7.SP.5/7.SP.8a) Optional Supplements and Adjustments Adjustment: Lesson 1.1.5 could be taught as a replacement lesson. Also, this is a one-day lesson so using it could “save” a day in pacing; but homework problems should be the problems to the left. 2-26 (7.NS.2d) Pre-requisite standards and skills 5.NF.B.3 Dividing whole numbers whose product is a fraction 5.NF.B.3 Dividing whole numbers whose product is a fraction None 5.NF.A.1 Add and subtract fractions 2-53 (7.NS.1d) 2-54 (7.NS.2d) 2-55 (7.NS.3) 6.NS.C.5 Explain the meaning of zero 6.NS.C.6a Recognize opposites on a number line Focus problems: 2-43: expressions 2-45: absolute value 2-46: zero pairs 6.NS.C.7c Understand absolute value is the distance from zero on a number line 5.NF.A.1 Add and subtract fractions Focus for Lesson MS-CCRS Specific Problem(s) Optional Supplements and Adjustments Pre-requisite standards and skills Desoto County Schools 7th Grade Core Connections 2 7.NS.A.1a, b, d 2.2.3 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. a) Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged. b) Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. d) Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. 7.NS.A.1d --- Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. d) Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. 7.NS.A.2a 2.2.4 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. a) Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (-1)(-1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Lesson MS-CCRS Taught 7.NS.A.2a 2.2.5 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. a) Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (-1)(-1) = 1 College Preparatory Mathematics This lesson basically provides students with additional practice on adding rational numbers with a heavy focus on integers. Focus should be around assisting students to understand and apply the rules of adding rational numbers. Focus problems: 2-58: after completing, add question, “Do you see any patterns in our solutions?” 2-60: focus is to practice with decimals and fractions. Linking integer rules learned above to adding positive and negative fractions. This lesson serves as the conceptual understanding piece of multiplication of integers and writing expressions using distributive property. Chapter 2 2-63 (7.NS.1a) 2-66 (7.NS.3) Adjustment: Berg – lesson on adding integers using rule, counters, and/or number line 6.NS.C.5 Explain the meaning of zero 6.NS.C.6a Recognize opposites on a number line 6.NS.C.7c Understand absolute value is the distance from zero on a number line 5.NF.A.1 Add and subtract fractions NA Adjustment: See Berg lesson – use Davis’s version and adjust. 02-79 (7.NS.1b) 5.NF.A.1 Add and subtract fractions No pre-requisite standards taught in prior grades. (2-74, 2-75, and 2-77) Focus for Lesson This lesson serves as a review of modeling how to multiply positive fractions and writing equations given a model. Working with negative values will be addressed in chapter 3. (2-89) MS-CCRS Specific Problem(s) 2-92 (7.NS.1b) 2-93 (7.NS.1d) 2-94 (7.SP.5) Optional Supplements and Adjustments Pre-requisite standards and skills No pre-requisite standards taught in prior grades. Desoto County Schools 7th Grade Core Connections 2 Chapter 2 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.NS.A.2a 2.2.6 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. a) Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (-1)(-1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Preparation for 7.RP.2a Determining proportional relationships. 2.3.1 Preparation for 7.RP.2b Identify the unit rate. Preparation for 7.RP.2a Determining proportional relationships. 2.3.2 This lesson also serves as a reminder to students on how to multiply mixed numbers using the rectangular array and area models. It also discusses converting mixed numbers to improper fractions in order to multiply. Working with negative values will be addressed in chapter 3. (2-98 and 2-99) These lesson deal with scaling and plotting points on a coordinate grid. They do not directly tie to a standard and therefore, can be eliminated. 2-101 (7.NS.2c) 2-103 (7.NS.2c) No pre-requisite standards taught in prior grades. 2-117 (7.NS.1d) 6.RP.A.2 Ratios and Proportional relationships is discussed in chapter 4 in section 2. 2-128 (7.SP.6) 2-130 (7.NS.2d) 2-132 (7.NS.1a) Preparation for 7.RP.2b Understand the concept of unit rate Adjustment: See focus notes – these lessons can be skipped if teachers choose. 6.RP.A.2 Understand the concept of unit rate Ratio and rate reasoning Assessment Understanding According to PARCC (Section Quiz and Chapter Assessment) Calculator or EOY or Math MS-CCRS Clarifications No PBA Practice Calculator 7.NS.A.1a College Preparatory Mathematics Ratio and rate reasoning 6.RP.A.3 Identify the unit rate. Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. a) Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged. 6.RP.A.3 EOY and PBA 5 Tasks require students to recognize or identify situations of the kind described in standard 7.NS.1a Chapter Mastery Now No Calculator Full mastery is expected of creating zero pairs. Future No future lesson. Desoto County Schools 7th Grade Core Connections 2 7.NS.A.1b – 1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. b) Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. EOY and PBA 5 and 7 Tasks do not have a context. Tasks are not limited to integers. Tasks involve a number line. Tasks do not require students to show in general that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0.: this aspect of standard 7.NS.1b may be Chapter 2 Now No Calculator assessed on the Grade 7 PBA. Full mastery is expected of understanding absolute value. Future No future lesson. 7.NS.A.1b – 2 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. b) Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. EOY and PBA 2, 3, and 5 Tasks require students to produce or recognize real-world contexts that correspond to given sums of rational numbers. Tasks are not limited to integers. Tasks do not require students to show in general that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0.: this aspect of standard 7.NS.1b may be assessed on the Grade 7 PBA. Now No Calculator Full mastery is expected of relating real world and expressions of sums. Future No future lesson. College Preparatory Mathematics Desoto County Schools 7th Grade Core Connections 2 MS-CCRS EOY or PBA Math Practice 7.NS.A.1d Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. d) Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. EOY and PBA 5 and 7 7.NS.A.2a – 1 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. a) Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (-1)(-1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Clarifications EOY and PBA 7 7.NS.A.2a – 2 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. a) Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. MS-CCRS College Preparatory Mathematics EOY and PBA 2 and 4 EOY or PBA Math Practice Tasks do not have a context. Tasks are not limited to integers. Tasks may involve sums and differences of 2 or 3 rational numbers. Tasks require students to represent additional and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line, or compute a sum or difference, or demonstrate conceptual understanding for example by producing or recognizing an expression equivalent to a given sum or difference. For example, given the sum -8.1 + 7.4, the student might be asked to recognize or produce the equivalent expression –(8.1 – 7.4). Tasks do not have context. Tasks are not computation tasks but rather require students to demonstrate conceptual understanding, for example by providing students with a numerical expression and requiring students to produce or recognize an equivalent expression using properties of operations, particularly the distributive property. For example, given the expression (-3)(6 + -4 + -3), the student might be asked to recognize that the given expression is equivalent to (-3)(6 + -4) + (-3)(-3). Chapter 2 Calculator or No Calculator Chapter Mastery Now Chapter 2 focuses on addition of rational numbers with properties. No Calculator Future Chapter 3 covers subtraction of rational numbers, meaning subtracting negative values. Now Chapter 2 focuses on addition of rational numbers with properties and multiplication as repeated addition. No Calculator Future Chapter 3 covers multiplication as repeated subtraction. Now None Multiplication as repeated addition. No Calculator Future Multiplication as repeated subtraction. Clarifications Calculator or No Calculator Chapter Mastery Desoto County Schools 7th Grade Core Connections 2 7.NS.A.2d 7.C.1.1 – Based explanations/reasoning on the properties of operations. Tasks should not require student to identify or name properties. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. d) Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. 7.C.2 – Base explanations/reasoning on the relationship between addition and subtraction or the relationship between multiplication and division. None PBA 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8 7.C.3 - Base explanations/reasoning on a number line diagram (whether provided in the prompt or constructed by the student in her response). None 7.C.6.1 – Construct, autonomously, chains of reasoning that will justify or refute propositions or conjectures. None 7.C.7.2 – Present solutions to multi-step problems in the form of valid chains of reasoning, using symbols such as equal signs appropriately (for example, rubrics award less than full credit for the presence of nonsense statements such as 1 + 4 = 5 + 7 = 12, even if the final answer is correct), or identify or describe errors in solutions to multi-step problems and present corrected solutions. None College Preparatory Mathematics Chapter 2 Now Calculator Full mastery is expected of converting fractions and decimals; understanding that decimal numbers either repeat or terminate. Future No future lesson. Desoto County Schools