I. The Sociological Perspective
advertisement

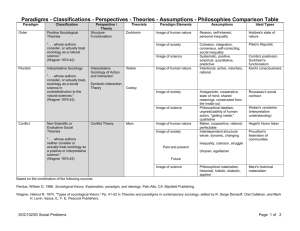
INTRODUCTION TO SOCIOLOGY SUMMARY COURSE OUTLINE American Sociological Association I. The Sociological Perspective A. Sociology as a field of inquiry Sociology as the study of social behavior How is sociology different from other social sciences? B. The Sociological Perspective The empirical basis of sociology The debunking tendency C. Central Sociological Concepts Social interaction Social structure Social Change D. The Emergence of Sociology The influence of the Enlightenment Classical sociological theory (Durkheim, Marx, Weber) The emergence of American sociology (Addams, Park, DuBois, Cooley, Mead, Thomas, Znaniecki) E. Sociological Theory Functionalism Conflict theory Symbolic interaction Exchange-rational choice Feminist theory II. Research Methods A. The Research Process Scientific method Stages of research Qualitative and quantitative research Inductive/deductive reasoning B. Methods of Inquiry Survey Research Interviews Participant observation Content Analysis Comparative and historical analysis C. Probability and Statistical Analysis D. Research Ethics III. Culture A. Group influence Social basis of belief – Asch experiments on social influence Authority and domination – Milgram experiments: obedience to authority Attribution theory – “fundamental attribution error” (bias towards attributing responsibility to individuals), accounts and accountability (Garfinkel) Interpersonal attraction – homophily (tendency to choose similar partners) B. The Social Construction of the Self The modern “self” as historical product of Christianity and the Enlightenment Cross-cultural variation in selves (Nisbett; Shweder) Selves as constructed out of situations – (Michels; Goffman, Collins) Rational choice – as socially constructed C. Characteristics and Elements of Culture Scripts, schema, and typifications Language Norms and Values Beliefs D. Cultural Diversity Ethnocentrism Subcultures and countercultures E. Culture in Society Culture as cohesive, functional Cultural as source of improvisation, diversity, innovation Popular culture and the mass media IV. Socialization A. The Social Construction of the Self B. Theories of Socialization Freud and the psychoanalytic perspective Social learning theory Cooley, Mead and symbolic interaction C. Agents of Socialization D. Socialization over the Life Course Rites of passage Adult socialization Conversion V. Social Organization A. Building Blocks Roles and Statuses Institutions Social networks o Depicting networks o Dimensions of networks o Using network analysis, e.g. Getting jobs, Fighting the AIDs epidemic B. Social Differentiation Size, scale, and differentiation Differentiation and specialization Changing bases of solidarity (mechanical and organic solidarity) Problems of cooperation and coordination in complex social systems C. Ways of organizing cooperation Kinship as a basis of organization o Historical and contemporary examples o Weaknesses of kinship-based systems Bureaucracy as a solution to weaknesses of kinship-based structures o Characteristics of bureaucracy (formal roles, specialization based on expertise, clear duties and obligations, hierarchical command and information structures, compliance based on career incentives, and formal records for control and planning) o Advantages of bureaucracy (efficiency; expertise; control) o Limitations of bureaucracy (flexibility; adaptability; power concentration) o Varieties of bureaucracy (e.g., typical western manufacturing firm; Japanese firm; professional nonprofit service organizations; “new economy” firms) Markets as social organizations (economic sociology) o What is a market and how sociologists differ from economists in looking at them o Markets as groups with roles and statuses o Markets as institutions (relation to law and government) o Virtues and limitations of markets as ways of organizing Informal networks o The persistent importance of informal networks in bureaucracies in markets o Informal networks and “social capital” o The dark side of informal networks (e.g., criminal networks) VI. Social Inequalities A. Social Class and Social Stratification Defining and measuring social class The consequences of class inequality Models of social class o Marx and class conflict o Weber's multidimensional model of class o contemporary class analyses The class structure of the United States o the distribution of wealth and income inequality o social mobility and status attainment o intersections of race, class, gender, and age Class consciousness Poverty and welfare Global stratification o rich and poor nations o world systems theory o international poverty B. Race and Ethnicity Definitions of race and ethnicity The social construction of race o racialization o racial formation theory Prejudice, discrimination and institutional racism Consequences of racial stratification o racial segregation o race, ethnicity, and life chances Diverse group experiences Intersections of class and race C. Gender Distinguish sex and gender; the social construction of gender Patterns of gender socialization Gender and sexual identity Gendered Institutions gender and work gender segregation The women's movement D. Age Social significance of aging Age stereotypes and age discrimination Aging and the life course Age cohorts Age stratification The demography of aging VII. Deviance and Conformity A. Sociological Definitions of Deviance Positive deviance Negative deviance Deviance and the Deviant Types of Youth Deviance B. Costs and Benefits of Deviance Functionalism Social Control Structural Strain o Anomie o Innovation o Ritualism o Retreatism o Rebellion Conflict Theory Labeling Theory C. Deviant Identities Deviant subcultures/communities Deviant careers Stigma D. Measuring Crime Crime o Juvenile Crime o White Collar Crime Crime Control o Deterrence o Retribution o Incarceration o Rehabilitation o Recidivism Terrorism E. Race, Class, Gender, and Crime F. Criminal Justice System Criminal Justice System Courts Law Enforcement Prisons VIII. Social Institutions A. Family Forms of kinship Diversity in family forms Marriage and divorce Family violence Families and social policy B. Education The rise of public education Education and social mobility Inequality and education o teacher expectations o tracking o educational segregation o inequality and educational testing o school funding and facilities o the digital divide and information technology Education and social reform/social policy C. Religion Measuring religiosity Influence of religion on social and political attitudes/behavior Forms of religion Diverse world religions Religious organizations/institutions Religion, secularization, and social change D. Work/Economy Influence of the Industrial revolution Comparative economies The occupational system o the division of labor o occupational distribution o occupational prestige o earnings Work and de-industrialization o the rise of contingent labor o growth of the service sector o unionization Worker alienation E. Power, Politics, and Government Power and authority Theories of power Political participation Government: who rules? Courts and the law Military F. Media and Culture Media conglomerates Studies of media effects (violence, etc.) Popular culture “High” culture G. Health Inequality and access to health care Structure of health care institutions Delivery of health care Death and Dying IX. Social Change A. Population, Urbanization and the Environment Demographic processes o birth rate/death rate o migration o population growth and composition (illustrate demographic transition theory) Urbanization o the evolution of cities o suburbanization and urban decline o segregation o megalopolis o the rural turnaround Environment and Human Ecology o environmental racism o ecofeminism o environmental policy B. Collective Behavior and Social Movements Theories of collective behavior o emergent norm theory o competition theory o convergence theory Types of collective behavior o Crowds Mobs and riots. Contagion and emergence theories. o Mass Behavior Rumor Public opinion and propaganda Panic and mass hysteria Fads and fashion Social Movements o How movements develop o Organization of social movements o Strategies and tactics o Theories of social movements: resource mobilization, political process, new social movement theory. C. Causes and Consequences of Social Change Demographic changes Collective behavior/social movements Technology and science Cultural diffusion War Modernization D. Theories of Social Change World systems theory Dependency theory Evolutionary theory