Global Winds Assessment
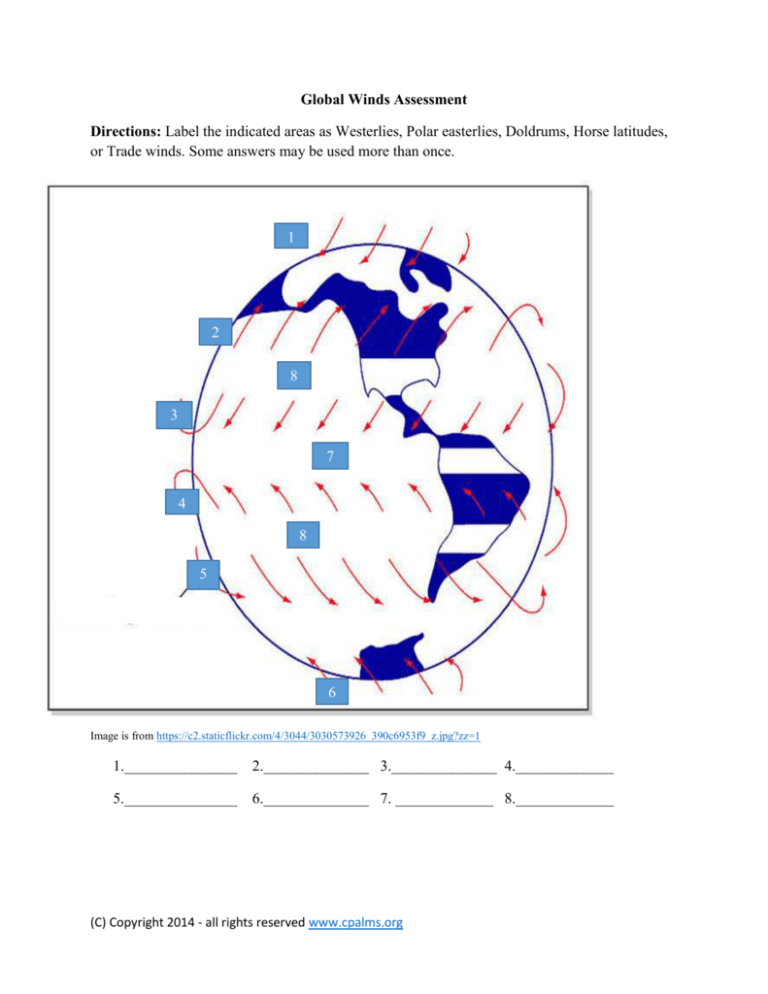
Directions: Label the indicated areas as Westerlies, Polar easterlies, Doldrums, Horse latitudes,
or Trade winds. Some answers may be used more than once.
1
2
8
3
7
4
8
5
6
Image is from https://c2.staticflickr.com/4/3044/3030573926_390c6953f9_z.jpg?zz=1
1._______________
2.______________ 3.______________ 4._____________
5._______________
6.______________ 7. _____________ 8._____________
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
9. Describe how energy from the sun influences global winds. Your response must include the
terms radiation and convection cells. Also, include the full influence of these two terms on
global wind movement.
10. Air rising and sinking in Earth’s atmosphere forms a pattern of smaller convection cells.
These convection cells create both high- and low-pressure belts. Where in the preceding diagram
are the low-pressure belts located?
A.
B.
C.
D.
A, D, G
B, D, F
C, D, E
D, E, F, G
11. Air currents are sensitive to changes in temperature and pressure. In general, how does air
move?
A. From areas of high temperature to areas of low pressure.
B. From areas of low temperature to areas of high pressure.
C. From areas of higher pressure to areas of lower pressure.
D. From areas of lower pressure to areas of higher pressure.
12. Winds can be characterized and classified using several different factors. How are winds
usually named?
A. Winds are usually named based on their altitude.
B. Winds are usually named based on their strength.
C. Winds are usually named based on the direction in which they are blowing.
D. Winds are usually named based on the direction from which they are blowing.
13. Air circulates in Earth’s atmosphere. Which of the following is the fundamental cause of air
circulation in Earth’s atmosphere?
A. Gravity
B. Ocean currents
C. The ozone layer
D. Temperature differences
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org
Answer Key:
1. Polar easterlies
2. Westerlies
3. Trade winds
4. Trade winds
5. Westerlies
6. Polar Easterlies
7. Doldrums
8. Horse latitudes
9. Energy from the sun reaches the Earth in the form of radiation. Some of this radiation reaches the
surface of the Earth and heats the air. The heated, less dense, low pressure air rises and is replaced
by cooler, denser and higher-pressure air. The movement of the cooler and warmer air form cycles at
the points of high and low pressure latitudes. This cycling is known as a convection cell. Energy from
the sun provides the heat to heat the air and allows for the movement of this air via convection cells.
10. B
11. C
12. D
13. D
*Note for teacher: Students will get one point each for the inclusion of each major component in their
response to #9: energy from sun, radiation, hot air rises, cold air falls, and convection cells.
Students will receive half credit if a part of a major component is incorrect or incomplete. Students will
receive no credit for parts completely left out.*
(C) Copyright 2014 - all rights reserved www.cpalms.org