Supplementary Material - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement
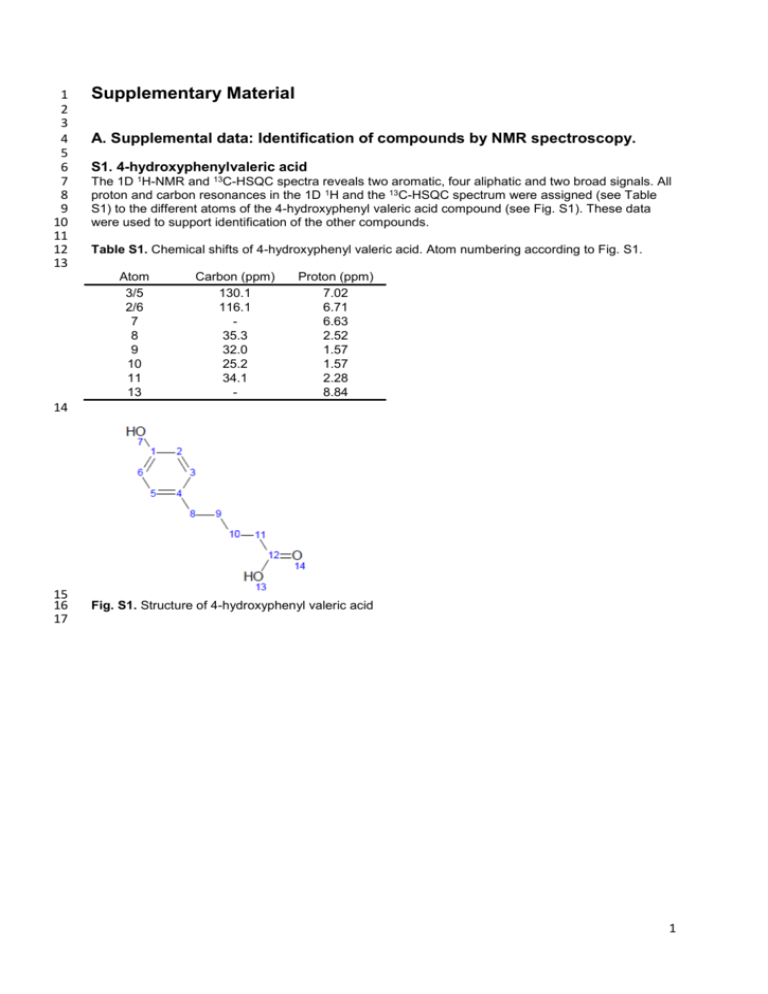
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Supplementary Material A. Supplemental data: Identification of compounds by NMR spectroscopy. S1. 4-hydroxyphenylvaleric acid The 1D 1H-NMR and 13C-HSQC spectra reveals two aromatic, four aliphatic and two broad signals. All proton and carbon resonances in the 1D 1H and the 13C-HSQC spectrum were assigned (see Table S1) to the different atoms of the 4-hydroxyphenyl valeric acid compound (see Fig. S1). These data were used to support identification of the other compounds. Table S1. Chemical shifts of 4-hydroxyphenyl valeric acid. Atom numbering according to Fig. S1. Atom 3/5 2/6 7 8 9 10 11 13 Carbon (ppm) 130.1 116.1 35.3 32.0 25.2 34.1 - Proton (ppm) 7.02 6.71 6.63 2.52 1.57 1.57 2.28 8.84 14 15 16 17 Fig. S1. Structure of 4-hydroxyphenyl valeric acid 1 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 S2. Compound 5 In the 1D 1H-NMR spectrum, three aliphatic and three aromatic 1H-NMR signals are observed. The edited 13C-HSQC identified the aliphatic signals as methylene CH2 groups. The COSY spectrum showed strong cross-peaks between the two aromatic protons #3 and #4 (doublet signals at 6.75 and 6.55 ppm) and between two of the methylene CH2 groups. The other methylene CH2 group #9 (singlet signal at 3.57 ppm), not having any cross-peaks in the COSY spectrum, showed on the other hand cross-peaks in the 13C-HMBC to the quaternary carbon atom #5 and the two carbon atoms #4 and #6 in the aromatic ring. In addition the methylene CH2 #9 signal has a cross-peak to a quaternary carbon atom at 208.6 ppm (atom #10) typical for a keto group. The most upfield shifted methylene CH 2 #13 signal (triplet signal at 2.44 ppm) showed a cross-peak to a quaternary carbon atom at 174.7 ppm that represents a carbonyl group #14. Based on the chemical formula obtained from the MS measurement and the assignment of all the resonances in the homo- and hetero-nuclear NMR spectra the structure was identified as 5-(3,4dihydroxyphenyl)-4-oxovaleric acid (see Fig. S2). The assignments for the proton and carbon resonances are listed in Table S2. Table S2. Chemical shifts of 5-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4-oxovaleric acid. Atom numbering is according to Fig. S2. Atom 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 12 13 14 Carbon (ppm) 145.9 145.0 116.2 122.3 128.3 117.5 49.41 208.6 28.4 37.3 174.7 Proton (ppm) 6.75 6.55 6.67 3.57 2.44 2.69 - 37 38 39 40 41 Fig. S2. Structure of compound 5. 2 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 S3. Compound 6 In the 1D 1H-NMR spectrum three aliphatic and three aromatic signals are observed. Based on the integrals, we can establish that the aliphatic signals are equivalent to 6 protons and the aromatic signals are equivalent to 4 protons. From the edited 13C-HSQC spectrum, the aliphatic signals were identified as methylene CH2 groups and it also revealed the overlap in the 1H dimension for the aromatic signals. In the aromatic region 4 cross-peaks are observed clearly identifying the overlap for the doublet 1H signals at 6.69 ppm. The COSY spectrum showed strong cross-peaks between the triplet signal of proton #3 (at 7.14 ppm) to the doublet signals of protons #2 and #4 (6.69 ppm). The methylene CH2 signals have identical cross-peak patterns in the different spectra as compound 1 and is therefore also identified as a 4-oxovaleric acid moiety. Based on the chemical formula obtained from the MS measurement and the assignment of all the resonances in the homo- and hetero-nuclear NMR spectra the structure was identified as 5-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxovaleric acid (see Fig. S3). The chemical shifts assignments are listed in Table S3. Table S3. Chemical shifts of 5-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxovaleric acid. Atom numbering according to Fig. S3. Atom 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 11 12 13 Carbon (ppm) 158.2 114.4 130.7 122.0 137.7 117.4 49.9 207.9 37.6 28.5 174.5 Proton (ppm) 6.69 7.14 6.69 6.66 3.67 2.72 2.46 - 59 60 61 62 Fig. S3. Structure of compound 6. 3 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 S4. Compound 8 In the 1D 1H-NMR spectrum three aliphatic and three aromatic signals are observed. Based on the integrals values, the aliphatic signals are equivalent to 8 protons and the aromatic signals are equivalent to 3 protons. The COSY spectrum reveals strong cross-peaks between the two aromatic protons #3 and #4 (doublet signals at 6.70 and 6.54 ppm). It also displays the same cross-peaks pattern between the aliphatic proton signals as observed for the reference compound, 4hydroxyphenylvaleric acid. Although the signals of protons #10 and #11 have the same chemical shift, the cross-peaks in the 13C-HSQC are resolved due to the differences in carbon chemical shift. In the 13C-HMBC cross-peaks are observed for the methylene CH signal #9 to the aromatic carbons and for 2 #12 to a carbon resonance typical for a carboxyl group. From the cross-peaks in the COSY combined with the cross-peak pattern in the 13C-HMBC and 13C-H2BC the second part of the molecule was identified as valeric acid. Because also the peak patterns for the aromatic protons in the NMR spectra are the same as for compound 1, the compound is found to relate both to the reference molecule (carboxylic tail) and compound 1 (aromatic head). Based on the chemical formula obtained from the MS measurement and the assignment of all the resonances in the homo- and hetero-nuclear NMR spectra the structure was identified as 5-(3,4dihydroxyphenyl) valeric acid (see Fig. S4). The chemical shifts assignments are listed in Table S4. Table S4. Chemical shifts of 5-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl) valeric acid. Atom numbering according to Fig. S4. Atom 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 11 12 13 Carbon (ppm) 143.6 145.6 102.9 116.1 135.8 116.4 35.4 31.8 25.3 34.1 175.1 Proton (ppm) 6.54 6.70 6.66 2.48 1.56 1.56 2.28 - 84 85 86 87 88 Fig. S4. Structure of compound 8. 4 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 S5. Compound 9 In the 1D 1H-NMR spectrum three aliphatic and four aromatic signals are observed. Based on the integrals, the aliphatic signals are equivalent to 8 protons and the aromatic signals are equivalent to 4 protons. Similar to the previous compound, from the cross-peaks in the COSY combined with the cross-peak pattern in the 13C-HMBC and 13C-H2BC the aliphatic part of the molecule was identified as valeric acid. The main difference between the NMR spectra of this compound and the reference compound is in the aromatic region. Instead of only two 1H signals for the reference compound due to symmetry, the isolated compound 9 has, just like for compound 2, four distinct 1H signals. The chemical shifts are slightly different than for compound 2, but the same cross-peak pattern is observed for the aromatic part of the molecule in all NMR spectra. Based on the chemical formula obtained from the MS measurement and the assignment of all the resonances in the homo- and hetero-nuclear NMR spectra the structure was identified as 5-(3hydroxyphenyl) valeric acid (see Fig. S5). The assigned chemical shifts are listed in Table S5. Table S5. Chemical shifts of 5-(3-hydroxyphenyl) valeric acid. Atom numbering according to Fig. S5. Atom 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 11 12 Carbon (ppm) 158.1 113.5 130.3 120.9 145.3 116.1 34.0 25.2 31.4 36.0 175.1 Proton (ppm) 6.61 7.10 6.70 6.64 2.29 1.57 1.60 2.55 - 106 107 108 109 110 Fig. S5. Structure of compound 9. 5 111 B. Supplemental figure. 112 113 114 Fig. S6. Reaction model for A-ring fission. 6







