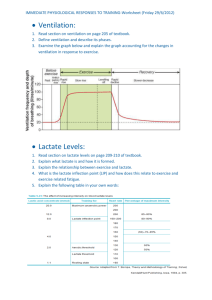
First Hours of Management in Life

First Hours of Management in Life-Threatening Infections
Time
Triage
Immediate
1st Hour
Does Patient
Qualify for EGDT?
Intervention
Screen for SIRS with vital signs
Screen for source by history and physical exam
Evaluate for organ dysfunction by assessing vital signs and level of consciousness
Assess ABCs
Establish definitive airway
Initiate NIPPVwhile preparing for intubation unless patient is apneic
Lung protective ventilator strategies
Obtain intravenous access (central or two peripheral)
Begin volume resuscitation
Avoid hyperoxia
Send labs including lactate and blood cultures
Establish source control via broad spectrum antimicrobials and/or definitive management
Check ABG to ensure adequate gas exchange and avoid hyperoxia
Check plateau pressure to avoid barotrauma
Consider bedside ultrasound to assess cardiac function and IVC collapse
Order appropriate imaging
SBP < 90mmHg after 20-30 cc/kg bolus
Lactate > 4 mmol/L
1st Two Hours
Two Hours
If EGDT eligible, place CVC in torso vein, assess
CVP, ScvO
2
If persistent hypotension (MAP < 65 mmHg), place arterial line
Repeat lactate and calculate clearance
Assess total volume input and urine output
Three Hours
Four to Six Hours
Reassess input/output; assess resuscitation goals; is patient still volume responsive?
Repeat labs to assess for correction of organ dysfunction
Final disposition
If resuscitation goals met, enter maintenance phase
If not met, reassess
Consider corticosteroids for vasopressor dependent hypotension
Assess need for glucose control
Serial reassessment of response to resuscitation
Every 20-30
Minutes
SIRS=systemic inflammatory response syndrome; ABC=Airway, Breathing, Circulation; IV=Intravenous;
IVC=inferior vena cava; SBP=systolic blood pressure; EGDT=early goal directed therapy; CVC=central venous catheter; CVP=central venous pressure; MAP=mean arterial pressure; NIPPV=Noninvasive
Positive Pressure Ventilation