Enzymes - OKBU.net
advertisement

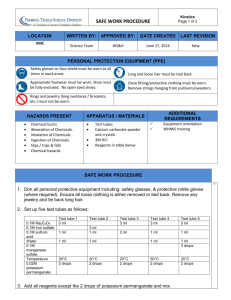
The Effects of Selected Variables on Enzyme Activity Enzymes are protein molecules that speed up chemical reactions. Enzymes possess a 3-dimensional shape that will bond only to a specific reaction molecule or molecules. The molecule to which an enzyme bonds is called the substrate molecule. Substrate molecules bond to a region of the enzyme called the active site. The active site is where the chemical reaction occurs between the enzyme and substrate molecules. Objective… Demonstrate an enzymatic reaction and determine the effects of selected variables on the rate of reactions involving enzymes. Materials and Method… A. Enzyme Specificity 1. Number 3 test tubes. 2. Measure 8 cm from bottom of each test tube and mark with wax pencil. 3. Fill to the 8 cm mark with deionized water (the gray faucet up front). 4. Place test tubes in test tube rack. 5. Perform the following procedures for the three tubes: The % transmission is actually how much light is able to pass through the liquid—so the lower the number the less light, or the more intense the color. The more intense the color, the greater the enzyme activity. Tube 1: Add 10 drops of enzyme and 10 drops of substrate. a) Using parafilm to seal, shake the test tube several times. b) After exactly 5 minutes (work quickly), pour some of the liquid into the smaller tube (about ¾ full) and place in spectroscope. c) Record % transmission. Tube 2: Add 10 drops of substrate only. Repeat steps a,b,c. Tube 3: Add 10 drops of enzyme and 10 drops of sucrose. Repeat steps a,b,c. Table 1: Enzyme Specificity Test Contents Tube 1 2 3 % Transmission Questions: (include these in your report) 1. Which of the three test tubes is the control group? 2. Which of the three test tubes demonstrated enzyme specificity? 3. Explain how this experiment shows that enzymes are specific to a substrate. 1 B. Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity 1. Rinse the tubes from the following activity and fill to the mark with deionized water. 2. Place each test tube in its designated environment: Tube 1: Place in ice bath (5°C) Tube 2: Place at room temperature (22°C) Tube 3: Place in hot water bath (80°C) 3. After 5 minutes, while still in their respective environments, add 10 drops of substrate and 10 drops of enzyme to each tube. Swirl to mix. a) After exactly 5 minutes (work quickly), pour some of the liquid into the smaller tube (about ¾ full) and place in spectroscope. b) Record % transmission. Table 2: Effect of Temperature and Enzyme Activity Test Environment Tube 1 Ice bath 2 Room 3 Hot water bath % Transmission Questions: (include these in your report) 1. Which test tube demonstrated the fastest reaction rate? 2. Why did the test tube you selected demonstrate the fastest reaction rate. C. Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Enzyme Activity 1. Rinse tubes and fill to the 8 cm mark with deionized water. 2. Perform the following procedures for the three tubes: . Tube 1: Add 3 drops of enzyme and 10 drops of substrate. a) Seal and shake the tube several times. b) After 5 minutes, record the % transmission. Tube 2: Add 9 drops of enzyme and 10 drops of substrate. (repeat steps a and b) Tube 3: Add 27 drops of enzyme and 10 drops of substrate. (repeat steps a and b) Table 3: Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Enzyme Activity Test Amount of Enzyme Tube 1 2 3 2 % Transmission Questions: (include these in your report) 1. Which test tube exhibited the fastest reaction rate? 2. Why did the test tube you selected in the fastest reaction rate? D. Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity 1. Rinse tubes and fill to the 8 cm mark with deionized water. 2. Perform the following procedures for the three tubes: Tube 1: Add 3 drops of substrate and 10 drops of enzyme. a) Seal and shake the tube several times. b) After 5 minutes, record the % transmission. Tube 2: Add 9 drops of substrate and 10 drops of enzyme. (repeat steps a and b) Tube 3: Add 27 drops of substrate and 10 drops of enzyme. (repeat steps a and b) Table 4: Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity Test Amount of Substrate Tube 1 2 3 % Transmission Questions: (include these in your report) 1. Which test tube had the fastest reaction rate? 2. Why did the test tube you selected in Question 1 exhibit the fastest reaction rate? Make sure each group member has a copy of the results. Using Excel, make separate bar graphs of the data from the preceding tables. Submit a standard report, including one of your graphs, answers to questions, and conclusions about the general behavior of enzymes with the observed variables. 3